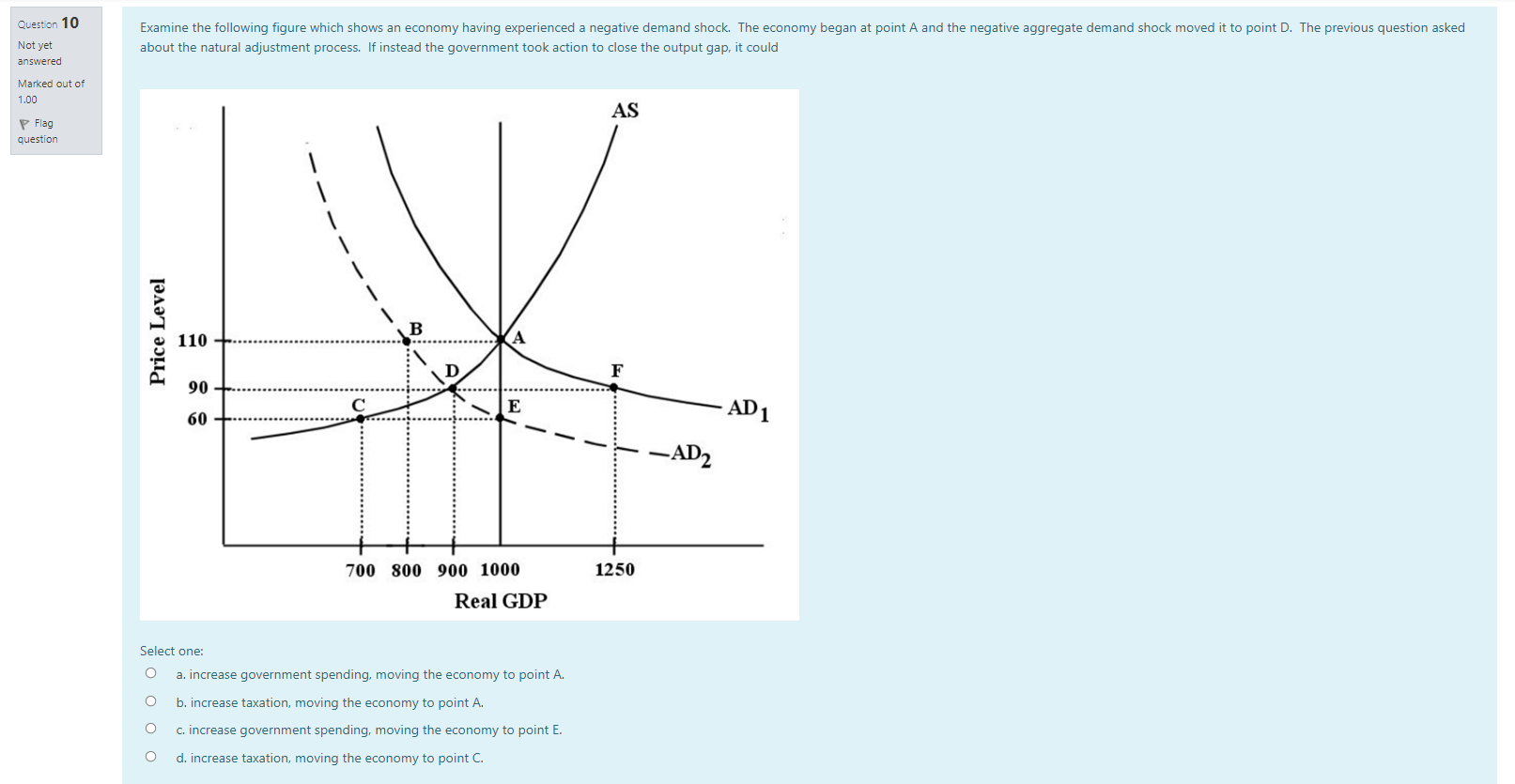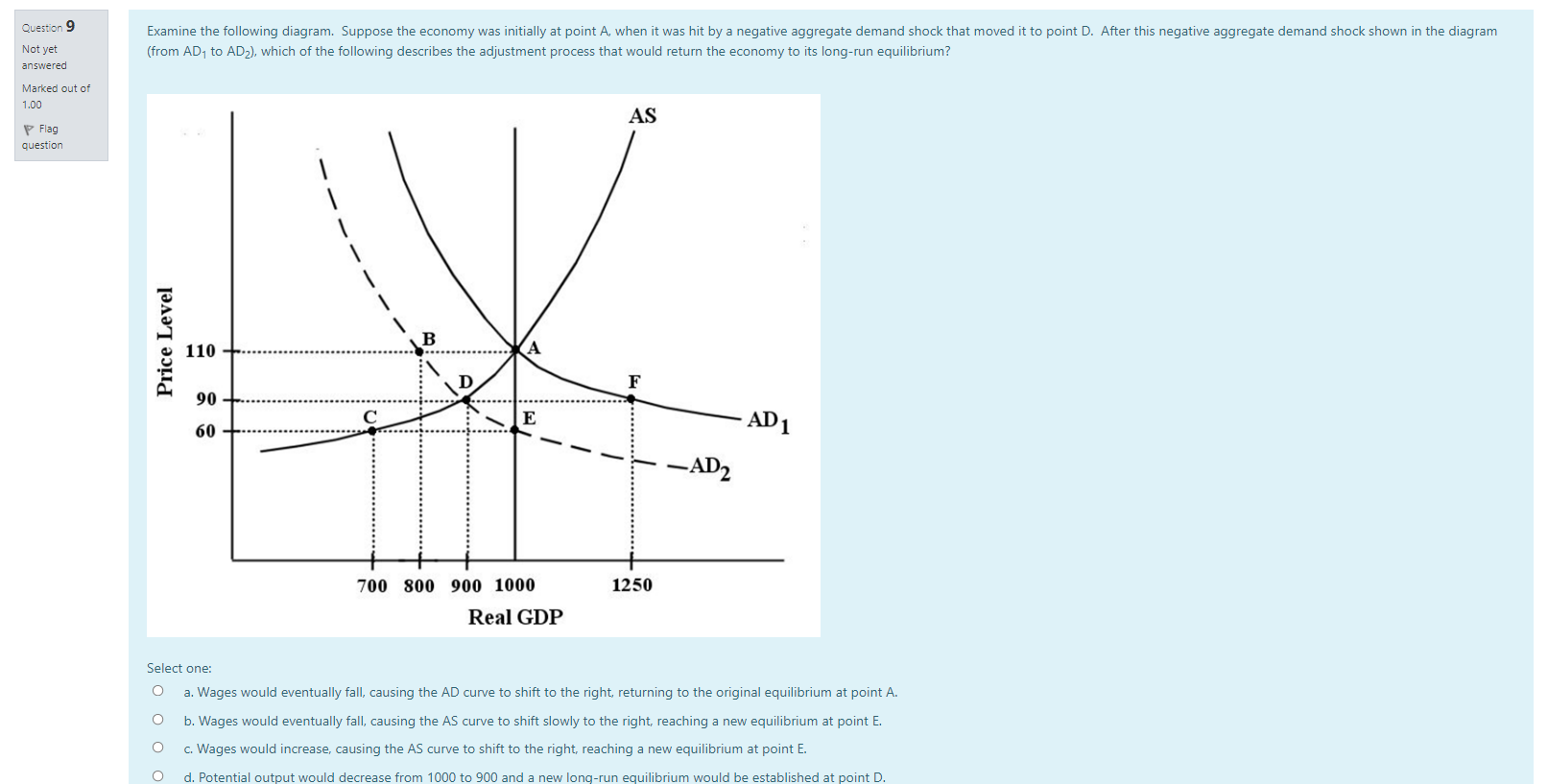
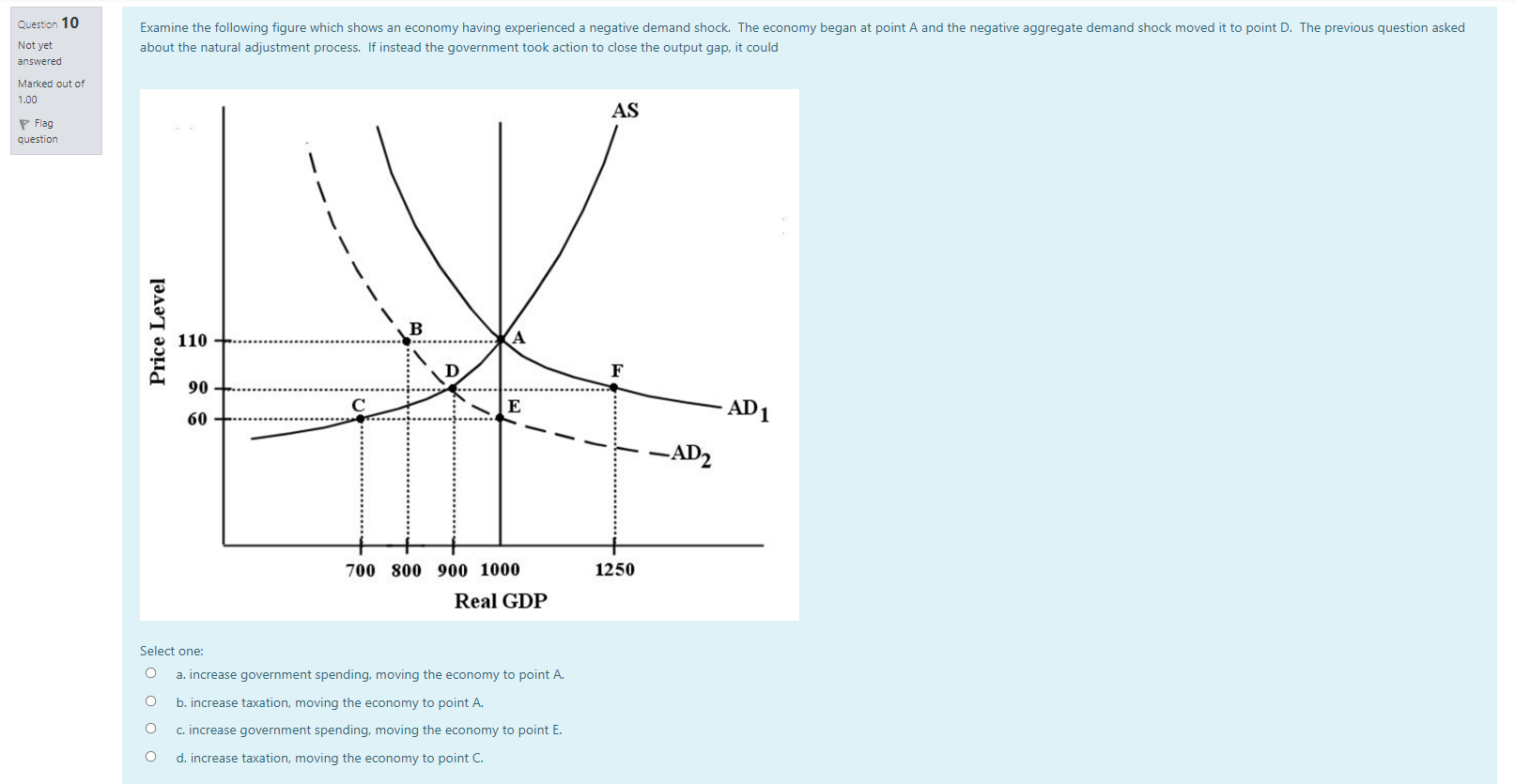
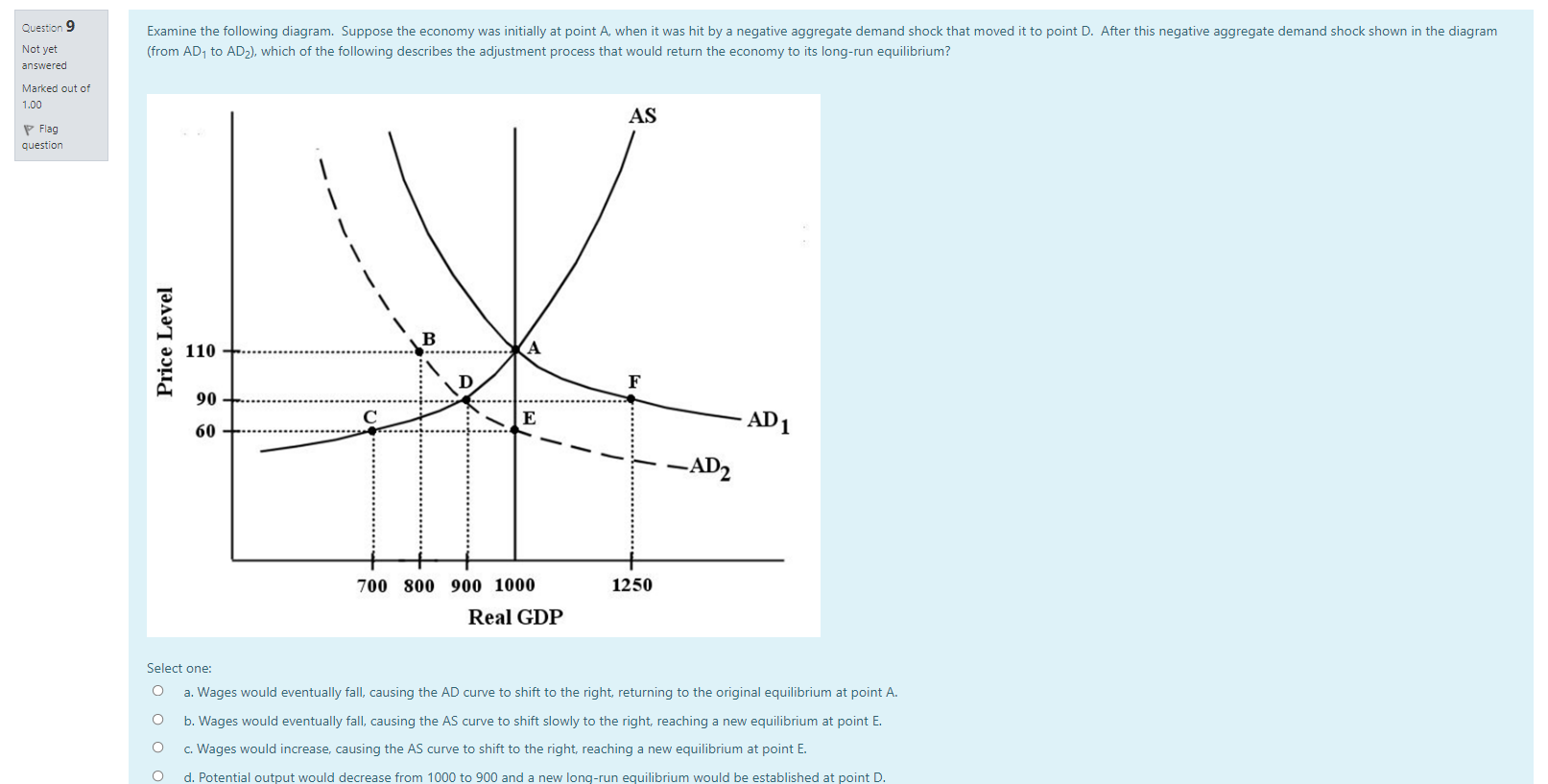
Question 19 In the long run, changes in average material living standards are best shown by Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. growth in real GDP. 1.00 P Flag b. population growth. question O c. growth in real per capita GDP. O d. improvements in fiscal policy. Question 20 The costs of economic growth include Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of a. declining future living standards. 1.00 Flag O b. reduced interest rates. question O c. the effects on workers whose skills are made obsolete by technical change. O d. higher income tax rates.Question 7 Which of the following scenarios would result in a short-run decrease in real GDP and a short-run increase in the price level? Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. Improving consumer confidence. 1.00 Flag O b. A rise in the tax rate. question O c. A technological improvement. d. An increase in the price of oil. Question 8 Which of the following scenarios would result in a short-run decrease in real GDP and a short-run decrease in the price level? Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. Improving consumer confidence. 1.00 Flag O b. A rise in the tax rate. question O C. A technological improvement. O d. An increase in the price of oil.Question 1 One of the reasons why the aggregate demand (AD) curve slopes downward is that Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. aggregate expenditure increases as the price level rises. 