Question: Question 1 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 2 What are three sources of between-groups variation in the two-way between-subjects ANOVA? :M Question 2 (Mandatory) (1

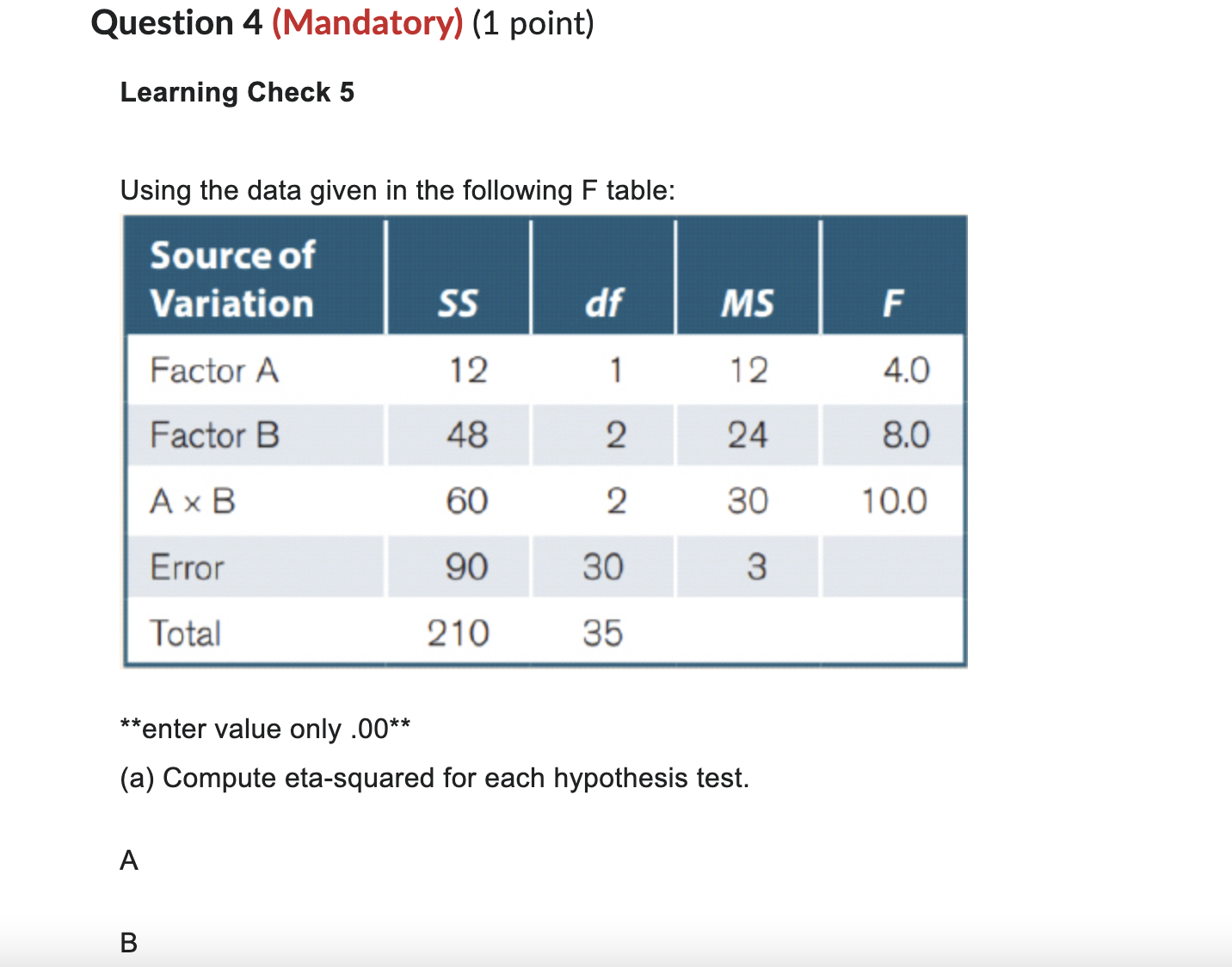

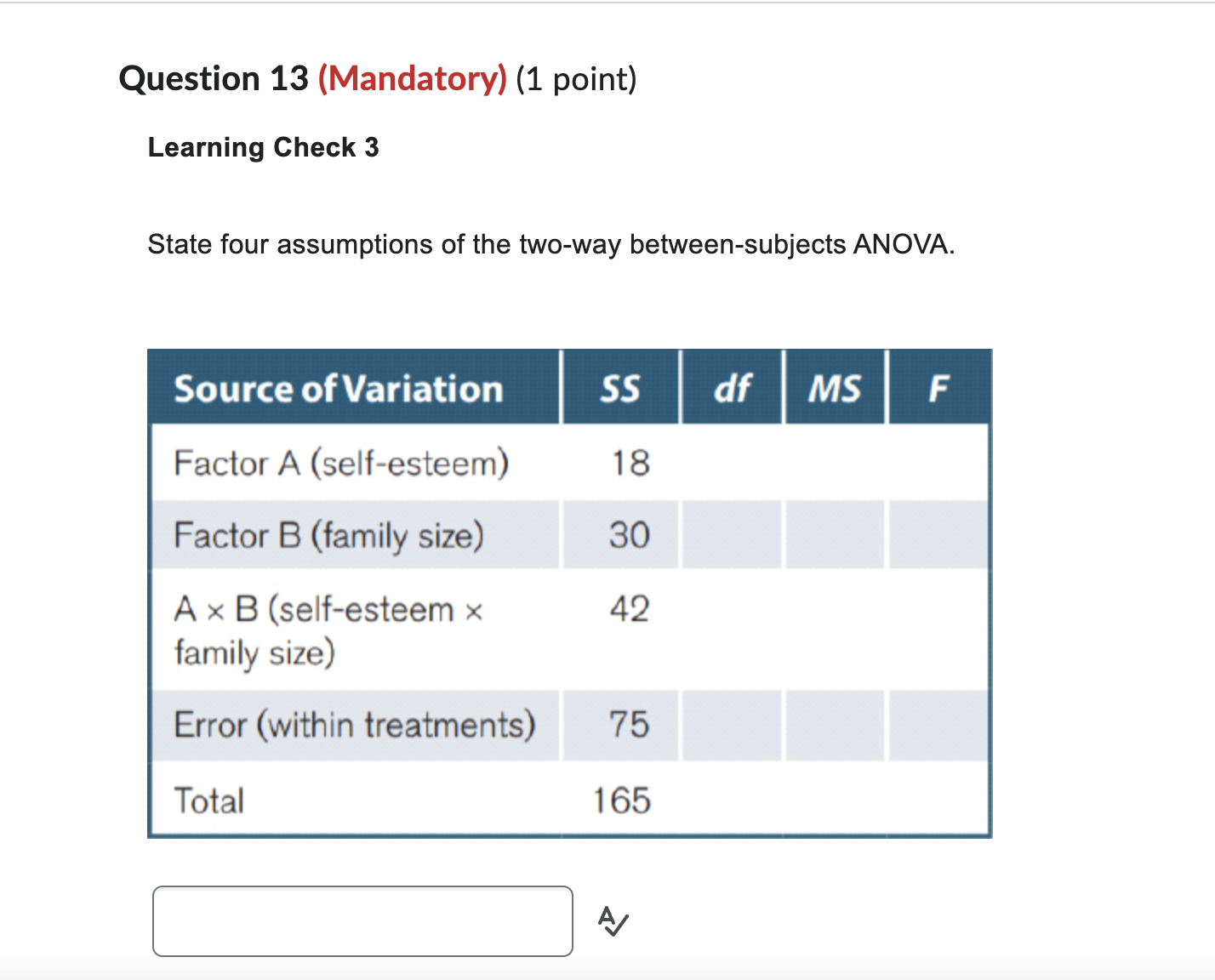
Question 1 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 2 What are three sources of between-groups variation in the two-way between-subjects ANOVA? :M Question 2 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 3 Make a decision for each hypothesis test found in the question with the below scenario. A researcher conducts a study to determine whether parents with different levels of self-esteem (low, high) and family size (1, 2. 3, 4, or 5 children) display different parenting styles. Six parents (n = 6 per cell) were observed using a between-subjects design. :J'v Question 3 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 4 What is the next step for analyzing a significant main effect? ~ Question 4 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 5 Using the data given in the following F table: Source of Variation Factor A Factor B A x B Error Total \"enter value only .00\" (a) Compute eta-squared for each hypothesis test. A B AXB (b) Compute omega-squared for each hypothesis test. A B AXB Blank # 1 A Blank # 2 A/ Blank # 3 A/ Blank # 4 A/ Blank # 5 A/ Blank # 6 A/Which of the following is the next step to analyze a significant A x B interaction in a two-way between-subjects ANOVA? O Compute simple main effect tests O Compute pairwise comparisons O Compute a two-way ANOVA Question 6 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 4 Simple main effect tests compare mean differences or simple main effects of one factor at of a second factor. A/Learning Check 4 State the steps for analyzing an interaction. Blank # 1 A Blank # 2 A/ Blank # 3 A/ Question 8 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 2 A researcher computes the two-way between-subjects ANOVA, and the results show a significant main effect and a