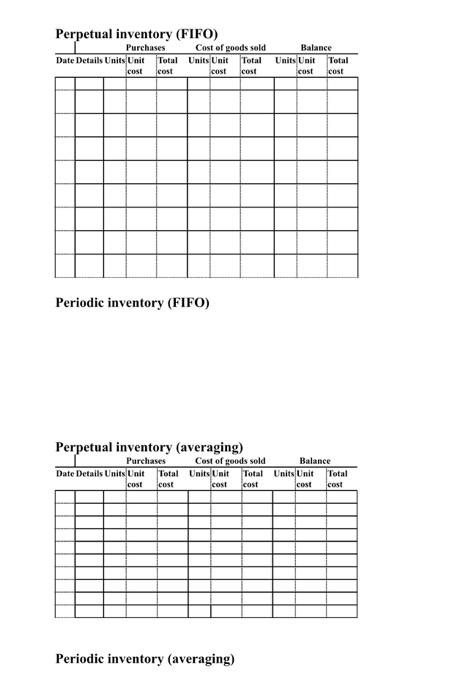
Question 2 Billy runs a small retail outlet selling various hiking and camping items including a special type of one-man tent that withstands high wind. On 1 May, Billy had a beginning inventory of 80 tents that had cost $200 each. Inventory transactions during May were: May 8 13 19 24 Bought 80 tents at $210 each Sold 120 tents for $450 each Bought 75 tents at S215 cach Sold 55 tents at $460 per unit A stocktake on 31 May found that only 58 tents were on hand (some had been lost or stolen). Three of the tents on hand were damaged and can only be sold for $150 cach. Work out the cost of goods sold, the inventory shortage expense (for the perpetual inventory system) and the amount for inventory on hand at 31 May under the following inventory systems and cost flow assumptions: 1. Perpetual inventory system and FIFO assumption (fill in the inventory record below). The missing inventory and the discount on the damaged inventory are recorded in the Inventory Shortage Expense account. On the inventory card you can show these amounts at the bottom of the Cost of Goods Sold column (after the total for Cost of Goods Sold). Show the closing inventory "pre stocktake" in the balance column and then adjust it to show what is actually left on hand and its current value. 2. Periodic inventory system and FIFO assumption (HINT: We assume the units on hand at the end of the month, confirmed by a stocktake, are the most recently purchased.) This method does not involve the use of an inventory record, simply use calculations to work out the amounts required. 3. Perpetual inventory system and averaging assumption (round to the nearest cent). 4. Periodic inventory system and averaging assumption (HINT: The total cost of Opening Inventory plus Purchases is divided by the total number of units available for sale to give the value of each item of closing inventory.) Perpetual inventory (FIFO) Purchases Cost of goods sold Date Details Units Unit Total Units Unit Total cost cost cost cost Balance Units Unit Total cost cost Periodic inventory (FIFO) Perpetual inventory (averaging) Purchases Cost of goods sold B alance Date Details Units Unit Total Units Unit Total Units Unit Total cost cost cost cost cost cost Periodic inventory (averaging)