1.00 Flag O b. increases in the price level cause consumers to substitute foreign goods for domestic goods. question O c. when the price level falls firms must be more competitive when output increases. O d. when the price level falls consumers increase their saving rate. Question 2 The economy's AS curve is often assumed to be relatively flat at low levels of real GDP. The underlying reasoning is that Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. consumer demand for most goods tends to be non-responsive to price when output is low. \\ Flag O b. consumer demand for most goods tends to be very responsive to price when output is low. question O c. at low levels of output, firms are faced with unused capacity and thus can increase output without significantly increasing their costs. O d. profits are normally high in this section of the AS curve, so firms are willing to expand output. Question 3 Consider the AD/AS macro model. Suppose there is an increase in aggregate demand and, simultaneously, a decrease in aggregate supply. The result will be a Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. rise in real GDP but price level changes will be indeterminate. 1.00 Flag O b. rise in real GDP and a rise in the price level. question O c. an indeterminate change in real GDP and a fall in the price level. O d. an indeterminate change in real GDP and a rise in the price level.Question 15 Consider an economy with a relatively steep AS curve. If there is a shift to the right in the AD curve, there will be a in the price level and a in national output. Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. small increase; large increase P Flag O b. small increase; large decrease question O c. large increase; small increase O d. large increase; small decrease Question 16 The major determinants of economic growth include all of the following EXCEPT Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. technological improvement. P Flag O b. growth in financial capital. question O c. growth in physical capital. O d. growth in human capital. Question 17 According to the Neoclassical