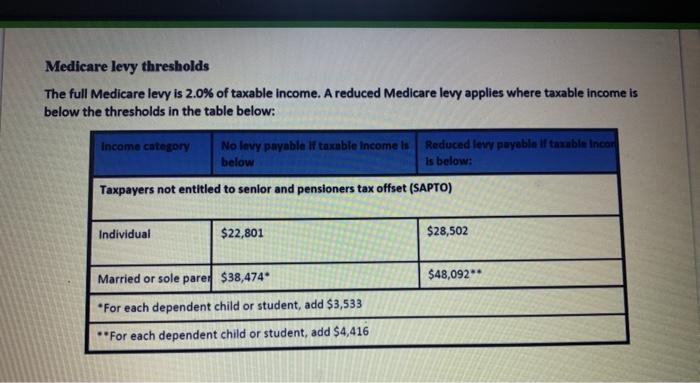
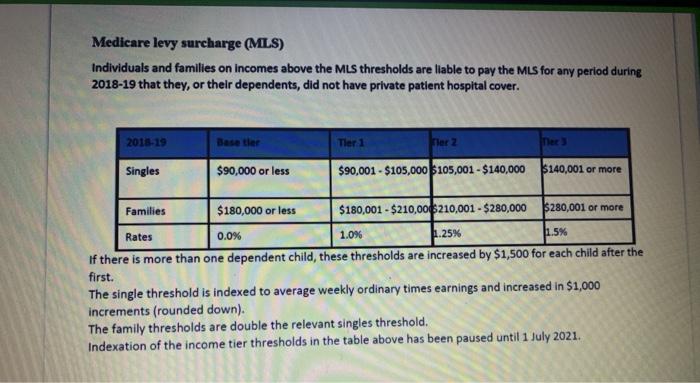
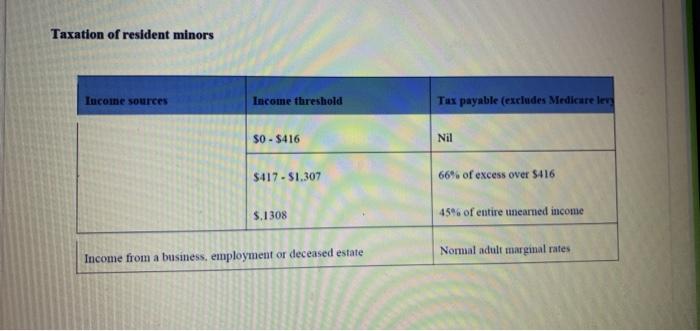
Question 2 - Calculating income tax payable Total marks - 25 Calculate Kim and Stewart's total tax liability (including Medicare). Their financial situation is as follows: Kim's salary is $140,000 p.a. In addition to this $140,000, her employer pays 10% employer superannuation on her behalf. Stewart earns $90,000 salary as well as a taxable allowance of $30,000. His employer pays superannuation guarantee of 9.5% on his salary (not the taxable allowance). In addition, Stewart salary sacrifices an additional amount so his total concessional contributions are $25,000. This salary sacrifice contribution reduces his assessable income Stewart and Kim both earn rent from a jointly owned investment property of $15,000 p.a. (combined) and have an interest only loan of $100.000 (combined) on this property at an interest rate of 5% p.a. Kim owns an Australian share portfolio valued at $50,000, paying 4. dividends, which is 70% franked (imputation credits attached). Stewart owns a cash management account valued at $50,000 paying 5% interest. Stewart has income protection insurance owned personally (non-superannuation) with an annual premium of $2.500 owned and paid by him personally. Kim donated $1.500 to a charity, which is a tax-deductible gift Kim and Stewart have private hospital insurance cover in place. . CELON Kim owns an Australian share portfolio valued at $50,000, paying 4% dividends, which is 70% franked (imputation credits attached). Stewart owns a cash management account valued at $50,000 paying 5% interest. Stewart has income protection insurance owned personally (non-superannuation) with an annual premium of $2.500 owned and paid by him personally. Kim donated $1,500 to a charity, which is a tax-deductible gift. Kim and Stewart have private hospital insurance cover in place. Calculate the tax payable for each of Kim and Stewart using the table below as a guide. Round all figures to the nearest whole dollar. Your response should include calculations to show: Assessable income Deductions Taxable income Income tax payable Medicare levy Tax offsets Final income tax payable . Q2 Medicare levy thresholds The full Medicare levy is 2.0% of taxable income. A reduced Medicare levy applies where taxable income is below the thresholds in the table below: Income category No levy payable if taxable income is Reduced levy payable Iftauable Incon below is below: Taxpayers not entitled to senior and pensioners tax offset (SAPTO) Individual $22,801 $28,502 Married or sole pare: $38,474 $48,092"* *For each dependent child or student, add $3,533 **For each dependent child or student, add $4,416 Medicare levy surcharge (MLS) Individuals and families on incomes above the MLS thresholds are liable to pay the MLS for any period during 2018-19 that they, or their dependents, did not have private patient hospital cover. 2018-19 Tler 1 Fler 2 Ter Singles $90,000 or less $90,001 - $105,000 $105,001 - $140,000 $140,001 or more Families $180,000 or less $180,001 - $210,006210,001 - $280,000 $280,001 or more Rates 0.0% 1.0% 1.5% 1.25% If there is more than one dependent child, these thresholds are increased by $1,500 for each child after the first. The single threshold is indexed to average weekly ordinary times earnings and increased in $1,000 increments (rounded down). The family thresholds are double the relevant singles threshold. Indexation of the income tier thresholds in the table above has been paused until 1 July 2021. Taxation of resident minors Income sources Income threshold Tax payable (excludes Medicare le $0-$416 Nil $417 - $1.307 66% of excess over $416 $.1308 45% of entire unearned income Normal adult marginal