Question
question 1 Synergy Airlines, an American airline, is planning to set up a wholly-owned subsidiary in Singapore to expand the market in Southeast Asia. The
question 1
Synergy Airlines, an American airline, is planning to set up a wholly-owned subsidiary in Singapore to expand the market in Southeast Asia. The project will last for 10 years. They expect sales revenues of S$30 million, S$33 million, and S$42 million in the first three years and the revenue would grow at 6.11% for the rest of the project, as suggested by the average GDP growth rate of Singapore. To start its operation, the airline will need a total investment of US$40 million that consists of US$28 million of fixed assets and US$12 million working capital. The fixed assets have a salvage value of S$7 million and the management allows the subsidiary to depreciate the asset at S$2.1 million per year. The airline will incur a total of $S16 million expense for leasing the aeroplanes, maintenance, and wages every year. The variable cost is expected to be 12% of the sales revenue every year. The subsidiary will remit 80% of the net cash flows to its parent company at the end of each year. The cost of capital of the parent is 12% but the Singaporean project is deemed to be riskier and will attract a 15% premium. Synergy Airlines enjoys a lower corporate tax rate of 15% for its Singaporean project. However, the Singaporean government will impose a withholding tax rate of 23%. The U.S. tax policy does not impose taxes on non-US source earnings and any inward remittance to the U.S. are tax-free. The current spot exchange rate for a Singapore dollar (SGD) is 1.2541 US dollars (USD). The management will use the exchange rate of USD 1.5158 / SGD for the entire duration of the capital budgeting. (a) Do a capital budgeting analysis for this Singaporean project by completing the spreadsheet below. [4 marks]
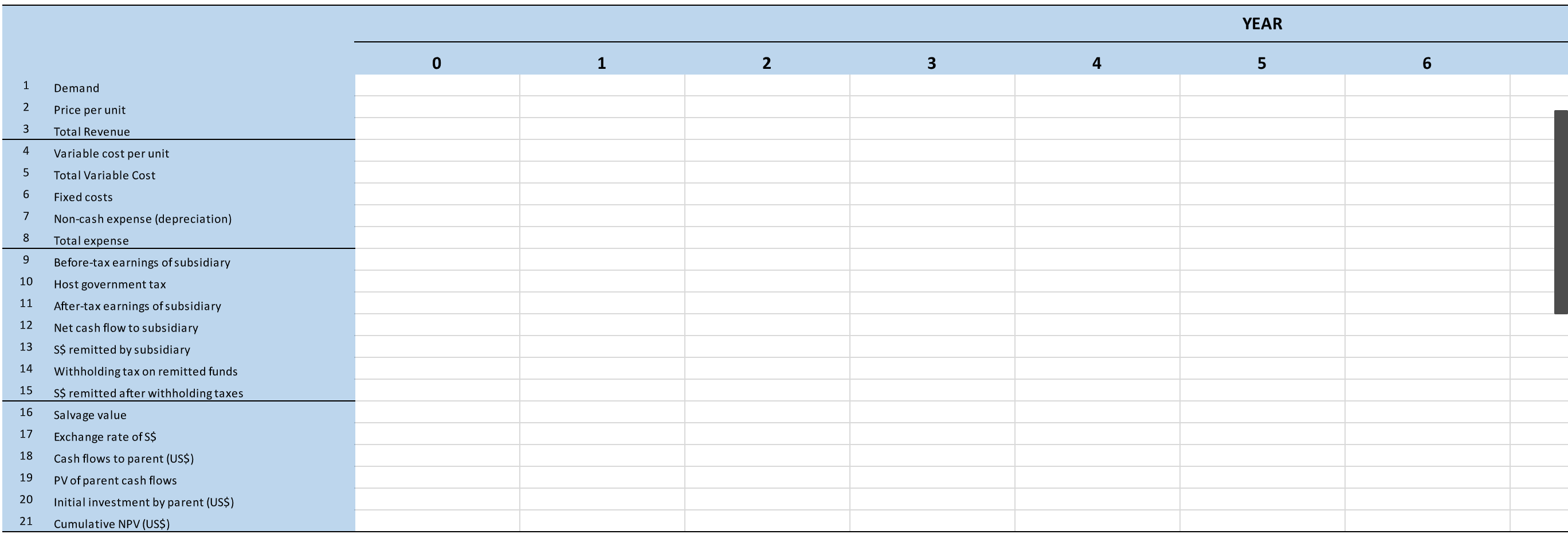
1 Demand 2 Price per unit 3 Total Revenue 4 Variable cost per unit 5 Total Variable Cost 6 Fixed costs 7 8 9 10 11 Non-cash expense (depreciation) Total expense Before-tax earnings of subsidiary Host government tax After-tax earnings of subsidiary 12 Net cash flow to subsidiary 13 S$ remitted by subsidiary 14 15 16 Withholding tax on remitted funds S$ remitted after withholding taxes Salvage value 17 Exchange rate of S$ 18 Cash flows to parent (US$) 19 PV of parent cash flows 20 21 Initial investment by parent (US$) Cumulative NPV (US$) YEAR 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