growth theory, sustained rising material living standards ultimately can only be explained by Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. growth in human capital. P Flag O b. growth in physical capital. question O c. growth in the labour force. O d. technological change. Question 18 Alleviation of poverty is more achievable in a growing economy mainly because Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Select one: P Flag O a. individuals are more likely to object to the redistribution of income when they earn more. question O b. everyone, including the poor, benefits equally from growth. O c. wage rates for low-income people are naturally rising. O d. nobody has to be made worse off when the increment to income caused by growth is redistributedQuestion 11 Many economists think discretionary fiscal policy is of limited effectiveness in stabilizing the economy because Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. there are long and uncertain lags in implementing fiscal policy. 1.00 Flag O b. changes in government spending and taxation are too small in relation to the size of the economy to have much effect. question O c. the multiplier effects associated with fiscal policy are very large. O d. governments are able to estimate the magnitude of shocks with high precision. Question 12 Suppose Canada's economy is in a long-run equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential output. Now suppose there is an increase in government spending. The long-run impact of this is Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of 1.00 O a. a rise in real GDP and a rise in the price level. Flag b. a rise in real GDP and no change to the price level. question O c. no change to real GDP and a rise in the price level. O d. no change to real GDP and no change to the price level. Question 13 An economy may not quickly and automatically eliminate a recessionary output gap because wages Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. never change in response to changes in the demand for labour. Flag O b. have a tendency to be sticky downward. question O c. have a tendency to fall too quickly. O d. have a tendency to rise too quickly. Question 14 Suppose the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap in the short run. The advantage of using a contractionary fiscal policy rather than allowing the economy's natural adjustment process to operate is that Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. it will reduce the upward pressure on the price level that would otherwise occur. P Flag O b. if private-sector expenditures increase on their own, the policy will stabilize real GDP. question O c. it will shorten what might otherwise be a long recession. O d. it will reduce the downward pressure on the price level that would otherwise occur.Question 4 In the basic AD/AS model, the effect of an aggregate demand shock is divided between a change in output and a change in the price level. How the effect is divided depends on the Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. amount of inflation in the economy. \\ Flag b. position of the AE curve. question O c. size of the simple multiplier. O d. slope of the AS curve. Question 5 Which of the following scenarios would result in a short-run increase in real GDP and a short-run increase in the price level? Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O 1.00 a. Improving consumer confidence. \\ Flag O b. A rise in the tax rate. question c. A technological improvement. O d. An increase in the price of oil. Question 6 Which of the following scenarios would result in a short-run increase in real GDP and a short-run decrease in the price level? Not yet answered Select one: Marked out of O a. Improving consumer confidence. 