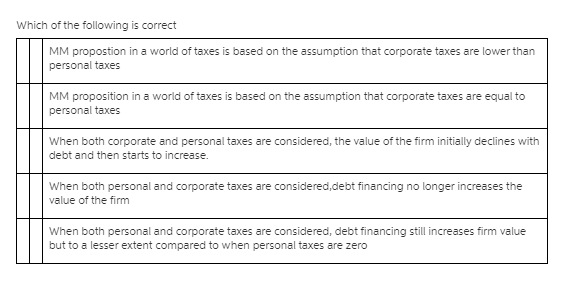
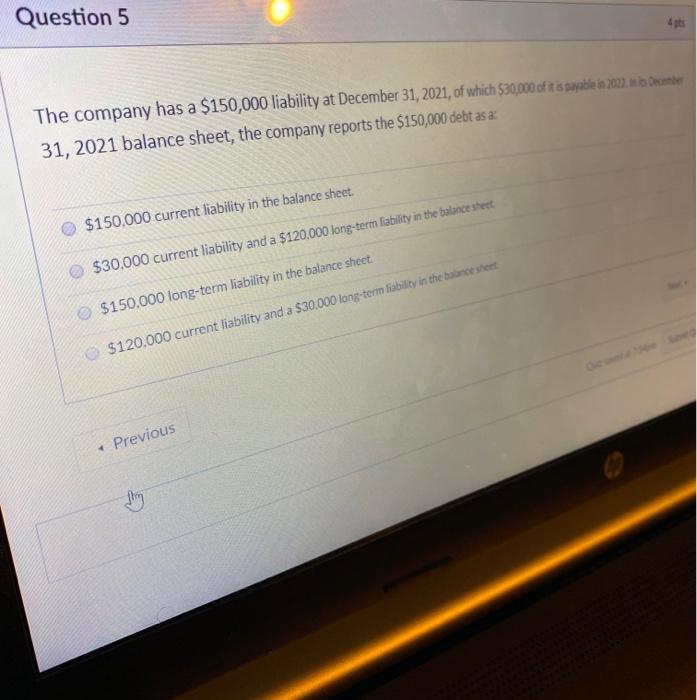
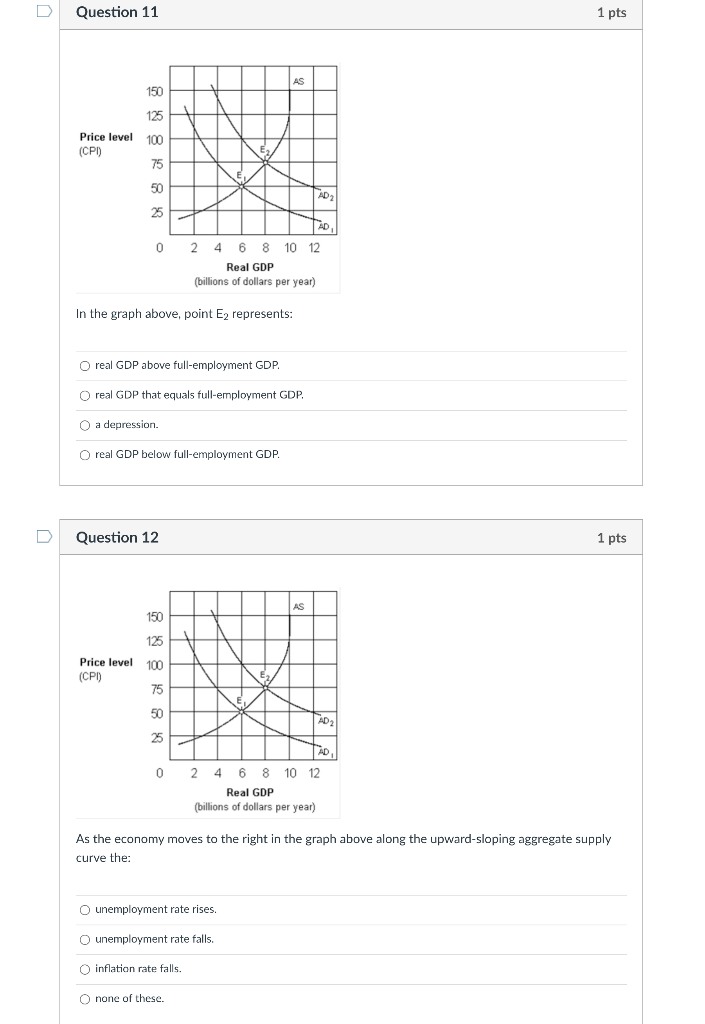
Question
Question 1: Consider all questions below Orange County Case : Use the details provided in class notes and the erisk.com case study for background. (A)
Question 1: Consider all questions below
Orange County Case : Use the details provided in class notes and the erisk.com case study for background.
(A) Suppose that the $7.5 billion portfolio was not leveraged, and simply invested in zero coupon bonds, with identical maturity T. Find T that would justify the losses suffered ($1.6 billion), given an increase in (short term) interest rates of 2.7% (from 3% to 5.7%) using a) Duration approximation for price change
(B) Bob Citron used the Repo Market to leverage up his position from $7.5 billion to a total portfolio value of about $20.5 billion. (i) Explain how such operation would work in practice (provide an example).
(C) A large portion of the total portfolio was invested in securities similar to inverse floaters. Inverse floaters are securities with coupon payments that are inversely related to a reference floating rate. Assume for simplicity that a fraction x of the $20.5 billion portfolio was invested in 1-year T-bills, and the other (1 ? x) was invested in inverse floaters, with annual coupon payments c (t) = 15% ? rTBill (t ? 1), and exactly 3-years to maturity. Assume for simplicity that rTBill (t ? 1)
(i) Generically speaking, how can we compute the duration of an inverse floater? Is it positive or negative? (no calculations)
(ii) Suppose the 1,2, and 3 year term structure of interest rates on Dec 31, 1993 were 3.64%, 4.20% and 4.46% respectively. The corresponding discount factors are 0.9642, 0.9193, 0.8747 respectively (continuous compounding). What is the duration of the inverse floater? (calculations needed)
(iii) Using the duration of the inverse floater from (ii) and the duration of the entire portfolio from part (B) find x.
(D) Convexity: Consider the portfolio in part (C). What is its convexity with respect to current interest rate? (Note that just as duration, the convexity of a portfolio is the value weighted sum of complexities of individual securities).
Question 2: Answer all questions below


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