significant interaction. Which significant result should the researcher analyze first? AWhat is the pattern in a graph that indicates that a signicant interaction is possible? Question 10 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 1 A researcher measures stress in a group of participants who travel different distances to work (none, short commute, long commute) from different demographic areas (urban, rural). In this example: (a) State the number of factors. (b) State the number of levels of each factor. Blank# 2 5/ Question 11 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 5 Which measure for proportion of variance is more conservative (eta-squared or omega-squared)? _'=/ A researcher conducts a study to determine whether parents with different levels of self-esteem (low, high) and family size (1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 children) display different parenting styles. Six parents (:1 = 6 per cell) were observed using a between-subjects design. Based on the information given here and in the table, answer the following questions. Hint: First complete the F table. **enter values only** (a) What are the degrees of freedom for the A x B interaction? (b) What is the value of mean square error? (c) What is the value for the test statistic for each main-effect and for the interaction? (Hypothesis will be used in another Question) Blank # 1 4/ Blank # 2 Blank # 3 Blank # 4 Blank # 5 Q' Question 13 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 3 State four assumptions of the two-way between-subjects ANOVA. Source of Variation SS df MS F Factor A (self-esteem) 18 Factor B (family size) 30 A x B (self-esteem x 42 family size) Error (within treatments) 75 Total 165 AQuestion 14 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 1 State two reasons that we observe two factors in a single study. _A~/ Question 15 (Mandatory) (1 point) Learning Check 2 What is the denominator for each hypothesis test in the two-way between-subjects ANOVA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