rates Income from a business, employment or deceased estate Question 2 - Calculating income tax payable Total marks - 25 Calculate Kim and Stewart's total tax liability (including Medicare). Their financial situation is as follows: Kim's salary is $140,000 p.a. In addition to this $140,000, her employer pays 10% employer superannuation on her behalf. Stewart earns $90,000 salary as well as a taxable allowance of $30,000. His employer pays superannuation guarantee of 9.5% on his salary (not the taxable allowance). In addition, Stewart salary sacrifices an additional amount so his total concessional contributions are $25,000. This salary sacrifice contribution reduces his assessable income Stewart and Kim both earn rent from a jointly owned investment property of $15,000 p.a. (combined) and have an interest only loan of $100.000 (combined) on this property at an interest rate of 5% p.a. Kim owns an Australian share portfolio valued at $50,000, paying 4. dividends, which is 70% franked (imputation credits attached). Stewart owns a cash management account valued at $50,000 paying 5% interest. Stewart has income protection insurance owned personally (non-superannuation) with an annual premium of $2.500 owned and paid by him personally. Kim donated $1.500 to a charity, which is a tax-deductible gift Kim and Stewart have private hospital insurance cover in place. . CELON Kim owns an Australian share portfolio valued at $50,000, paying 4% dividends, which is 70% franked (imputation credits attached). Stewart owns a cash management account valued at $50,000 paying 5% interest. Stewart has income protection insurance owned personally (non-superannuation) with an annual premium of $2.500 owned and paid by him personally. Kim donated $1,500 to a charity, which is a tax-deductible gift. Kim and Stewart have private hospital insurance cover in place. Calculate the tax payable for each of Kim and Stewart using the table below as a guide. Round all figures to the nearest whole dollar. Your response should include calculations to show: Assessable income Deductions Taxable income Income tax payable Medicare levy Tax offsets Final income tax payable . Q2 Medicare levy thresholds The full Medicare levy is 2.0% of taxable income. A reduced Medicare levy applies where taxable income is below the thresholds in the table below: Income category No levy payable if taxable income is Reduced levy payable Iftauable Incon below is below: Taxpayers not entitled to senior and pensioners tax offset (SAPTO) Individual $22,801 $28,502 Married or sole pare: $38,474 $48,092"* *For each dependent child or student, add $3,533 **For each dependent child or student, add $4,416 Medicare levy surcharge (MLS) Individuals and families on incomes above the MLS thresholds are liable to pay the MLS for any period during 2018-19 that they, or their dependents, did not have private patient hospital cover. 2018-19 Tler 1 Fler 2 Ter Singles $90,000 or less $90,001 - $105,000 $105,001 - $140,000 $140,001 or more Families $180,000 or less $180,001 - $210,006210,001 - $280,000 $280,001 or more Rates 0.0% 1.0% 1.5% 1.25% If there is more than one dependent child, these thresholds are increased by $1,500 for each child after the first. The single threshold is indexed to average weekly ordinary times earnings and increased in $1,000 increments (rounded down). The family thresholds are double the relevant singles threshold. Indexation of the income tier thresholds in the table above has been paused until 1 July 2021. Taxation of resident minors Income sources Income threshold Tax payable (excludes Medicare le $0-$416 Nil $417 - $1.307 66% of excess over $416 $.1308 45% of entire unearned income Normal adult marginal rates Income from a business, employment or deceased estate