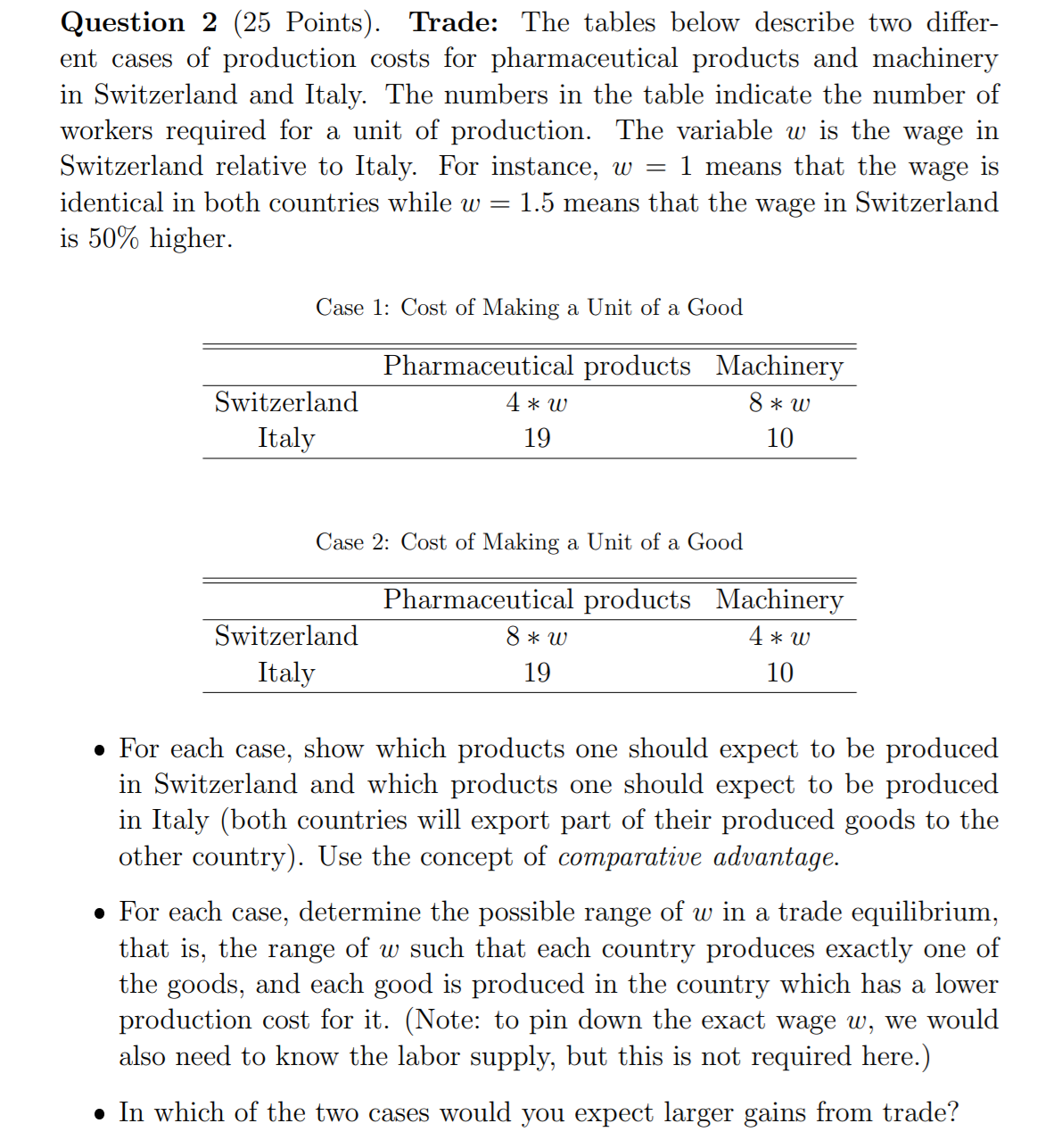
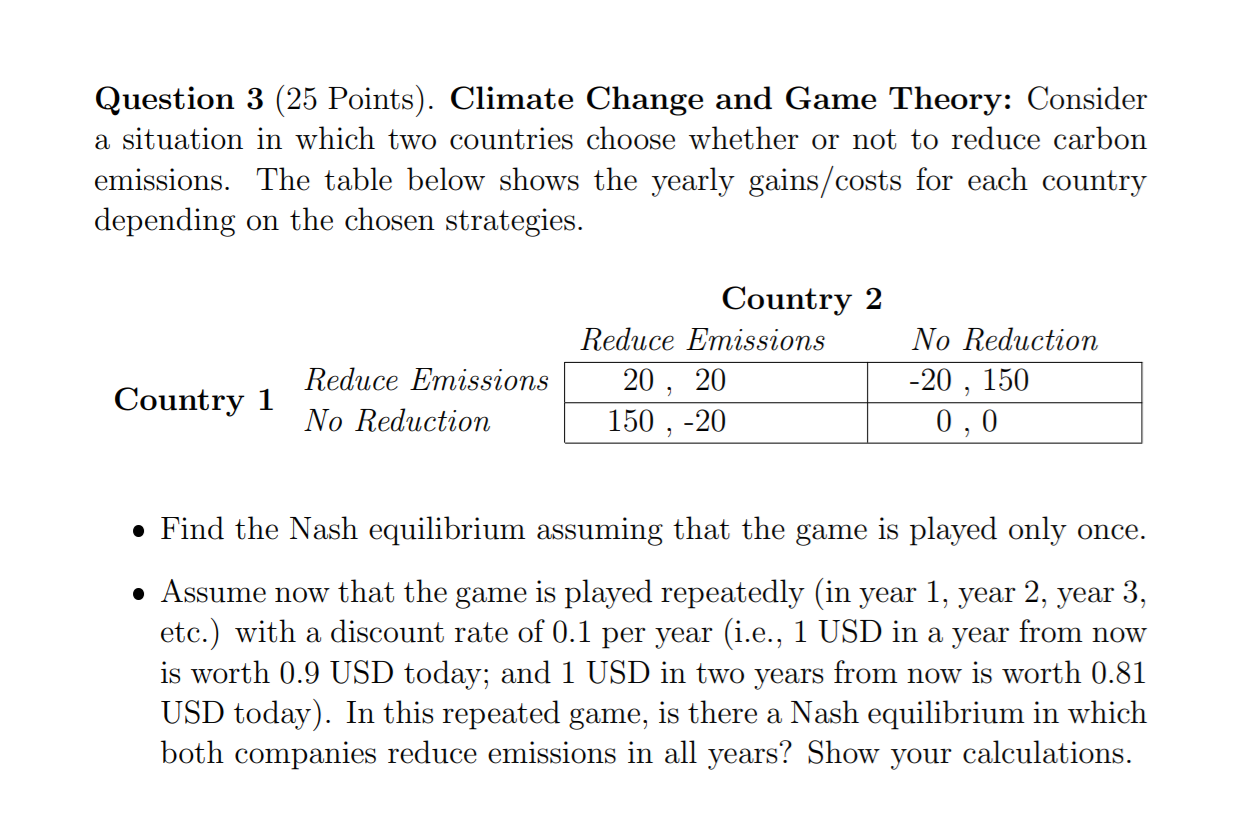
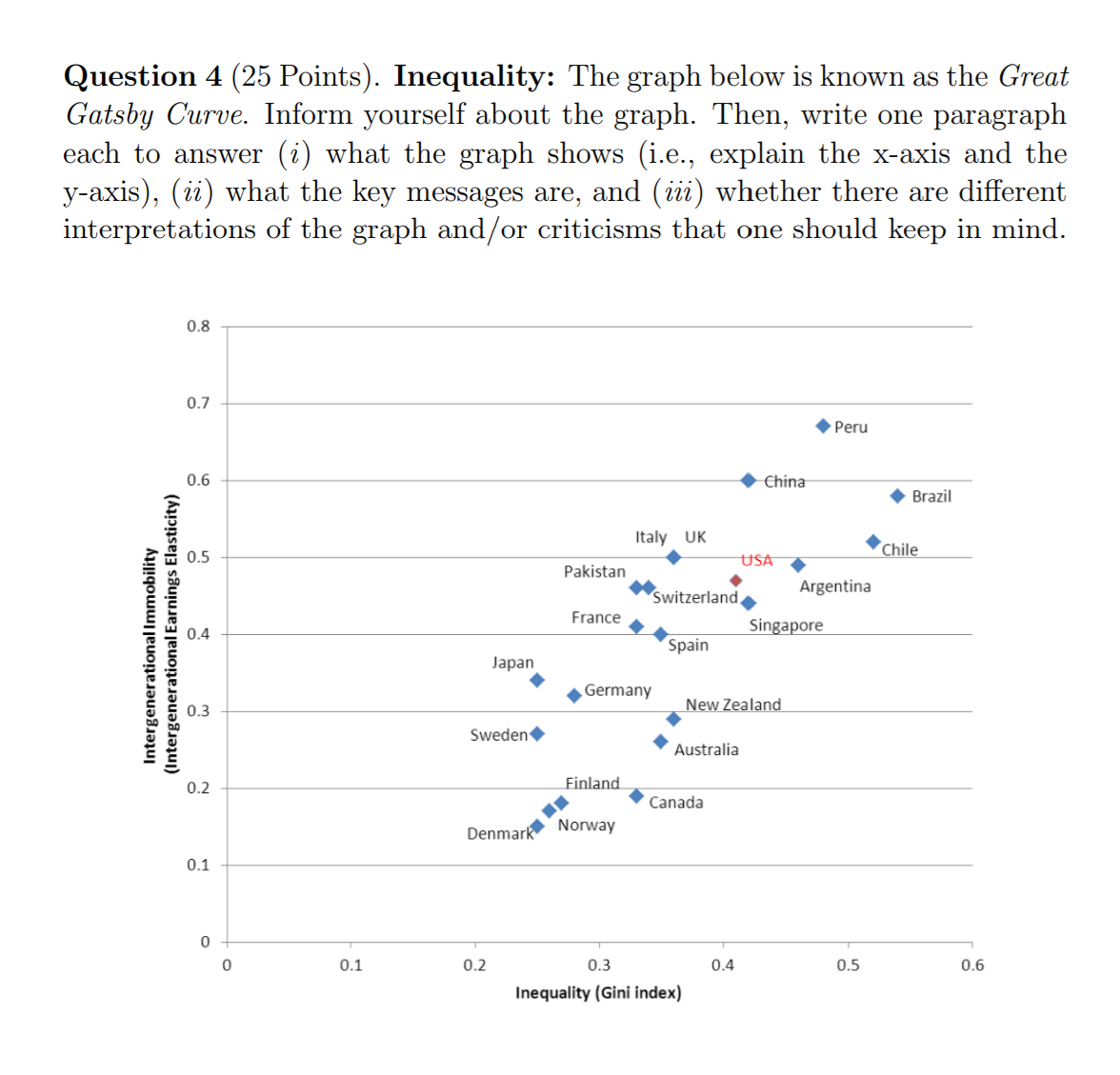
Question 2 (25 Points). Trade: The tables below desoribe two differ ent cases of production costs for pharmaceutical products and machinery in Switzerland and Italy. The numbers in the table indicate the number of workers required for a unit of production. The variable w is the wage in Switzerland relative to Italy. For instance, w = 1 means that the wage is identical in both countries while to = 1.5 means that the wage in Switzerland is 50% higher. Case 1: Cost of Making a Unit of a Good Pharmaceutical products Machinery Switzerland 4 a: w 8 * to Italy 19 10 Case 2: Cost of Making a Unit of a Good Pharmaceutical products Machinery Switzerland 8 a: w 4 =0: 10 Italy 19 10 o For each case, show which products one should expect to be produced in Switzerland and which products one should expect to be produced in Italy (both countries will export part of their produced goods to the other country). Use the concept of comparative advantage. 0 For each case, determine the possible range of w in a trade equilibrium, that is, the range of to such that each country produces exactly one of the goods, and each good is produced in the country which has a lower production cost for