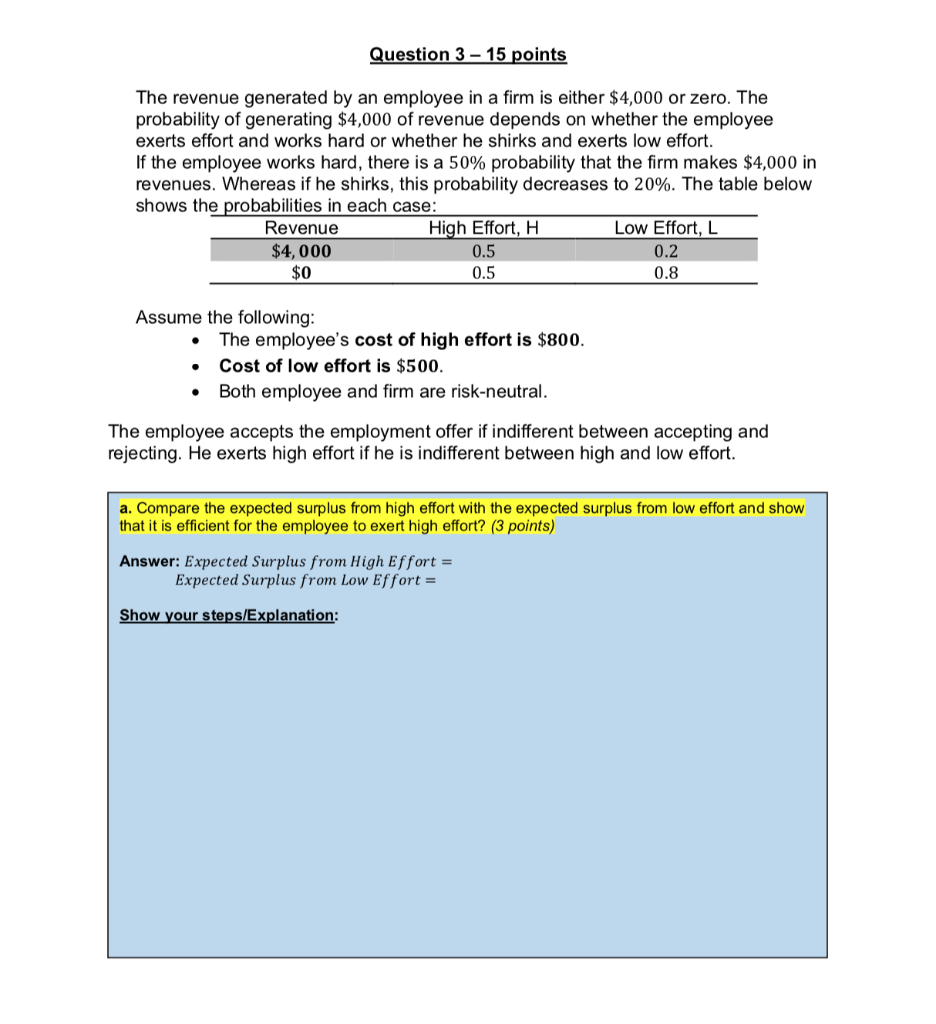



Question 3 - 15 points The revenue generated by an employee in a firm is either $4,000 or zero. The probability of generating $4,000 of revenue depends on whether the employee exerts effort and works hard or whether he shirks and exerts low effort. If the employee works hard, there is a 50% probability that the firm makes $4,000 in revenues. Whereas if he shirks, this probability decreases to 20%. The table below shows the probabilities in each case: Revenue High Effort, H Low Effort, L $4,000 0.5 0.2 $0 0.5 0.8 Assume the following: The employee's cost of high effort is $800. Cost of low effort is $500. Both employee and firm are risk-neutral. . . The employee accepts the employment offer if indifferent between accepting and rejecting. He exerts high effort if he is indifferent between high and low effort. a. Compare the expected surplus from high effort with the expected surplus from low effort and show that it is efficient for the employee to exert high effort? (3 points) Answer: Expected Surplus from High Effort = Expected Surplus from Low Effort = Show your steps/Explanation: Question 3 (contd.) Suppose the employer (firm) cannot observe or monitor employee effort. So, he offers a variable wage contract where the employee receives a high wage, w if the firm makes high revenues and a low wage w if the firm makes zero revenues. b. Write down the Incentive Constraint that will get the employee to exert high effort in his employment. (2 points) Answer: Incentive Constraint (IC): Show your steps: c. Write down the Participation Constraint that will get the employee to accept employment with high effort. (2 points) Answer: Participation Constraint (PC): Show your steps: Question 3 (contd.) Assume that the employer exactly meets both its constraints in choosing its variable wage contract, i.e., the employer chooses w and w such that both the incentive constraint and participation constraint hold with equality. d. Solve the incentive constraint and participation constraints as equations to find the equilibrium wH and wl*? (3 points) Answer: WH* WL* = Show your steps: e. Separate out the fixed compensation and bonus from the variable wage obtained in part d). (2 points) Hint: The fixed compensation is the lowest amount the employee receives in the firm no matter what its revenues. The bonus is the additional compensation the employee receives when the firm makes high revenues. Answer: Fixed Compensation = Bonus = Show your steps: Question 3 (contd.) f. Explain in words how the fixed compensation and bonus derived in part e) will need to be adjusted if the employee were risk-averse. Be sure to explain the trade-off between fixed and variable compensation in the context of risk-aversion