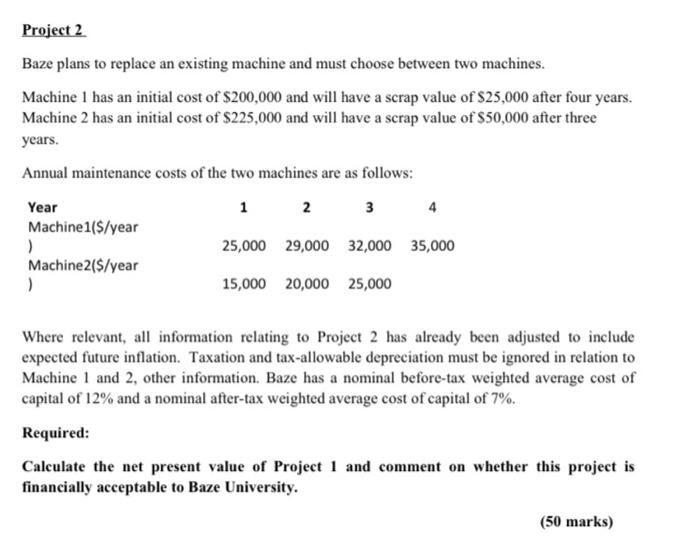
QUESTION 1 Discuss the following using a practical references and examples from the Nigerian Financial Markets: 1. Treasury Bills 11. Treasury certificates III. Bonds IV. Finance Bill 2020 (25 marks). QUESTION 2 Baze University is produces a range of central heating systems for sale to builders' merchants. As a result of increasing demand for the businesses' products, the directors have decided to expand production. The cost of acquiring new plants and machinery and the increase in working capital requirements are planned to be financed by a mixture of long-term and short-term borrowing, Required a) As the director of finance of Baze University, discuss the major factors that should be considered when deciding on the appropriate mix of long-term borrowing necessary to finance the expansion programme. b) List and explain the appropriate finance mix to Baze University as follows: 1. Three short-term sources of finance II. Three long-term sources of finance (25 marks) QUESTION 3 Baze University is evaluating two investment projects, as follows. Project 1 This is an investment in new machinery to produce a recently-developed product. The cost of the machinery, which is payable immediately, is $1.5 million, and the scrap value of the machinery at the end of four years is expected to be $100,000. Tax-allowable depreciation can be claimed on this investment on a 25% reducing balance basis. Information on future returns from the investment has been forecast to be as follows: Year Sales Volume (unit/Year) Selling Price (S/unit) Variable Cost (S/unit) Fixed cost (year) 1 2 3 4 140,00 50,000 95.000 0 75,000 25 24 23 23 10 12 12.5 105,00 115,00 125,00 125,00 0 0 0 0 This information must be adjusted to allow for selling price inflation of % per year and variable cost inflation of 2.5% per year. Fixed costs, which are wholly attributable to the project, have already been adjusted for inflation. Baze pays profit tax of 30% per year one year in arrears. Project 2 Baze plans to replace an existing machine and must choose between two machines. Machine 1 has an initial cost of $200,000 and will have a scrap value of $25,000 after four years. Machine 2 has an initial cost of $225,000 and will have a scrap value of $50,000 after three years. Annual maintenance costs of the two machines are as follows: Year 1 2 3 4 Machinel($/year ) 25,000 29,000 32,000 35,000 Machine 2($/year ) 15,000 20,000 25,000 Where relevant, all information relating to Project 2 has already been adjusted to include expected future inflation. Taxation and tax-allowable depreciation must be ignored in relation to Machine 1 and 2 other information. Baze has a nominal before-tax weighted average cost of capital of 12% and a nominal after-tax weighted average cost of capital of 7%. Required: Calculate the net present value of Project 1 and comment on whether this project is financially acceptable to Baze University. (50 marks) QUESTION 1 Discuss the following using a practical references and examples from the Nigerian Financial Markets: 1. Treasury Bills 11. Treasury certificates III. Bonds IV. Finance Bill 2020 (25 marks). QUESTION 2 Baze University is produces a range of central heating systems for sale to builders' merchants. As a result of increasing demand for the businesses' products, the directors have decided to expand production. The cost of acquiring new plants and machinery and the increase in working capital requirements are planned to be financed by a mixture of long-term and short-term borrowing, Required a) As the director of finance of Baze University, discuss the major factors that should be considered when deciding on the appropriate mix of long-term borrowing necessary to finance the expansion programme. b) List and explain the appropriate finance mix to Baze University as follows: 1. Three short-term sources of finance II. Three long-term sources of finance (25 marks) QUESTION 3 Baze University is evaluating two investment projects, as follows. Project 1 This is an investment in new machinery to produce a recently-developed product. The cost of the machinery, which is payable immediately, is $1.5 million, and the scrap value of the machinery at the end of four years is expected to be $100,000. Tax-allowable depreciation can be claimed on this investment on a 25% reducing balance basis. Information on future returns from the investment has been forecast to be as follows: Year Sales Volume (unit/Year) Selling Price (S/unit) Variable Cost (S/unit) Fixed cost (year) 1 2 3 4 140,00 50,000 95.000 0 75,000 25 24 23 23 10 12 12.5 105,00 115,00 125,00 125,00 0 0 0 0 This information must be adjusted to allow for selling price inflation of % per year and variable cost inflation of 2.5% per year. Fixed costs, which are wholly attributable to the project, have already been adjusted for inflation. Baze pays profit tax of 30% per year one year in arrears. Project 2 Baze plans to replace an existing machine and must choose between two machines. Machine 1 has an initial cost of $200,000 and will have a scrap value of $25,000 after four years. Machine 2 has an initial cost of $225,000 and will have a scrap value of $50,000 after three years. Annual maintenance costs of the two machines are as follows: Year 1 2 3 4 Machinel($/year ) 25,000 29,000 32,000 35,000 Machine 2($/year ) 15,000 20,000 25,000 Where relevant, all information relating to Project 2 has already been adjusted to include expected future inflation. Taxation and tax-allowable depreciation must be ignored in relation to Machine 1 and 2 other information. Baze has a nominal before-tax weighted average cost of capital of 12% and a nominal after-tax weighted average cost of capital of 7%. Required: Calculate the net present value of Project 1 and comment on whether this project is financially acceptable to Baze University. (50 marks)