Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Solution 19.29 Solution 19.34: Solution 19.36: Kindly paraphrase it This remark fails to recognise the fact that the identification
Question 1

Question 2

Question 3

Solution 19.29

Solution 19.34:

Solution 19.36:
Kindly paraphrase it
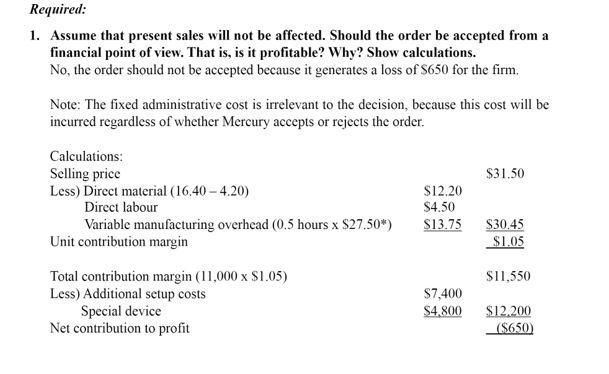
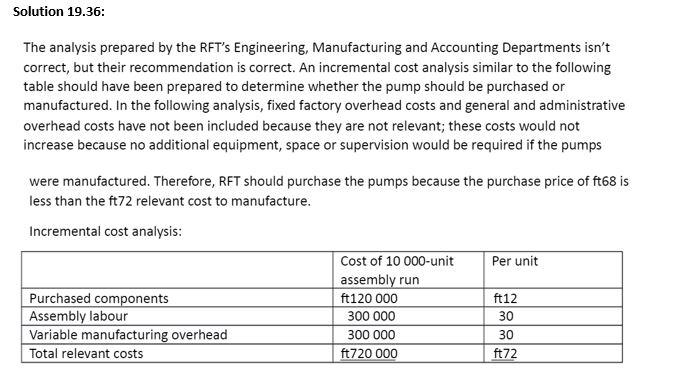
This remark fails to recognise the fact that the identification of relevant information depends on the decision. Data that are relevant to one decision may be irrelevant to another decision. Therefore, it would be impossible for the management accounting system to produce only information that is relevant to all decisions. Answer: 1. The relevant cost of the theolite to be used in producing the special order is the fi29,000 sales value that the company will forego if it uses the chemical. This is an example of an opportunity cost. 2. A) fi29,000 sales value B) fi32,000 carrying amount (8000 kg * f14 per kg): This is irrelevant as this is a sunk cost and no decision now can change it C) fi38,400 current purchase price (8000 kg * fi4.80 per kg); this is irrelevant as the company will not be buying any more theolite. Allocated expenses such as utilities, depreciation on building and manager's salary should not be included in this profit analysis as they are irrelevant to the decision to be mase in this case because these expenses do not change no matter what the decision is. 2. Provide a correct analysis and assess whether or not the gelato bar should be continued Sales 135.000 Less Cost of Goods Sold 60.000 Gross margin $75,000 Less Operating expenses Wages of counter staff 36,000 Paper products 12.000 Depreciation on counter equipment and furnishings 7,500 Total operating expenses $55.500 Gain on Gelato bar if retained $19,500 As there is a gain on the gelato bar of S19,500, the gelato bar should be continued. If the gelato bar is closed the deli will be worse off by S19,500. Dear Managing Director, We recommend against processing banolide into kitrocide. The incremental cost of further processing, ft16 200, exceeds the incremental revenue, ft15 000. This ft15 000 incremental revenue is the difference between the sales value of the kitrocide, ft20 000, and the sales value of the banolide, ft5000. Also, we would like to point out that the cost of the joint process, ft40 000, and the allocation of that cost to the joint products is irrelevant to the decision. Yours sincerely, I.M. Student Partner, Student Consulting Associates Required: 1. Assume that present sales will not be affected. Should the order be accepted from a financial point of view. That is, is it profitable? Why? Show calculations. No, the order should not be accepted because it generates a loss of S650 for the firm. Note: The fixed administrative cost is irrelevant to the decision, because this cost will be incurred regardless of whether Mercury accepts or rejects the order. Calculations: Selling price $31.50 Less) Direct material (16,40 -4.20) $12.20 Direct labour $4.50 Variable manufacturing overhead (0.5 hours x $27.50*) S13.75 $30.45 Unit contribution margin $1.05 S11,550 Total contribution margin (11,000 x $1.05) Less) Additional setup costs Special device Net contribution to profit $7,400 $4.800 $12.200 ($650) *Fixed manufacturing overhead = $750,000 / 60,000 = $12.50 per hour *Variable manufacturing overhead = $40 - $12.50 = $27.50 2. Assume that Mercury's current production activity consumes 70 per cent of planned machine-hour activity. Can the company accept the order and meet Venus' deadline? No, Mercury lacks adequate machine capacity to manufacture the entire order. Calculations: Planned machine hours (5,000 x 3 months) Current usage (15,000 x 70%) Available hours 15,000 10,500 4,500 Required machine hours (11,000 x 0.5 hours) 5,500 3. What options might Mercury consider if management truly wanted to do business with Venus in hopes of building a long-term relationship with the firm? Options include the following: reducing the sales made to other regular" customers in the hope that a long-term relationship with Venus can be established and proves to be profitable acquiring more machine capacity Outsourcing the manufacture of some units working overtime Solution 19.36: The analysis prepared by the RFT's Engineering, Manufacturing and Accounting Departments isn't correct, but their recommendation is correct. An incremental cost analysis similar to the following table should have been prepared to determine whether the pump should be purchased or manufactured. In the following analysis, fixed factory overhead costs and general and administrative overhead costs have not been included because they are not relevant; these costs would not increase because no additional equipment, space or supervision would be required if the pumps were manufactured. Therefore, RFT should purchase the pumps because the purchase price of ft68 is less than the ft72 relevant cost to manufacture. Incremental cost analysis: Per unit Purchased components