QUESTION 1 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and
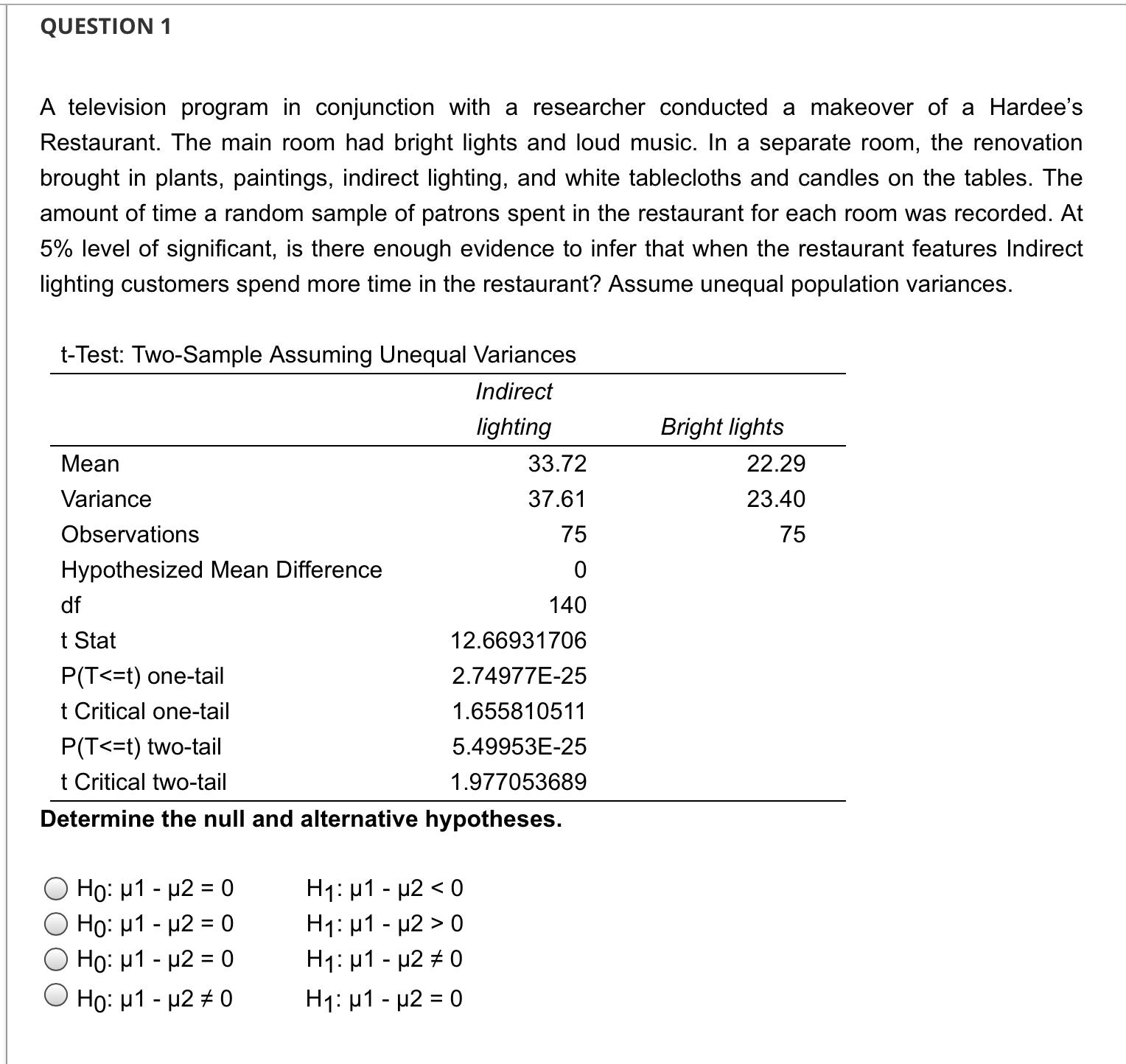
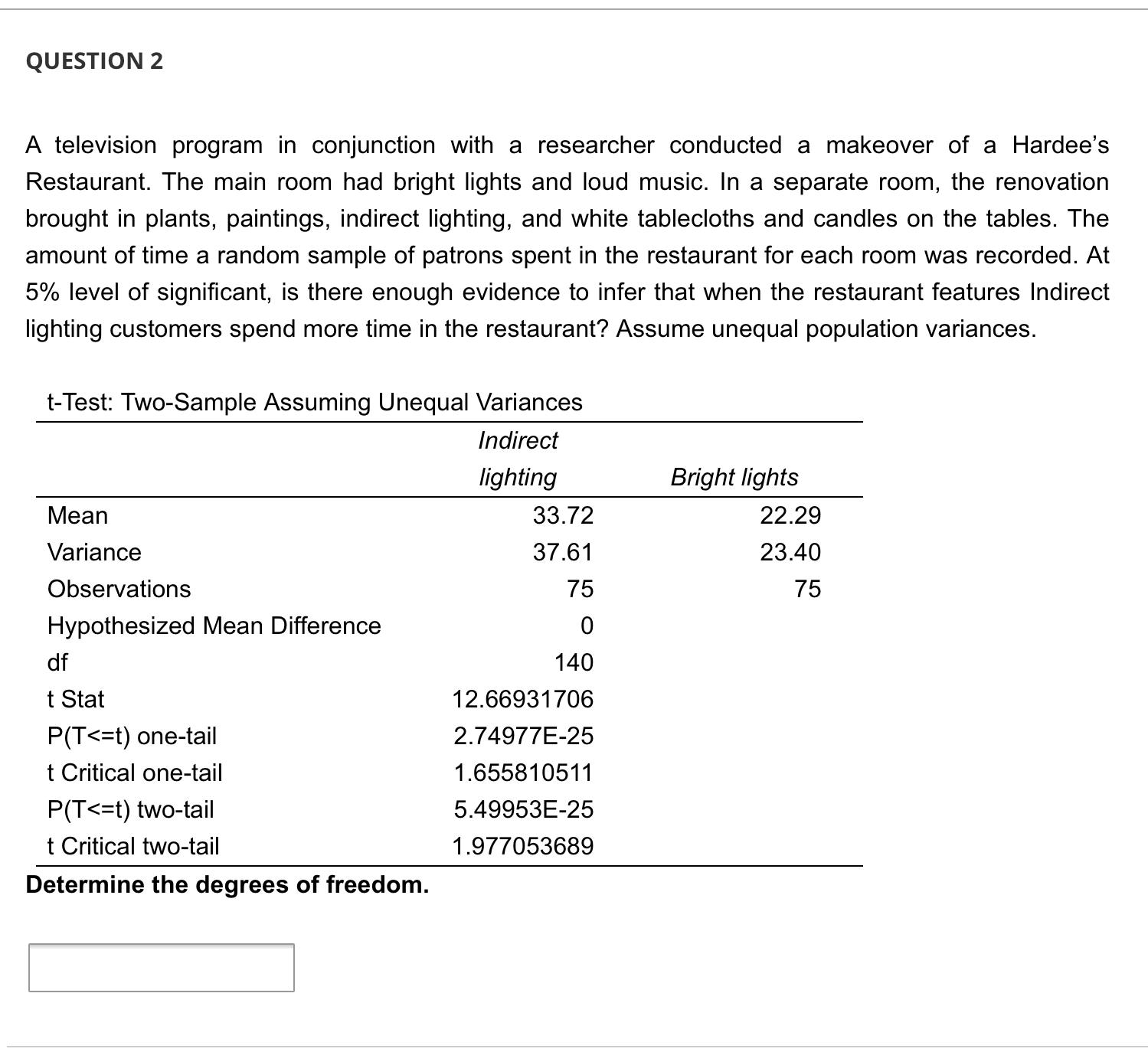
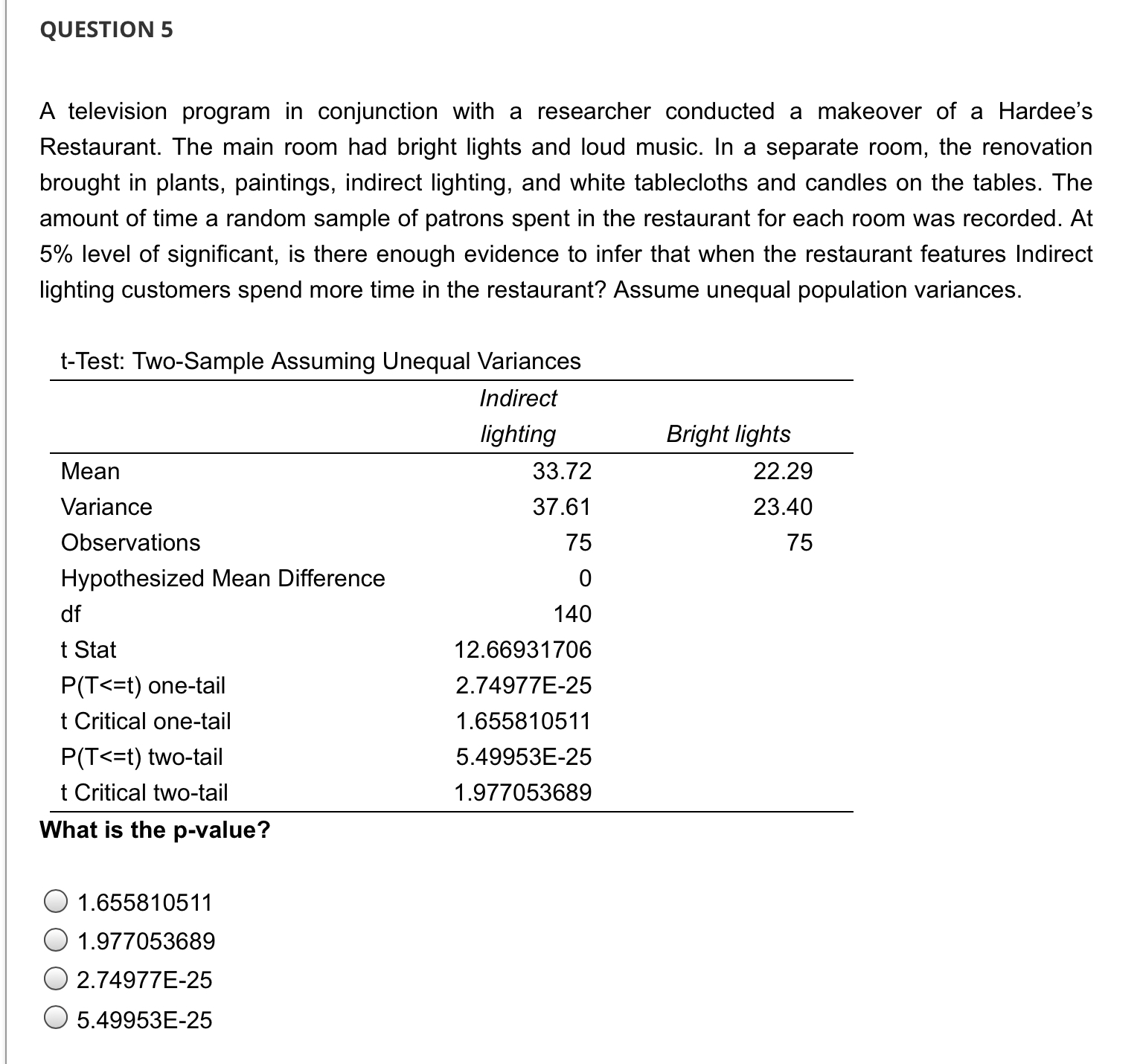

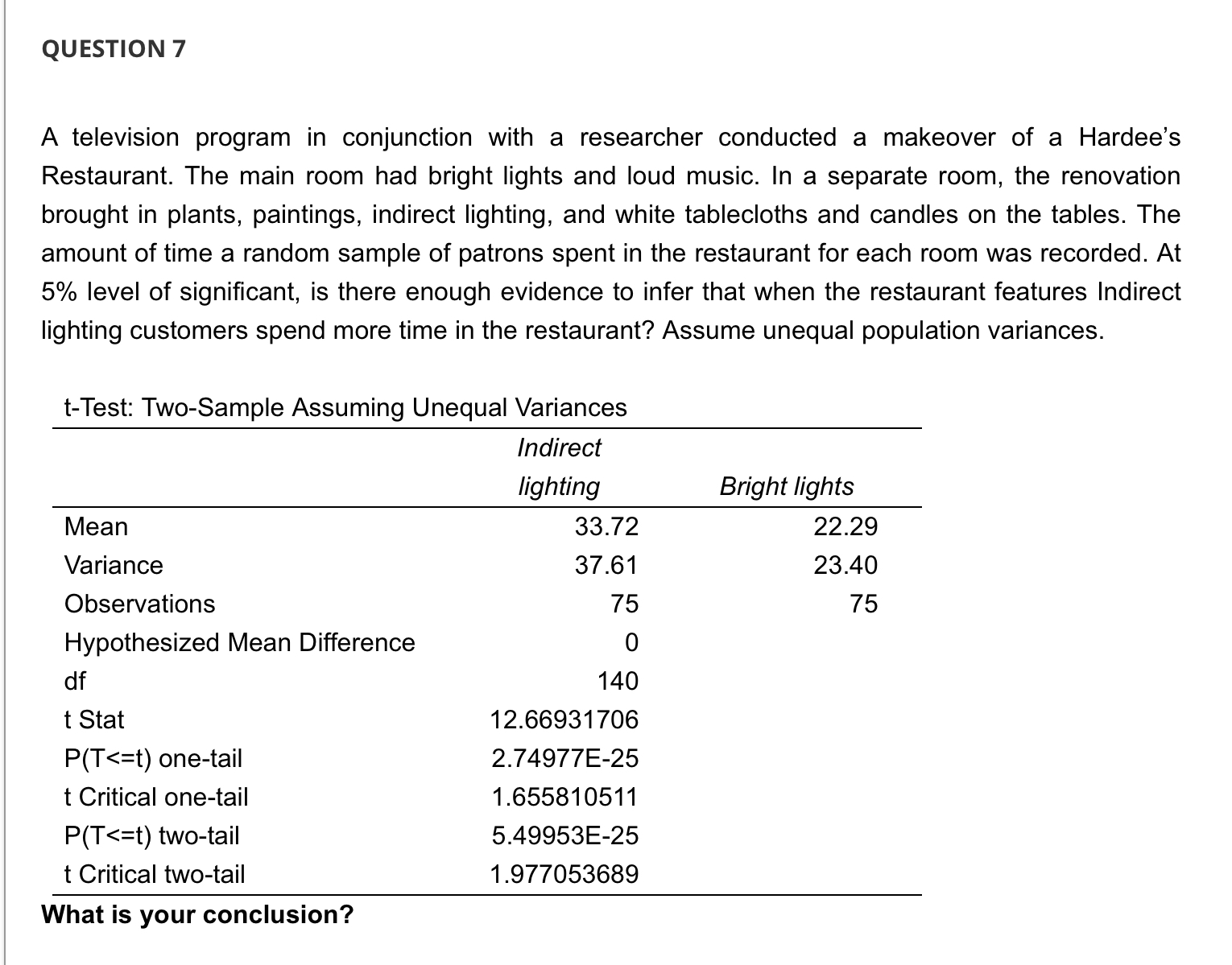
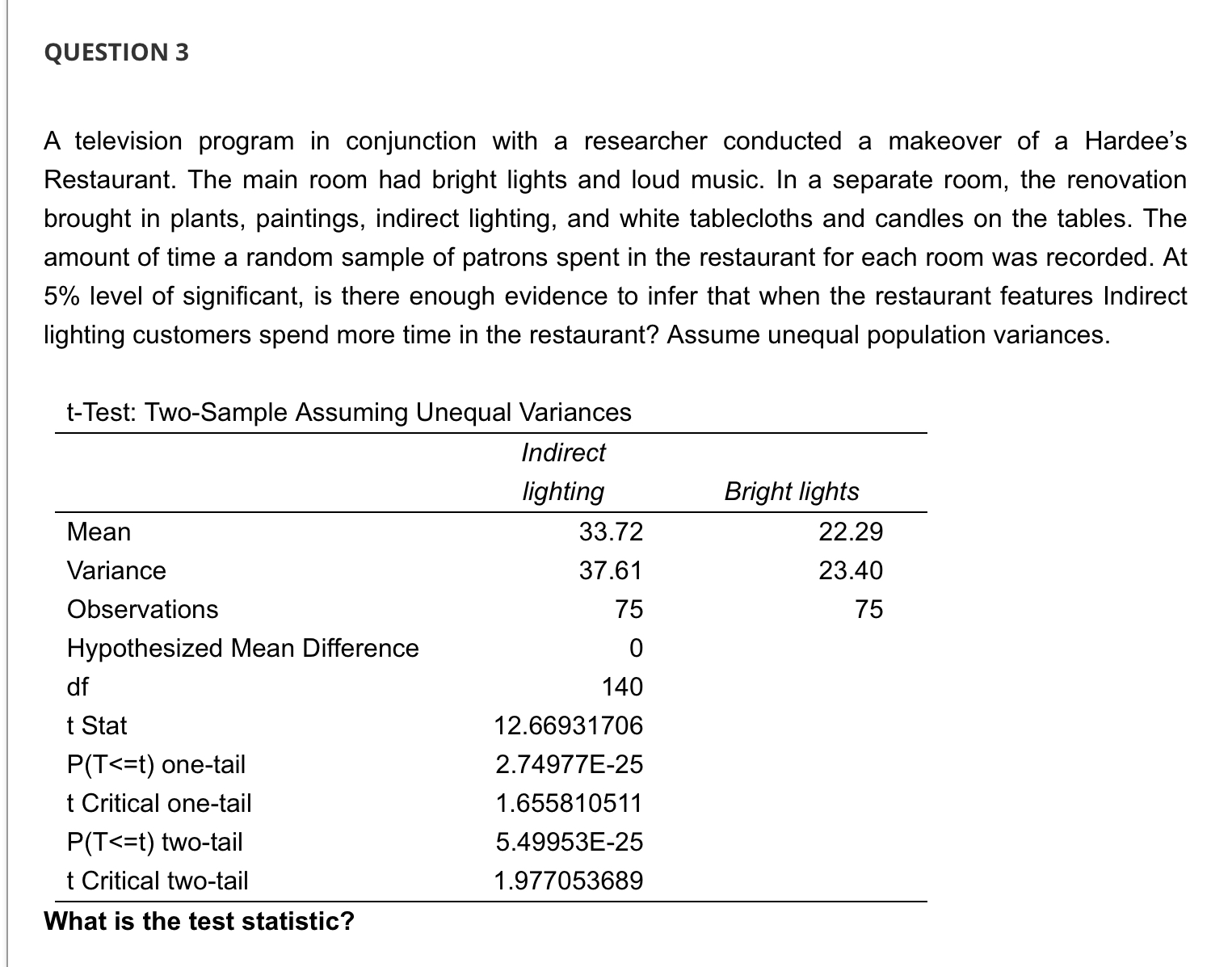
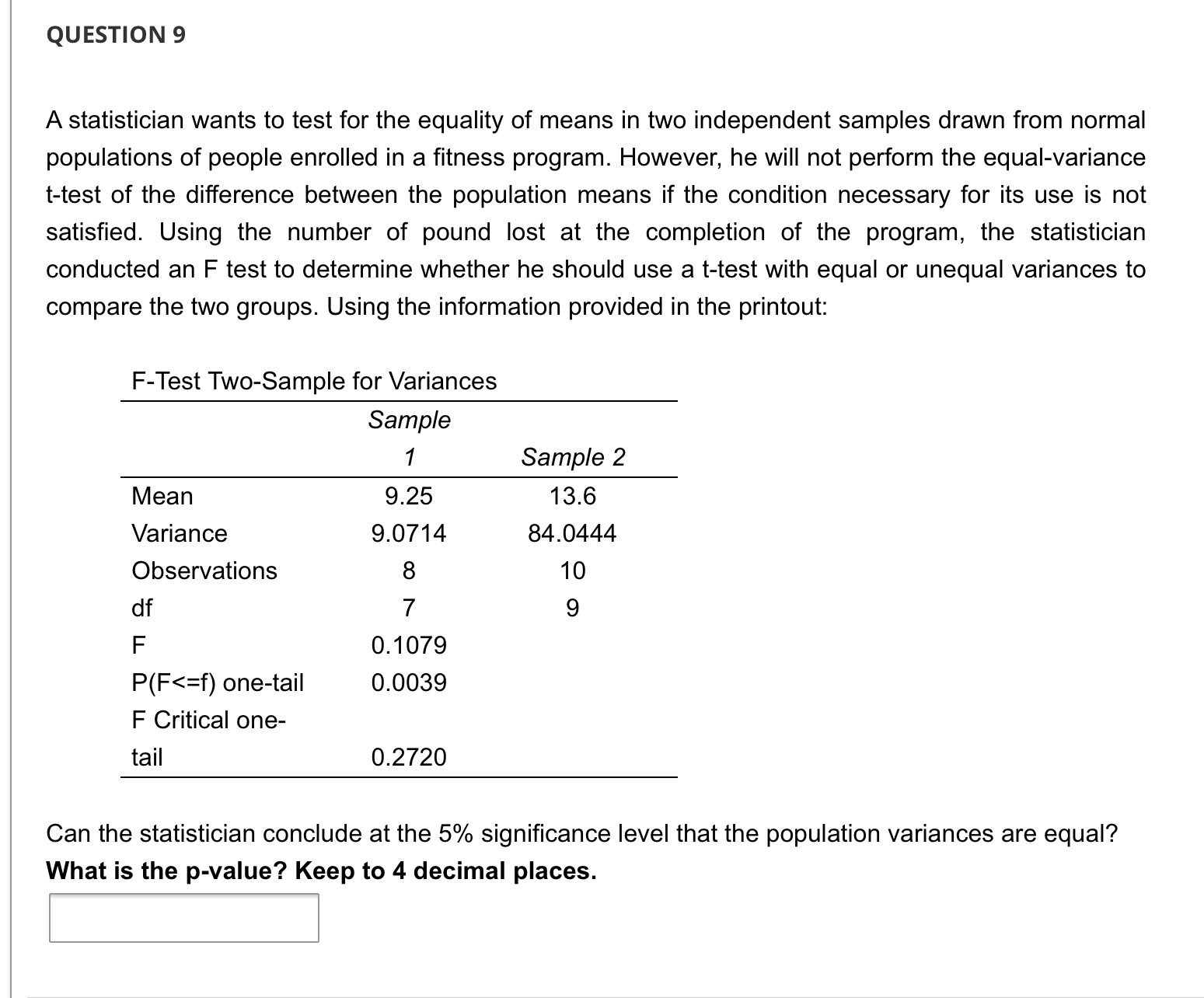
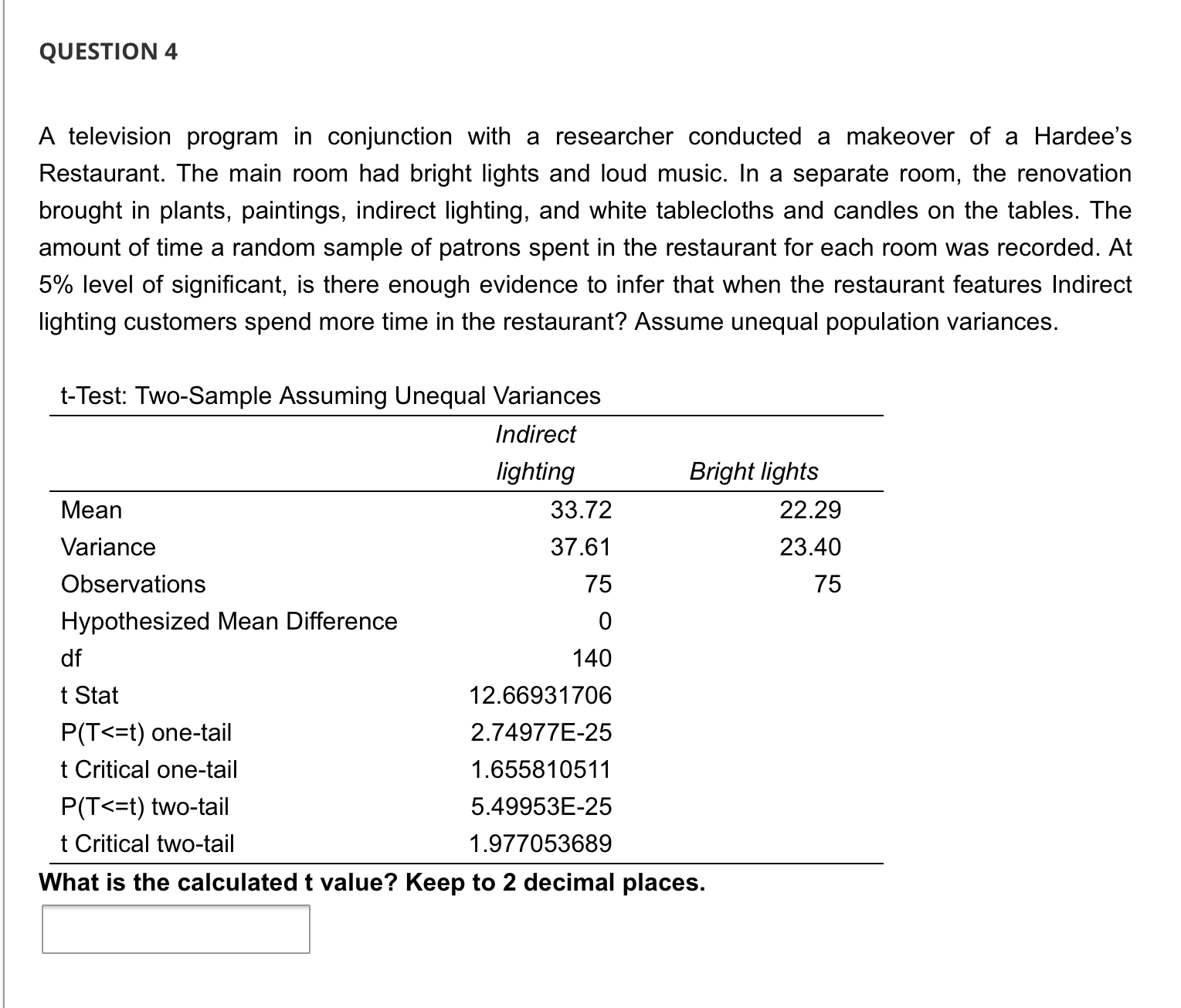
