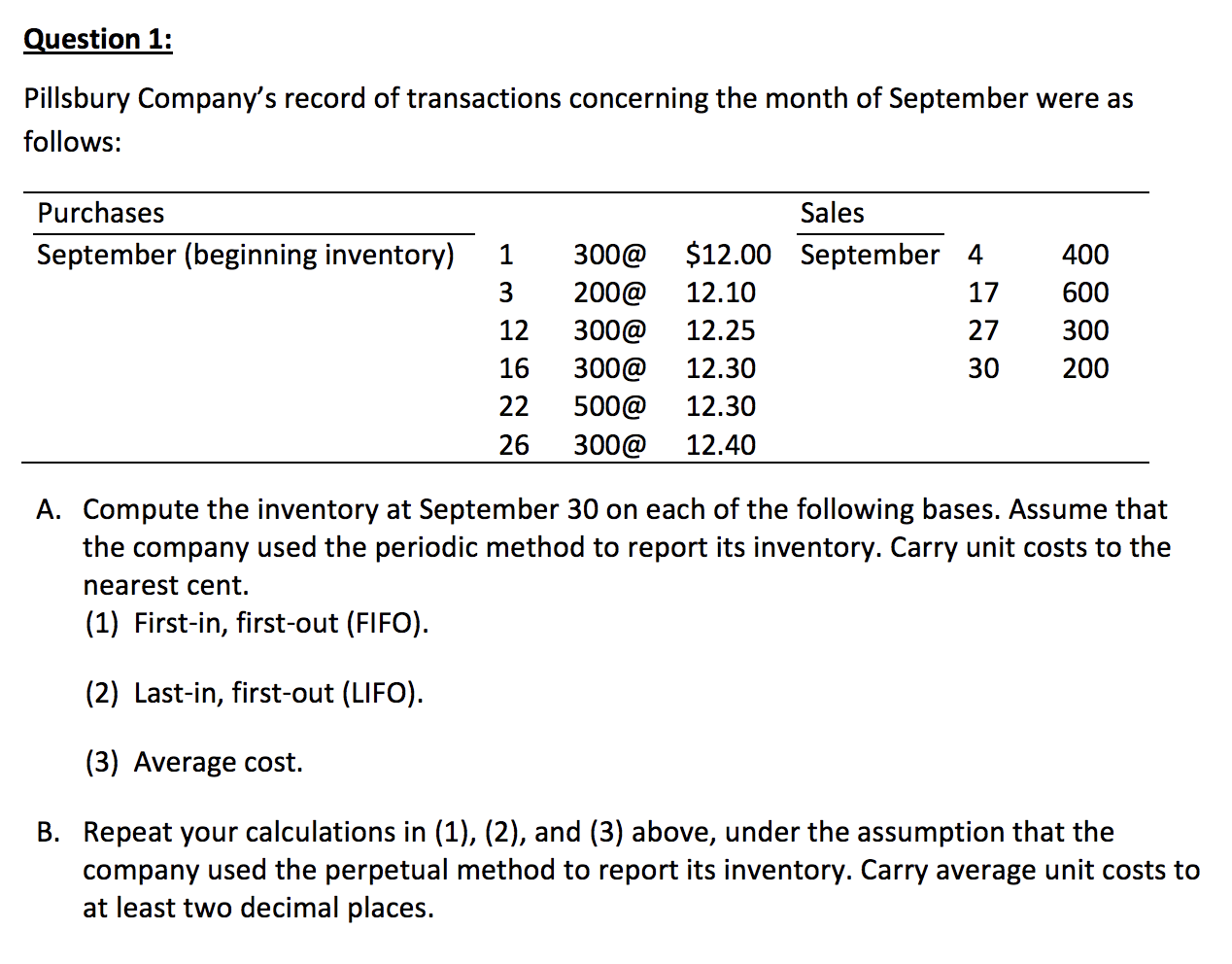
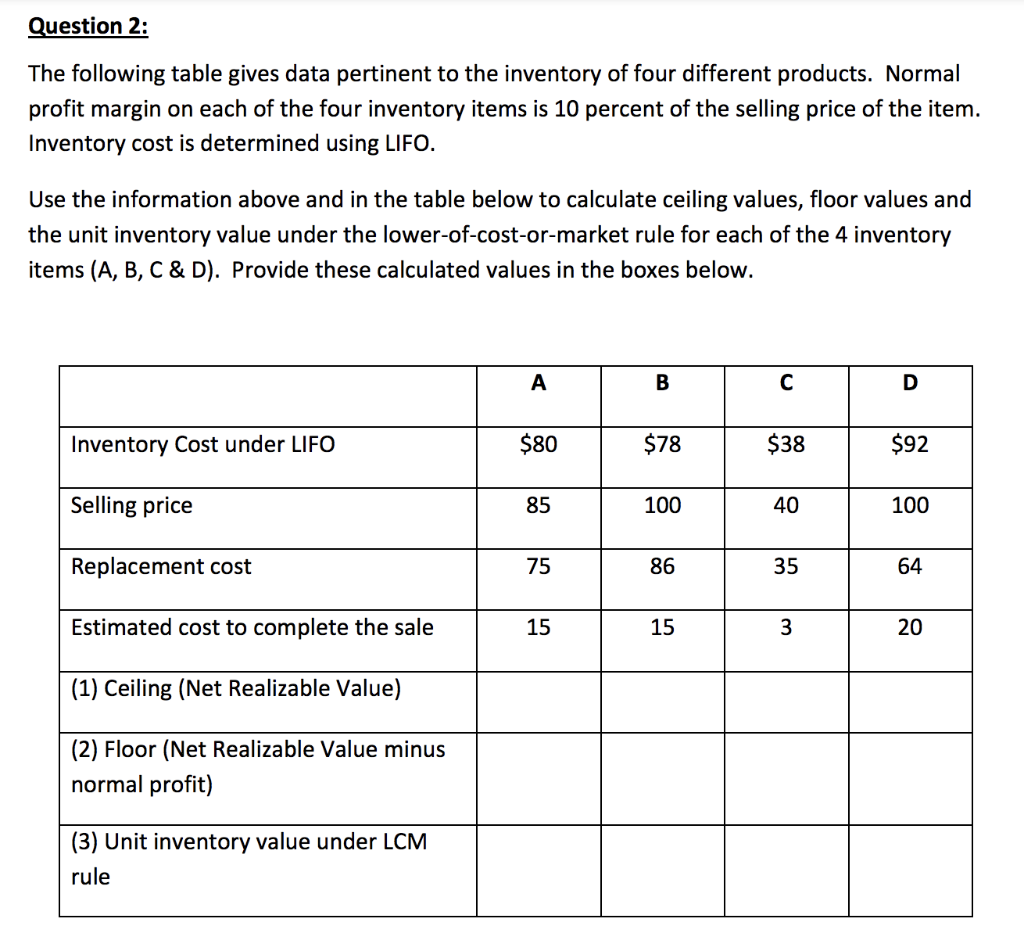
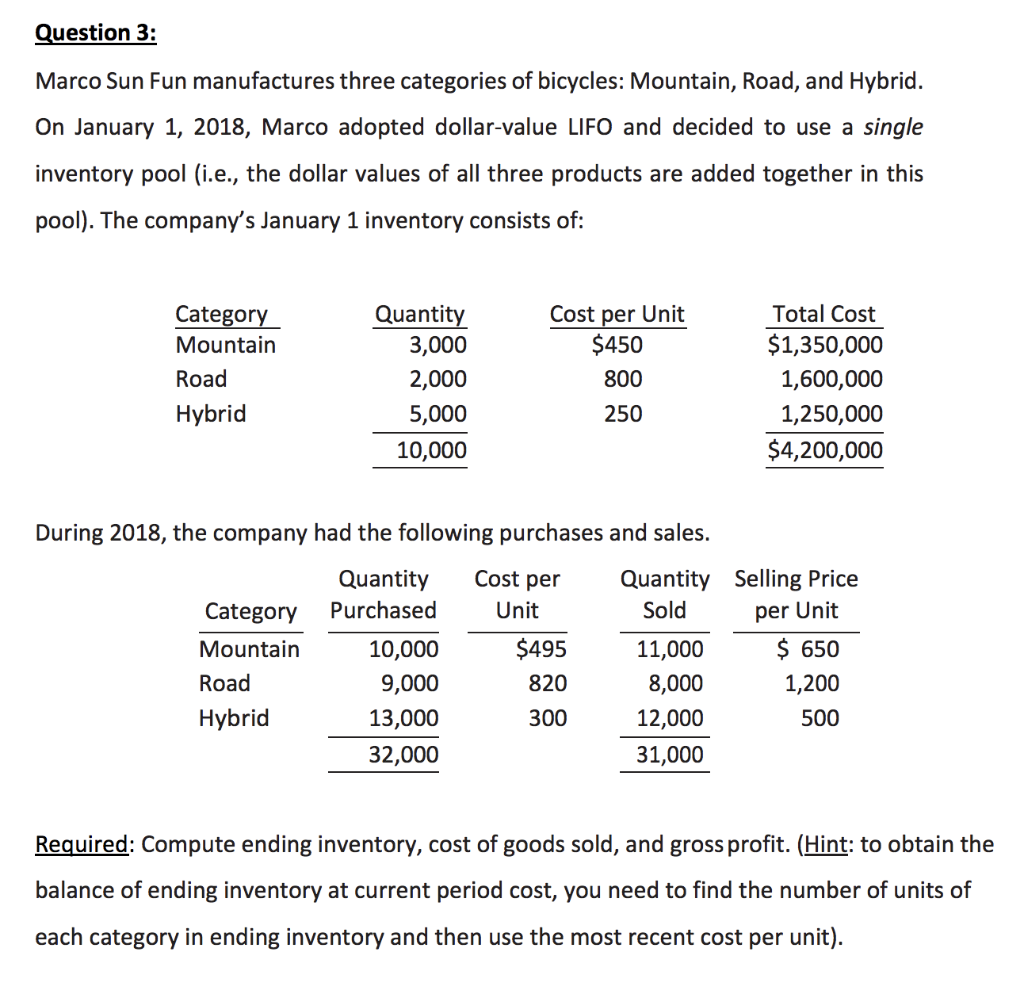
Question 1: Pillsbury Company's record of transactions concerning the month of September were as follows: Purchases September (beginning inventory) 1 3 12 16 22 26 300@ 200@ 300@ 300@ 500@ 300@ Sales $12.00 September 4 12.10 17 12.25 27 12.30 30 12.30 12.40 400 600 300 200 A. Compute the inventory at September 30 on each of the following bases. Assume that the company used the periodic method to report its inventory. Carry unit costs to the nearest cent. (1) First-in, first-out (FIFO). (2) Last-in, first-out (LIFO). (3) Average cost. B. Repeat your calculations in (1), (2), and (3) above, under the assumption that the company used the perpetual method to report its inventory. Carry average unit costs to at least two decimal places. Question 2: The following table gives data pertinent to the inventory of four different products. Normal profit margin on each of the four inventory items is 10 percent of the selling price of the item. Inventory cost is determined using LIFO. Use the information above and in the table below to calculate ceiling values, floor values and the unit inventory value under the lower-of-cost-or-market rule for each of the 4 inventory items (A, B, C & D). Provide these calculated values in the boxes below. A B D Inventory Cost under LIFO $80 $78 $38 $92 Selling price 85 100 40 100 Replacement cost 75 86 35 64 Estimated cost to complete the sale 15 15 3 20 (1) Ceiling (Net Realizable Value) (2) Floor (Net Realizable Value minus normal profit) (3) Unit inventory value under LCM rule Question 3: Marco Sun Fun manufactures three categories of bicycles: Mountain, Road, and Hybrid. On January 1, 2018, Marco adopted dollar-value LIFO and decided to use a single inventory pool (i.e., the dollar values of all three products are added together in this pool). The company's January 1 inventory consists of: Category Mountain Road Hybrid Quantity 3,000 2,000 5,000 10,000 Cost per Unit $450 800 Total Cost $1,350,000 1,600,000 1,250,000 $4,200,000 250 Cost per During 2018, the company had the following purchases and sales. Quantity Quantity Category Purchased Unit Sold Mountain 10,000 $495 11,000 Road 9,000 820 8,000 Hybrid 13,000 300 12,000 32,000 31,000 Selling Price per Unit $ 650 1,200 500 Required: Compute ending inventory, cost of goods sold, and gross profit. (Hint: to obtain the balance of ending inventory at current period cost, you need to find the number of units of each category in ending inventory and then use the most recent cost per unit)