it. (Note: to pin down the exact wage to, we would also need to know the labor supply, but this is not required here.) 0 In which of the two cases would you expect larger gains from trade? Question 3 (25 Points). Climate Change and Game Theory: Consider a situation in which two countries choose whether or not to reduce carbon emissions. The table below shows the yearly gains/costs for each country depending on the chosen strategies. Country 2 Reduce Emissions N0 Reduction Reduce Emissions 20 , 20 20 , 150 Country 1 N0 Reduction 150 , 20 m c Find the Nash equilibrium assuming that the game is played only once. . Assume now that the game is played repeatedly (in year 1, year 2, year 3, etc.) with a discount rate of 0.1 per year (i.e., 1 USD in a year from now is worth 0.9 USD today; and 1 USD in two years from now is worth 0.81 USD today). In this repeated game, is there a Nash equilibrium in which both companies reduce emissions in all years? Show your calculations. Question 4 (25 Points). Inequality: The graph below is known as the Great Gatsby Curve. Inform yourself about the graph. Then, write one paragraph each to answer (2) what the graph shows (i.e., explain the x-axis and the y-axis), (ii) what the key messages are, and (iii) whether there are different interpretations of the graph and/or criticisms that one should keep in mind. 0.8 0.7 Peru 0.6 China Brazil Italy UK Chile 0.5 USA Pakistan switzerland Argentina France Singapore (Intergenerational Earnings Elasticity) 0.4 Spain Intergenerational Immobility Japan Germany 0.3 New Zealand Sweden Australia 0.2 Finland Canada Denmark Norway 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Inequality (Gini index)Question 1 (25 Points). Supply and Demand: A. Use supply and demand diagrams to show how the equilibrium price and quantity of smartphones is affected by the following changes in market conditions. a A recession hits the economy and consumer demand for smartphones decreases. u The price of tablets, a substitute for smartphones, increases. a The economy is booming and as a result consumer incomes increase. At the same time, an improvement in the production process reduces the manufacturing costs of smartphones. - New medical reports indicate that the health risks associated with ex cessive use of smartphones are higher than previously thought. B. Use supply and demand diagrams to discuss the effect of a minimum wage on (2') employment, and (ii) the distribution of market surplus. Recall that in the labor market the demand comes from rms (they want to buy labOr) and the supply side are the workers (they want to sell labor)