Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 2 a. In the summer, which is the peak season for tourists, the price of hotels is typically higher than it is in
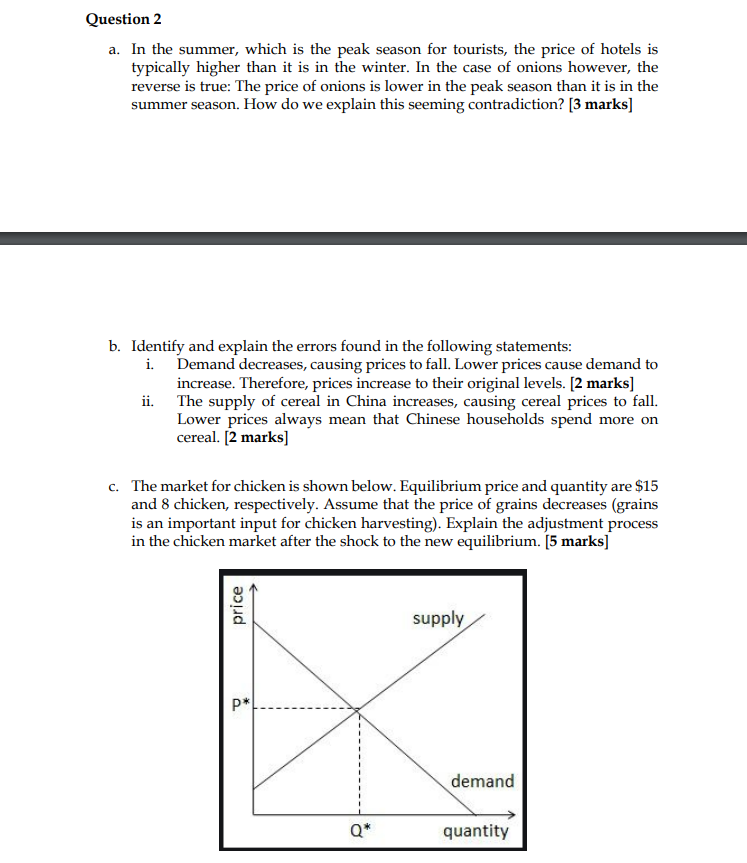
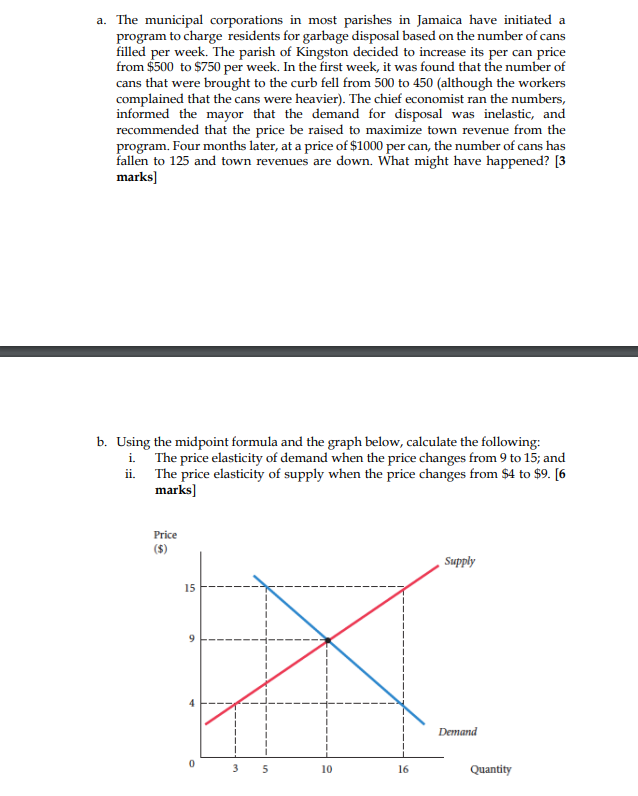

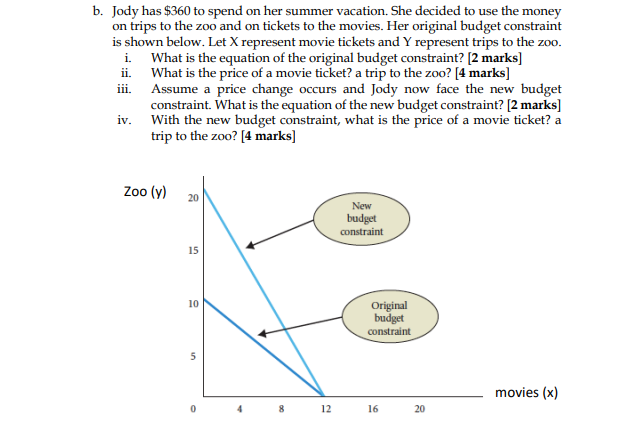
Question 2 a. In the summer, which is the peak season for tourists, the price of hotels is typically higher than it is in the winter. In the case of onions however, the reverse is true: The price of onions is lower in the peak season than it is in the summer season. How do we explain this seeming contradiction? [3 marks] b. Identify and explain the errors found in the following statements: i. Demand decreases, causing prices to fall. Lower prices cause demand to increase. Therefore, prices increase to their original levels. [2 marks] ii. The supply of cereal in China increases, causing cereal prices to fall. Lower prices always mean that Chinese households spend more on cereal. [2 marks] c. The market for chicken is shown below. Equilibrium price and quantity are $15 and 8 chicken, respectively. Assume that the price of grains decreases (grains is an important input for chicken harvesting). Explain the adjustment process in the chicken market after the shock to the new equilibrium. [5 marks] price P* supply demand Q* quantity a. The municipal corporations in most parishes in Jamaica have initiated a program to charge residents for garbage disposal based on the number of cans filled per week. The parish of Kingston decided to increase its per can price from $500 to $750 per week. In the first week, it was found that the number of cans that were brought to the curb fell from 500 to 450 (although the workers complained that the cans were heavier). The chief economist ran the numbers, informed the mayor that the demand for disposal was inelastic, and recommended that the price be raised to maximize town revenue from the program. Four months later, at a price of $1000 per can, the number of cans has fallen to 125 and town revenues are down. What might have happened? [3 marks] b. Using the midpoint formula and the graph below, calculate the following: i. The price elasticity of demand when the price changes from 9 to 15; and The price elasticity of supply when the price changes from $4 to $9. [6 marks] ii. Price ($) 15 - 0 3 5 10 16 Supply Demand Quantity c. Using the table below