Question 1: Consider all questions below
1. Compare the monthly payments and total loan costs for the following pairs of loan options. Assume that both loans are fixed rate and have the same closing costs.
You need a ?$200,000 loan.
Option? 1: a? 30-year loan at an APR of 9.5?%.
Option? 2: a? 15-year loan at an APR of 9%.
Find the monthly payment for each option.
The monthly payment for option 1 is ?$
The monthly payment for option 2 is ?$
?(Do not round until the final answer. Then round to the nearest cent as? needed.)
Find the total amount paid for each option.
The total payment for option 1 is ?$
The total payment for option 2 is ?$
?(Use the answers from the previous step to find this answer. Round to the nearest cent as? needed.)
Compare the two options. Which appears to be the better? option?
A. Option 2 is the better? option, but only if the borrower can afford the higher monthly payments over the entire term of the loan.
B. Option 1 is the better? option, but only if the borrower plans to stay in the same home for the entire term of the loan.
C. Option 2 will always be the better option
D. Option 1 will always be the better option.
2. Compare the monthly payments and total loan costs for the following pairs of loan options. Assume that both loans are fixed rate and have the same closing costs.
You need a ?$80,000 loan.
Option? 1: a? 30-year loan at an APR of 5.55?%.
Option? 2: a? 15-year loan at an APR of 5.15?%.
Find the monthly payment for each option.
The monthly payment for option 1 is ?$
The monthly payment for option 2 is ?$
?(Do not round until the final answer. Then round to the nearest cent as? needed.)
Find the total amount paid for each option.
The total payment for option 1 is ?$
The total payment for option 2 is ?$
?(Use the answers from the previous step to find this answer. Round to the nearest cent as? needed.)
Compare the two options. Which appears to be the better? option?
A. Option 2 is the better? option, but only if the borrower can afford the higher monthly payments over the entire term of the loan.
B. Option 1 is the better? option, but only if the borrower plans to stay in the same home for the entire term of the loan.
C. Option 2 will always be the better option
D. Option 1 will always be the better option
Question 2: Answer all questions below
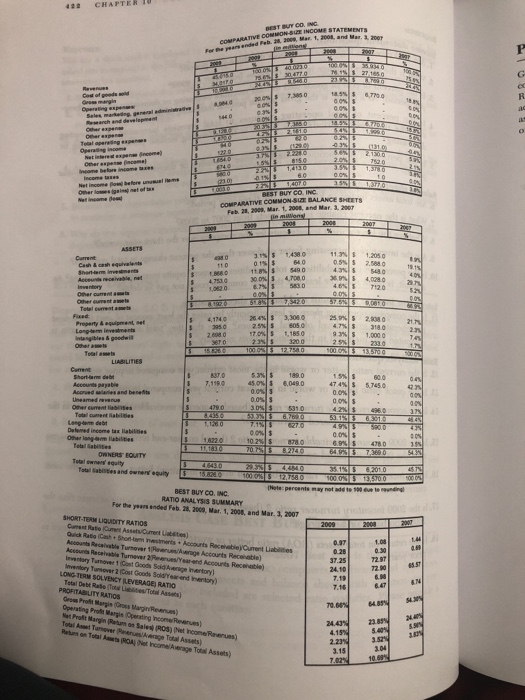
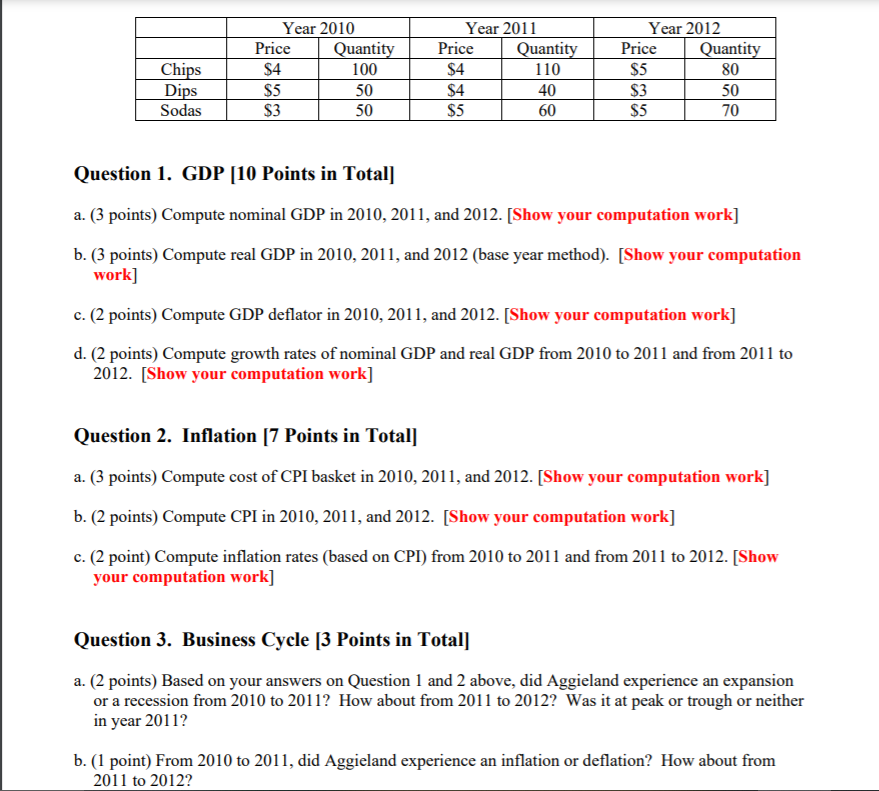
LONG-TERM ASSETS 121 REQUIRED Income statement questions: 1. Are total revenues higher or lower over the three-year period? 2. What is the percent change in total revenues from 2007 to 2009? 3. Is the percent of cost of goods sold to total revenues increasing or decreasing over the three- year period? As a result, is the gross margin percent increasing or decreasing" 4. Is the percent of total operating expenses to total revenues increasing or decreasing over the three-year period? As a result, is the operating income percent increasing or decreasing? 5. Is the percent of net income to total revenue increasing or decreasing over the three-year period? Balance sheet questions: 6. Are total assets higher or lower over the three-year period? 7. What is the percent change in total assets from 2007 to 2009? 