Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 13 Deflation is defined as a decrease in the general price level of goods and services, occurring when the inflation rate falls below
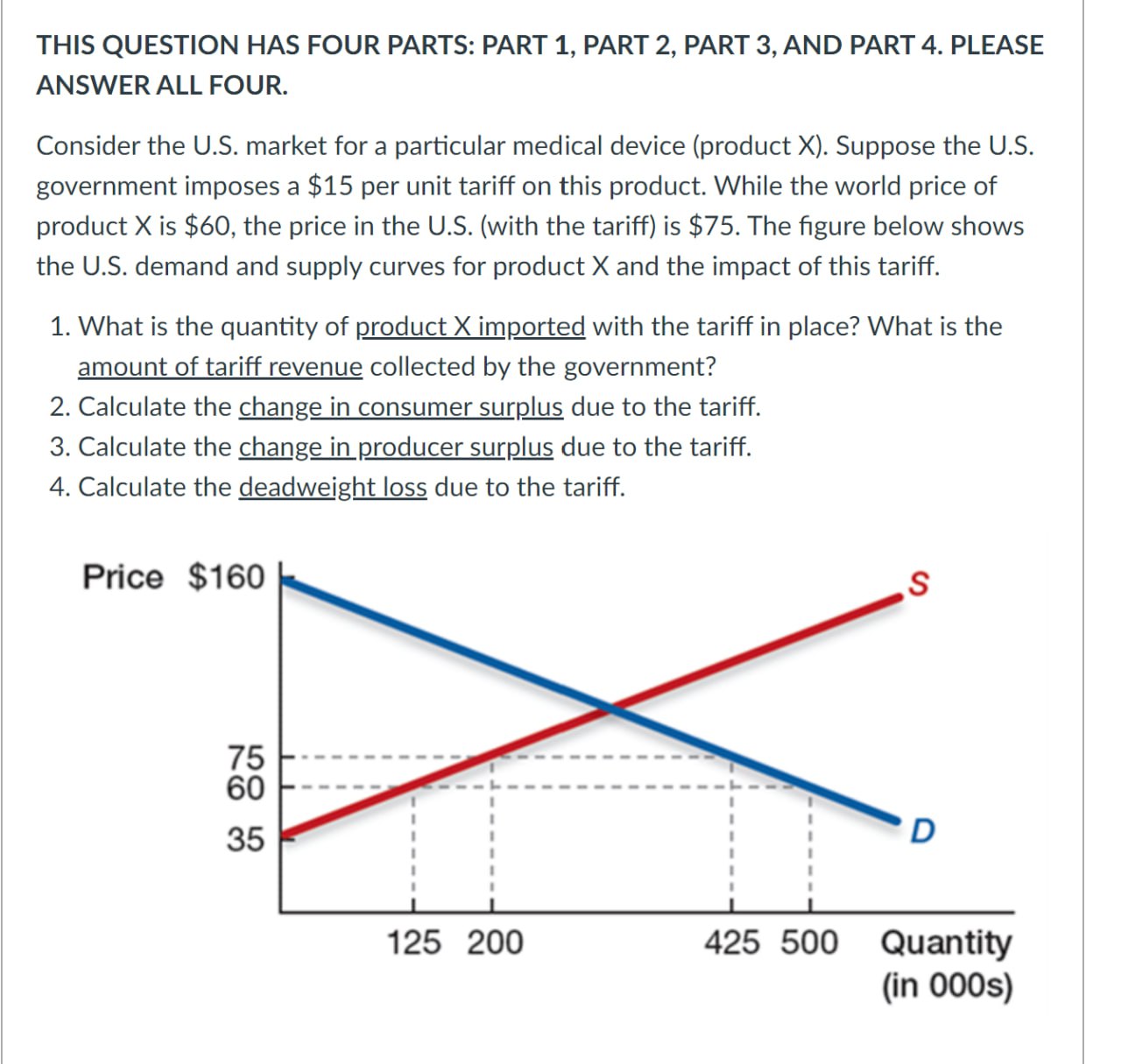
Question 13 Deflation is defined as a decrease in the general price level of goods and services, occurring when the inflation rate falls below 0%. The following passage from former Fed Chairman Bernanke explains some of the differences between a normal recession and a deflationary recession: "However, a deflationary recession may differ in one respect from "normal" recessions in which the inflation rate is at least modestly positive: Deflation of sufficient magnitude may result in the nominal interest rate declining to zero or very close to zero. Once the nominal interest rate is at zero, no further downward adjustment in the rate can occur, since lenders generally will not accept a negative nominal interest rate when it is possible instead to hold cash. At this point, the nominal interest rate is said to have hit the "zero bound."" What are the main consequences of deflation for firms and households if the nominal interest rate hits zero? What would be the real interest rate in this case? Which other tools do Central Banks employ to address the threat of deflation? Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt v Paragraph 10 pts B I U A < T: THIS QUESTION HAS FOUR PARTS: PART 1, PART 2, PART 3, AND PART 4. PLEASE ANSWER ALL FOUR. Consider the U.S. market for a particular medical device (product X). Suppose the U.S. government imposes a $15 per unit tariff on this product. While the world price of product X is $60, the price in the U.S. (with the tariff) is $75. The figure below shows the U.S. demand and supply curves for product X and the impact of this tariff. 1. What is the quantity of product X imported with the tariff in place? What is the amount of tariff revenue collected by the government? 2. Calculate the change in consumer surplus due to the tariff. 3. Calculate the change in producer surplus due to the tariff. 4. Calculate the deadweight loss due to the tariff. Price $160 75 60 35 125 200 S D 425 500 Quantity (in 000s)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
PART 1 Quantity of Product X Imported and Tariff Revenue Based on the information provided in the figure we can determine the quantity of Product X im...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