1.00 \\ Flag O b. A rise in the tax rate. question O C. A technological improvement. O d. An increase in the price of oil.Question 10 Examine the following figure which shows an economy having experienced a negative demand shock. The economy began at point A and the negative aggregate demand shock moved it to point D. The previous question asked Not yet about the natural adjustment process. If instead the government took action to close the output gap, it could answered Marked out of 1.00 AS P Flag question Price Level B 110 -+. ...... F 90 60 - E AD 1 -AD2 700 800 900 1000 1250 Real GDP Select one: O a. increase government spending, moving the economy to point A. O b. increase taxation, moving the economy to point A. O c. increase government spending, moving the economy to point E. O d. increase taxation, moving the economy to point C.Question 9 Examine the following diagram. Suppose the economy was initially at point A, when it was hit by a negative aggregate demand shock that moved it to point D. After this negative aggregate demand shock shown in the diagram Not yet (from AD, to AD2), which of the following describes the adjustment process that would return the economy to its long-run equilibrium? answered Marked out of 1.00 AS P Flag question - - --- Price Level B 110 -...... 90 E 60 - .... AD 1 -AD2 700 800 900 1000 1250 Real GDP Select one: O a. Wages would eventually fall, causing the AD curve to shift to the right, returning to the original equilibrium at point A. O b. Wages would eventually fall, causing the AS curve to shift slowly to the right, reaching a new equilibrium at point E. O c. Wages would increase, causing the AS curve to shift to the right, reaching a new equilibrium at point E. O d. Potential output would decrease from 1000 to 900 and a ne equilibrium would be esta blished at point D