8. What are the largest asset investments for the company over the three-year period? 9. Are the inventories increasing faster or slower than the percent change in total revenues? 10. Is the percent of total liabilities to total liabilities + owners' equity increasing or decreasing? As a result, is there more or less risk that the company could not pay its debts? Integrative income statement and balance sheet question: 1 1. Is the company operating more or less efficiently by using the least amount of asset investment to generate a given level of total revenues? Note that the "total asset turnover" ratio is computed and included in the "ratio analysis summary". Ratio analysis questions: 12. Is the current ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 13. Is the quick ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 14. Is the accounts receivable turnover ratio I (based on average receivables) better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 15. Is the 2009 accounts receivable turnover ratio 2 (based on year-end receivables) better or worse than the 2009 ratio based on an average? 16. Is the inventory turnover ratio I (based on average inventory) better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 17. Is the 2009 inventory turnover ratio 2 (based on year-end inventory) better or worse than the 2009 ratio based on an average? 18. Is the return on total assets (ROA) ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years?CHAPTER BEST BUT CO. ING. COMPARATIVE COMMON-BUT INCOME STATEMENTS I De pearsended Feb. H Hop, Mar 1, Itg), and Her. $. For God of ponds gold Be march ind developrant 1131 0 213010 8150 1, 370 BEST BUY CO INC COMPARATIVE COMMON-BUT BALANCE SHEETS Feb. 21, 1903, Mar. 1, 2908, and Mar. J. NOT in miWongi ASSETS Current 11.8 9 30 04 4.024 0 Insuntory 10130 TIZO Oner cumnl itabs Talal commit ain't Fond Property A equipment, Fit 4.7% 318 0 1. 185 0 Invinny bles I poodail 1.0010 100 03 5 13 7910 LIABILITIES Short-form that 7. 178.0 8,049.0 47AN 30%$ 531.0 2710 4 79 On lined Income tax listitnon 1.4220 10 2% OWNERS EQUITY Total camps' equity Foul Nabilities and careers equity 314 5 63010 10ON 8 12 7580 100.05 4 1275100 BEST BUY CO. INC IHole- percents may not add to The hat to RATIO ANALYSIS SUMMARY For the yours anded Fab. 28, 2009, Mar, 1, 2010, and Mar. 3, 3907 SHORT-TEAM LIQUIDITY RATIOS 2080 Quick Ratio Cinch + Shortom Insulmints + Account Rych biel Curent Liabilities 1.09 Ancouch Recaleable Turnover 1 Haverun Average Accounts Recunable] /Yearend Accounts Reophable) 37.25 Inwwwtory Turnover 2 [Cost Goods Bold/fair-and Inantory) LONG-TERM SOLVENCY (LEVERAGE) RATIO 7.1 Total Debt Rule (Toul Libifyou Tool Anmetal 7.10 PROFITABILITY RATIOS Grow Prof Bugin (Crops Magin Revrun) Operating Profit Margin Operating Income Revenues Net Profit Margin [Barn on Sales) (803) [het hcome Revenues) 24.AJK Tokill Anget Turnover Pierces/Average Total Assets) 4.15% Butum on Total Arts (RCA) (Net heamalAwrage Total Assets) 2.23% 3.15 1.04 7.02% 10 89Year 2010 Year 2011 Year 2012 Price Quantity Price Quantity Price Quantity Chips $4 100 $4 110 $5 80 Dips $5 50 $4 40 $3 50 Sodas $3 50 $5 60 $5 70 Question 1. GDP [10 Points in Total] a. (3 points) Compute