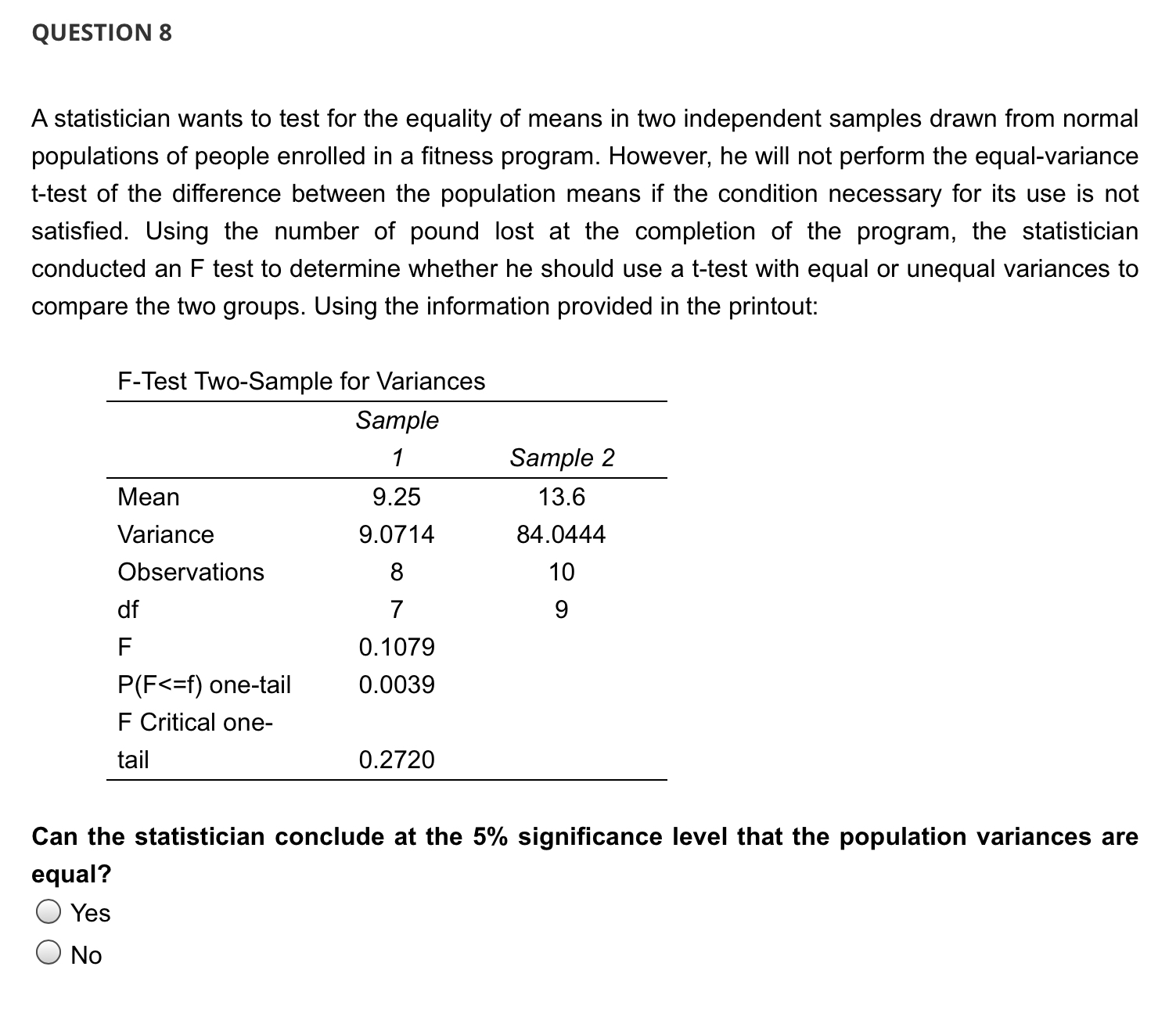
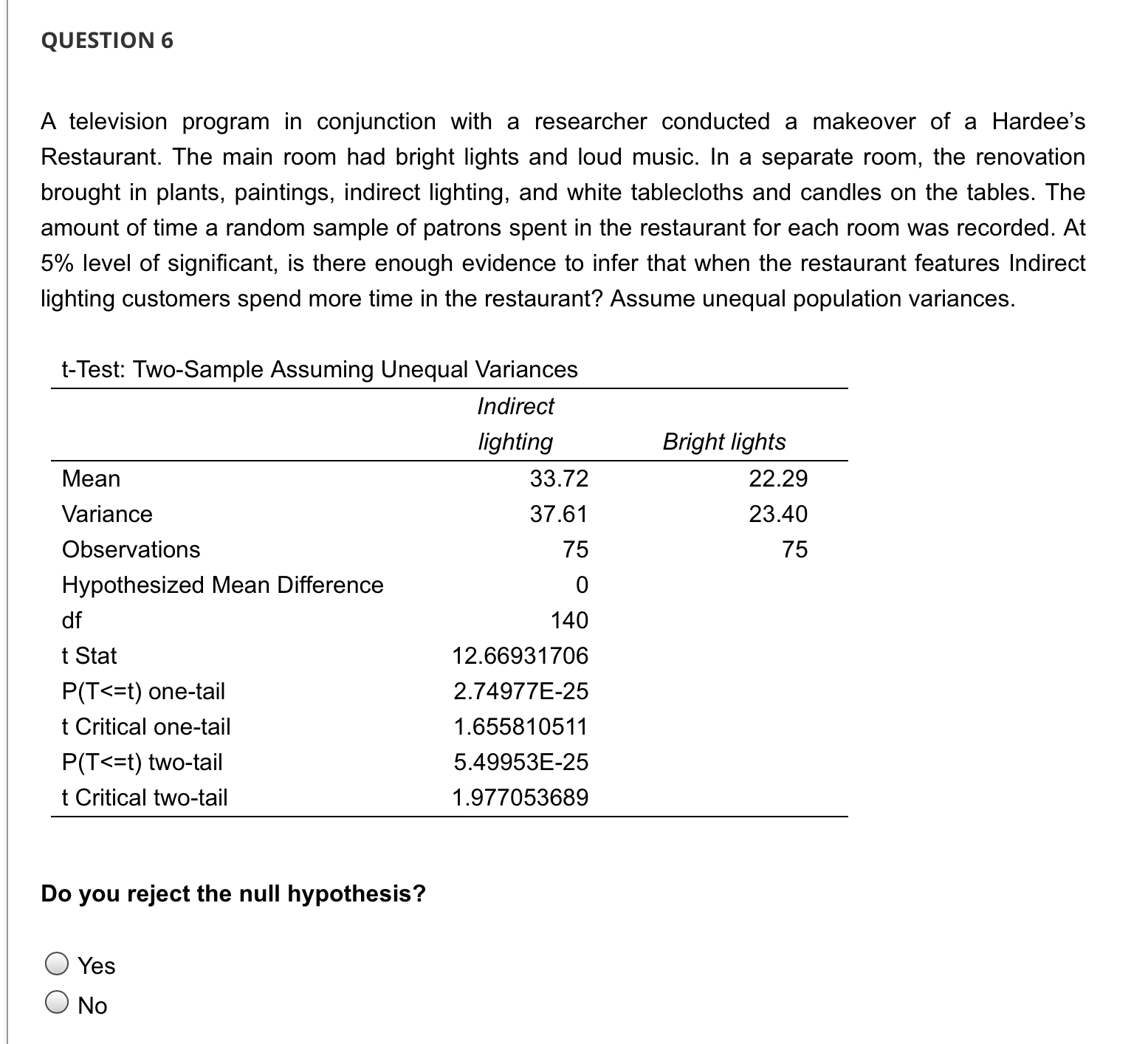

QUESTION 1 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T QUESTION 2 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T QUESTION 5 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T Because the p-value 0.05, we cannot conclude that there is sufficient evidence to infer that