Question
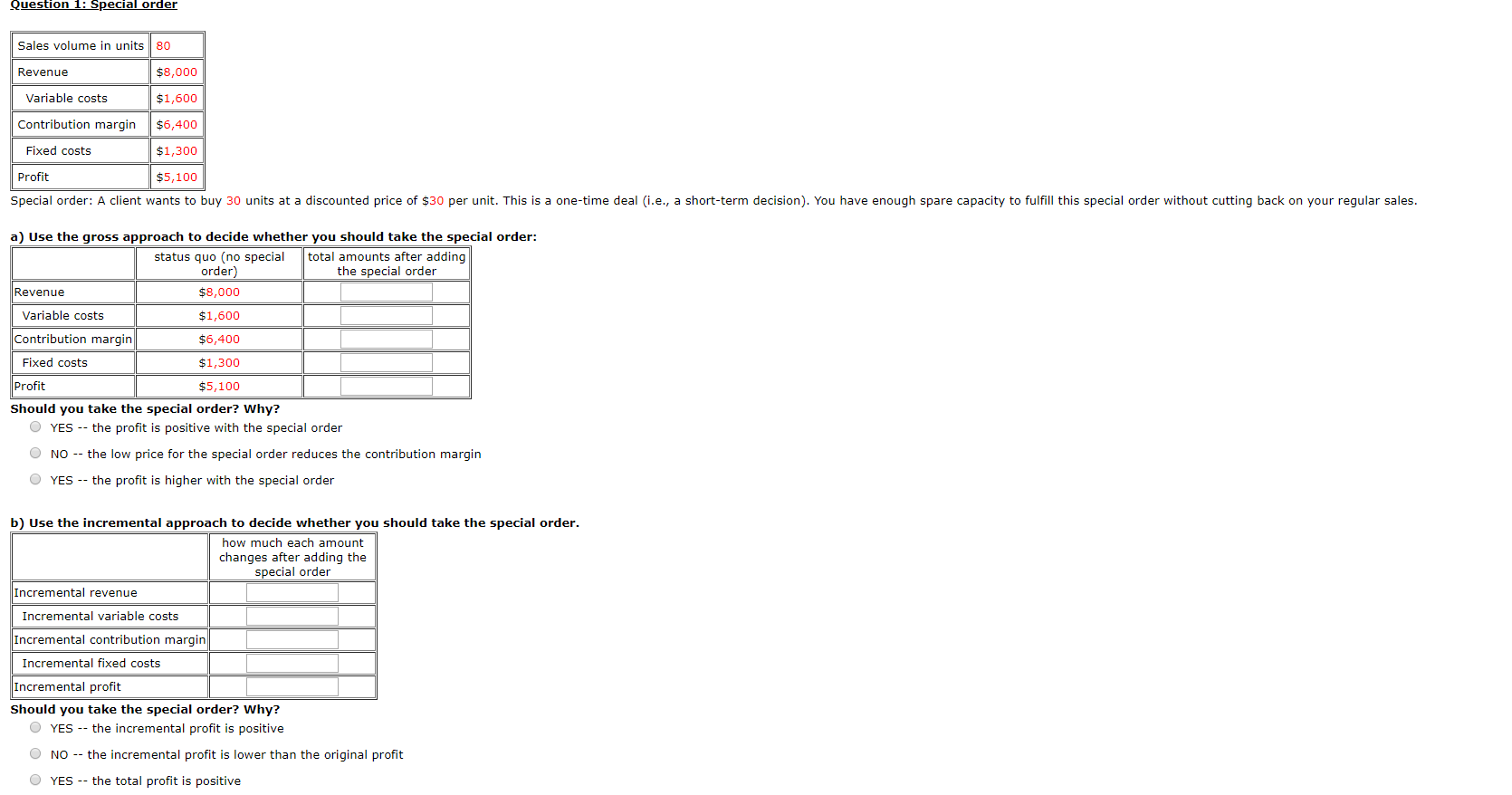
Question 1: Special order Sales volume in units 80 Revenue $8,000 Variable costs $1,600 Contribution margin $6,400 Fixed costs $1,300 Profit $5,100 Special order: A
Question 1: Special order
| Sales volume in units | 80 |
| Revenue | $8,000 |
| Variable costs | $1,600 |
| Contribution margin | $6,400 |
| Fixed costs | $1,300 |
| Profit | $5,100 |
Special order: A client wants to buy 30 units at a discounted price of $30 per unit. This is a one-time deal (i.e., a short-term decision). You have enough spare capacity to fulfill this special order without cutting back on your regular sales. a) Use the gross approach to decide whether you should take the special order:
| status quo (no special order) | total amounts after adding the special order | |
| Revenue | $8,000 | |
| Variable costs | $1,600 | |
| Contribution margin | $6,400 | |
| Fixed costs | $1,300 | |
| Profit | $5,100 |
Should you take the special order? Why?
YES -- the profit is positive with the special orderNO -- the low price for the special order reduces the contribution margin YES -- the profit is higher with the special order
b) Use the incremental approach to decide whether you should take the special order.
| how much each amount changes after adding the special order | |
| Incremental revenue | |
| Incremental variable costs | |
| Incremental contribution margin | |
| Incremental fixed costs | |
| Incremental profit |
Should you take the special order? Why?
YES -- the incremental profit is positive
NO -- the incremental profit is lower than the original profit
YES -- the total profit is positive
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


