Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. A frame (C) is initially coincident with frame (A). (C) is first rotated about the , axis by angle 6, and then the

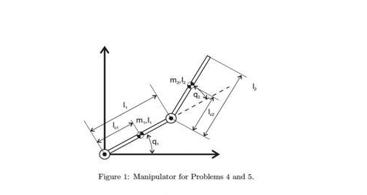

1. A frame (C) is initially coincident with frame (A). (C) is first rotated about the , axis by angle 6, and then the resulting frame is rotated about the , axis by angle o (a) Draw and label the rotations. (b) Give the rotation matrix. "R, which changes the description of vector V given in frame (C), VC, to the same vector described in frame (4). (e) What properties mast a matrix have to be considered a rotation matrix? (d) Show that R* is a rotation matrix for the values given above. 2. Write a Matlah or python script to plot the workspace boundaries of two of the following manipulator arm robotic (a) Articulated RRR (b) SCARA RRP (e) Spherical RRP (d) Cylindrical RPP Set all link lengths to 1. Please print your plots and upload your code to Blackboard. 3. In each of the following questions, prove your answer. Is the product of two: (a) symmetric matrices symmetric? (b) positive definite matrices positive definite? (c) symmetric positive definite matrices positive definite? (d) symmetric positive definite matrices symmetric positive definite? 4. Consider a two link manipulator with revolute joints and link lengths, I and lg. Assume that the end effector is subject to a unit force acting towards joint 1, its "shoulder." (a) What variables constitute the manipulator's configuration? (b) Calculate the force vector acting on the end effector as a function of the joint angles. (e) Calculate the joint torques required to maintain static equilibrium as a function of the joint angles. (d) Plot the joint torques as a function of the joint angles in degrees. Use the Matlab function "mesh' to get a decent looking 3D plot. Type help mesh' to learn how to use the function L ml mal Figure 1: Manipulator for Problems 4 and 5. 5. Now consider the same manipulator is oriented in the vertical plane such that gravity is acting on the two links. Calculate and plot the joint torques required to maintain static equilibrium as a function of the manipulator's configuration. Hint: think back to your first static's class. Simply sum the torques caused by all of the forces. 6. Consider the situation where we want to move the endpoint of a manipulator from its current position, x = [136], to the surface: 3x + 2y + = 1. The goal is to find the closest point on the surface to the manipulator's current location. (a) Write a function defining the Euclidean distance, d, from the current position to some location on the surface. (b) Using Lagrange Multipliers, minimize the distance subject to the constraint defined by the surface. What is the closest point on the surface to the manipulator's current point? (c) Check your answer by plugging the values back into the constraint equation.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.39 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