Assembly labour Variable manufacturing overhead Total relevant costs Cost of 10 000-unit assembly run ft120 000 300 000 300 000 ft720 000 ft12 30 30 ft72 This remark fails to recognise the fact that the identification of relevant information depends on the decision. Data that are relevant to one decision may be irrelevant to another decision. Therefore, it would be impossible for the management accounting system to produce only information that is relevant to all decisions. Answer: 1. The relevant cost of the theolite to be used in producing the special order is the fi29,000 sales value that the company will forego if it uses the chemical. This is an example of an opportunity cost. 2. A) fi29,000 sales value B) fi32,000 carrying amount (8000 kg * f14 per kg): This is irrelevant as this is a sunk cost and no decision now can change it C) fi38,400 current purchase price (8000 kg * fi4.80 per kg); this is irrelevant as the company will not be buying any more theolite. Allocated expenses such as utilities, depreciation on building and manager's salary should not be included in this profit analysis as they are irrelevant to the decision to be mase in this case because these expenses do not change no matter what the decision is. 2. Provide a correct analysis and assess whether or not the gelato bar should be continued Sales 135.000 Less Cost of Goods Sold 60.000 Gross margin $75,000 Less Operating expenses Wages of counter staff 36,000 Paper products 12.000 Depreciation on counter equipment and furnishings 7,500 Total operating expenses $55.500 Gain on Gelato bar if retained $19,500 As there is a gain on the gelato bar of S19,500, the gelato bar should be continued. If the gelato bar is closed the deli will be worse off by S19,500. Dear Managing Director, We recommend against processing banolide into kitrocide. The incremental cost of further processing, ft16 200, exceeds the incremental revenue, ft15 000. This ft15 000 incremental revenue is the difference between the sales value of the kitrocide, ft20 000, and the sales value of the banolide, ft5000. Also, we would like to point out that the cost of the joint process, ft40 000, and the allocation of that cost to the joint products is irrelevant to the decision. Yours sincerely, I.M. Student Partner, Student Consulting Associates Required: 1. Assume that present sales will not be affected. Should the order be accepted from a financial point of view. That is, is it profitable? Why? Show calculations. No, the order should not be accepted because it generates a loss of S650 for the firm. Note: The fixed administrative cost is irrelevant to the decision, because this cost will be incurred regardless of whether Mercury accepts or rejects the order. Calculations: Selling price $31.50 Less) Direct material (16,40 -4.20) $12.20 Direct labour $4.50 Variable manufacturing overhead (0.5 hours x $27.50*) S13.75 $30.45 Unit contribution margin $1.05 S11,550 Total contribution margin (11,000 x $1.05) Less) Additional setup costs Special device Net contribution to profit $7,400 $4.800 $12.200 ($650) *Fixed manufacturing overhead = $750,000 / 60,000 = $12.50 per hour *Variable manufacturing overhead = $40 - $12.50 = $27.50 2. Assume that Mercury's current production activity consumes 70 per cent of planned machine-hour activity. Can the company accept the order and meet Venus' deadline? No, Mercury lacks adequate machine capacity to manufacture the entire order. Calculations: Planned machine hours (5,000 x 3 months) Current usage (15,000 x 70%) Available hours 15,000 10,500 4,500 Required machine hours (11,000 x 0.5 hours) 5,500 3. What options might Mercury consider if management truly wanted to do business with Venus in hopes of building a long-term relationship with the firm? Options include the following: reducing the sales made to other regular" customers in the hope that a long-term relationship with Venus can be established and proves to be profitable acquiring more machine capacity Outsourcing the manufacture of some units working overtime Solution 19.36: The analysis prepared by the RFT's Engineering, Manufacturing and Accounting Departments isn't correct, but their recommendation is correct. An incremental cost analysis similar to the following table should have been prepared to determine whether the pump should be purchased or manufactured. In the following analysis, fixed factory overhead costs and general and administrative overhead costs have not been included because they are not relevant; these costs would not increase because no additional equipment, space or supervision would be required if the pumps were manufactured. Therefore, RFT should purchase the pumps because the purchase price of ft68 is less than the ft72 relevant cost to manufacture. Incremental cost analysis: Per unit Purchased components Assembly labour Variable manufacturing overhead Total relevant costs Cost of 10 000-unit assembly run ft120 000 300 000 300 000 ft720 000 ft12 30 30 ft72Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