nominal GDP in 2010, 2011, and 2012. [Show your computation work] b. (3 points) Compute real GDP in 2010, 2011, and 2012 (base year method). [Show your computation work] c. (2 points) Compute GDP deflator in 2010, 2011, and 2012. [Show your computation work] d. (2 points) Compute growth rates of nominal GDP and real GDP from 2010 to 2011 and from 2011 to 2012. [Show your computation work] Question 2. Inflation [7 Points in Total] a. (3 points) Compute cost of CPI basket in 2010, 2011, and 2012. [Show your computation work] b. (2 points) Compute CPI in 2010, 2011, and 2012. [Show your computation work] c. (2 point) Compute inflation rates (based on CPI) from 2010 to 2011 and from 2011 to 2012. [Show your computation work] Question 3. Business Cycle [3 Points in Total] a. (2 points) Based on your answers on Question 1 and 2 above, did Aggieland experience an expansion or a recession from 2010 to 2011? How about from 2011 to 2012? Was it at peak or trough or neither in year 2011? b. (1 point) From 2010 to 2011, did Aggieland experience an inflation or deflation? How about from 2011 to 2012?QUESTION 15 which of the following counts as US GDP? 50 Boeing 737 produced in Seattle and sold to Chinese airline Air China 5000 Focus produced by a Ford company in Beijing, China O 10,000 bottles of expensive wine imported from Northern Italy, Brescia, consumed in San Diego 5 million copies of Adele CDs produced in London, and purchased by US Adele fans QUESTION 16 As published by the BEA in September, the Nominal GDP for the second quarter of 2019 is and the real GDP growth rate the second quarter of 2019 is O $ 17.03 trillion, 3% O $ 21.34 trillion, 2.1% C $ 17.03 trillion, 1.2% O $ 19.25 trillion, 1.2%QUESTION 30 1. Table 23-6 The table below contains data for the country of Batterland, which produces only waffles an d pancakes. The base year is 2013. Year Price of Quantity of Price of Quantity of Waffles Waffles Pancakes Pancakes 2010 $2.00 80 $1.00 100 2011 $2.00 100 $2.00 120 2012 $2.00 120 $3.00 150 2013 $4.00 150 $3.00 200 Refer to Table 23-6. In 2010, this country's nominal GDP was $260 $440 $620 $760 QUESTION 31 Sheri, a U.S. citizen, works only in Germany. The value she adds to production in Germany i +'s included in both German GDP and U.S. GDP in German GDP, but is not included in U.S. GDP ET C in U.S. GDP, but is not included in German GDP in neither German GDP nor U.S. GDP QUESTION 32 Disposable personal income is the income that "households have left after paying taxes and non-tax payments to the government businesses have left after paying taxes and non-tax payments to the government households and noncorporate businesses have left after paying taxes and non- tax payments to the government households and businesses have left after paying taxes and non- tax payments to the government QUESTION 33 Gross domestic product adds together many different kinds of goods and services into a singl e measure of the value of economic activity. To do this, GDP makes use of C market prices " statistical estimates of the value of goods and services to consumers. prices based on the assumption that producers make no profits the maximum amount consumers would be willing to pay