calculate the cross-price elasticity of flour with respect to rice [4 marks] P1 P2 Q1 Q2 Flour $9 Rice $4.45 $12 $6.75 40 25 150 125 Question 4 a. Suppose the demand for shoes is given by Qd = 40-5P and the supply for shoes is given by Qs=10P-20, where P = price (per shoes). i. Graph the supply and demand schedules for shoes. [3 marks] ii. iii. What is the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity using the equations provided? [5 marks] What would happen if suppliers set the price of shoes at $8? Illustrate this problem [3 marks] iv. Explain the market adjustment process of the problem in part (iii) [2 marks] b. Identify the flaw in this analysis: "If more Trinidadians go on a vegan diet, the demand for beef will fall. The decrease in the demand for beef will cause the price of beef to fall. The lower price, however, will then increase the demand. In the new equilibrium, Trinidadians might end up consuming more beef than they did initially." [3 marks] Question 5 a. Assume that Sophia has $1000 per month to spend between dinners at a Thai restaurant and evenings at MECA, a local club. Assume that going to MECA costs $200 and eating at the Thai restaurant costs $100. i. ii. Draw Sophia's budget constraint. Restaurants on the Y axis. [3 marks] Assume that Sophia's income rises and she can now spend $2000 per month. Draw her new budget constraint in relation to the old. [2 marks] iii. Suppose the price of evenings at MECA increase to $1200, while Sophia's income and the price of the Thai restaurant is unchanged from part (i). Illustrate the new budget line in relation to the old [2 marks] i. ii. b. Jody has $360 to spend on her summer vacation. She decided to use the money on trips to the zoo and on tickets to the movies. Her original budget constraint is shown below. Let X represent movie tickets and Y represent trips to the zoo. What is the equation of the original budget constraint? [2 marks] What is the price of a movie ticket? a trip to the zoo? [4 marks] Assume a price change occurs and Jody now face the new budget constraint. What is the equation of the new budget constraint? [2 marks] With the new budget constraint, what is the price of a movie ticket? a trip to the zoo? [4 marks] iii. iv. Zoo (y) 20 15 10 10 10 5 New budget constraint 12 Original budget constraint movies (x) 16 16 20
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


