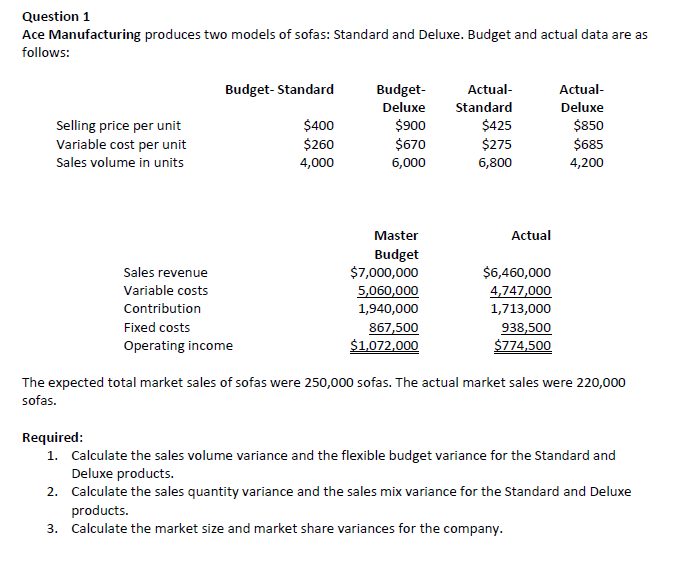
Question 1 Ace Manufacturing produces two models of sofas: Standard and Deluxe. Budget and actual data are as follows: Budget- Standard Budget Actual- Actual- Deluxe Standard Deluxe Selling price per unit 5400 $900 $425 $850 Variable cost per unit 5260 $620 $225 $635 Sela volume in units 4,000 6,000 6,300 4,200 Master Actual Budget Sales revenue $2,000,000 $6,460,000 Variable 005125 5,060,0m 4,?4?,00D Contribution 1,940,003 1,?13,000 Fixed costs 807,500 933,500 Operating inoome $1,039,000 $?74,500 The expected total market sales of sofas were 250,000 sofas. The actual market sala were 220,000 sofas. Required: 1. Calculate the sales volume variance and the flexible budget variance for the Standard and Deluxe products. 2. Calculate the sales quantityr variance and the sales mix variance for the Standard and Deluxe products. 3. Calculate the market size and market share variances for the company. Question 2 Armstrong Manufacturing Inc. (AMI) manufactures mattresses. It makes two types, the "Comfy" and the "Super Comfy". The marketing group has reviewed the year-end profitability reports but are unsure as to how well the company fared compared to the original budget. AMI anticipated combined sales volume of 80,000 units, for the Comfy and the Super- Comfy, when it developed the current year budget. The Comfy had typically accounted for 62.5% of the company's sales in the past and Ralph had used that percentage in calculating the current year's budget, although he was hopeful that the Super-Comfy's proportion would grow. In the budget, the Comfy had a unit selling price of $350.00. Variable manufacturing costs were budgeted at $175.00 per unit. The only variable operating cost was a commission of 6% of the unit selling price that was paid to the sales representatives. The Super- Comfy is a higher quality mattress that uses better materials and is more labour intensive to manufacture than the Comfy. The Super- Comfy mattress was budgeted to sell at $600.00. The variable manufacturing costs were budgeted at 40% of the budgeted selling price. The commission paid on the Super Comfy was 10% in order to encourage sales. Due to a failing economy, sales during the year were slower than was anticipated in the budget. While the company was able to maintain the selling price on the Comfy model, it reduced the selling price of the Super-Comfy by an average of 15% for the year. The company increased the sales commission paid on the Super-Comfy to 14% of the actual selling price. Following is a summary of other relevant product information for the year: Comfy Super-Comfy Budgeted sales volume 50,000 30,000 Actual sales volume 55,000 24,000 Actual variable manufacturing costs per unit $190.00 $265.00 Fixed manufacturing and fixed marketing costs were anticipated to be $12,000.000. Actual fixed costs were very close to budget. Anticipated industry volume was 1,200,000 units per year. Actual industry volume was 10% less than anticipated. 1. What was the budgeted operating income for the current year? (4 marks) 2. What was the actual operating income for the current year? (3 marks) 3. Prepare a variance analysis from the information provide by calculating the following variances: 1. Flexible budget variance for both products. (2 marks) 2. Sales volume variance for both products. (2 marks) 3. Sales quantity variance for both products. (2 marks) 4. Mix variance for both products. (2 marks) 4. Calculate the market size and market share variance for the gadgets. (4 marks) 5. Assess the company's performance for the year. (2 marks)