when the restaurant features bright lights and loud music customers spend less time in the restaurant. QUESTION 7 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T QUESTION 3 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T QUESTION 9 A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. Using the number of pound lost at the completion of the program, the statistician conducted an F test to determine whether he should use a t-test with equal or unequal variances to compare the two groups. Using the information provided in the printout: F-Test Two-Sample for Variances Sample 1 Sample 2 Mean 9.25 13.6 Variance 9.0714 84.0444 Observations 8 10 df 7 9 F 0.1079 P(F QUESTION 4 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Indirect lighting Bright lights Mean 33.72 22.29 Variance Observations 37.61 23.40 75 75 Hypothesized Mean Difference df 0 140 t Stat 12.66931706 P(T QUESTION 8 A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. Using the number of pound lost at the completion of the program, the statistician conducted an F test to determine whether he should use a t-test with equal or unequal variances to compare the two groups. Using the information provided in the printout: F-Test Two-Sample for Variances Sample 1 Sample 2 Mean 9.25 13.6 Variance 9.0714 84.0444 Observations 8 10 df 7 9 F 0.1079 P(F QUESTION 6 A television program in conjunction with a researcher conducted a makeover of a Hardee's Restaurant. The main room had bright lights and loud music. In a separate room, the renovation brought in plants, paintings, indirect lighting, and white tablecloths and candles on the tables. The amount of time a random sample of patrons spent in the restaurant for each room was recorded. At 5% level of significant, is there enough evidence to infer that when the restaurant features Indirect lighting customers spend more time in the restaurant? Assume unequal population variances. t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances Mean Variance Observations Hypothesized Mean Difference df t Stat P(T t = x S (x1-x2)-(41-12) (+) (x1-x2)-(41-42) S S + 2 + (1-2)ta/21
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