and moral hazard. (3 points) Explanation: Question 3 - 15 points The revenue generated by an employee in a firm is either $4,000 or zero. The probability of generating $4,000 of revenue depends on whether the employee exerts effort and works hard or whether he shirks and exerts low effort. If the employee works hard, there is a 50% probability that the firm makes $4,000 in revenues. Whereas if he shirks, this probability decreases to 20%. The table below shows the probabilities in each case: Revenue High Effort, H Low Effort, L $4,000 0.5 0.2 $0 0.5 0.8 Assume the following: The employee's cost of high effort is $800. Cost of low effort is $500. Both employee and firm are risk-neutral. . . The employee accepts the employment offer if indifferent between accepting and rejecting. He exerts high effort if he is indifferent between high and low effort. a. Compare the expected surplus from high effort with the expected surplus from low effort and show that it is efficient for the employee to exert high effort? (3 points) Answer: Expected Surplus from High Effort = Expected Surplus from Low Effort = Show your steps/Explanation: Question 3 (contd.) Suppose the employer (firm) cannot observe or monitor employee effort. So, he offers a variable wage contract where the employee receives a high wage, w if the firm makes high revenues and a low wage w if the firm makes zero revenues. b. Write down the Incentive Constraint that will get the employee to exert high effort in his employment. (2 points) Answer: Incentive Constraint (IC): Show your steps: c. Write down the Participation Constraint that will get the employee to accept employment with high effort. (2 points) Answer: Participation Constraint (PC): Show your steps: Question 3 (contd.) Assume that the employer exactly meets both its constraints in choosing its variable wage contract, i.e., the employer chooses w and w such that both the incentive constraint and participation constraint hold with equality. d. Solve the incentive constraint and participation constraints as equations to find the equilibrium wH and wl*? (3 points) Answer: WH* WL* = Show your steps: e. Separate out the fixed compensation and bonus from the variable wage obtained in part d). (2 points) Hint: The fixed compensation is the lowest amount the employee receives in the firm no matter what its revenues. The bonus is the additional compensation the employee receives when the firm makes high revenues. Answer: Fixed Compensation = Bonus = Show your steps: Question 3 (contd.) f. Explain in words how the fixed compensation and bonus derived in part e) will need to be adjusted if the employee were risk-averse. Be sure to explain the trade-off between fixed and variable compensation in the context of risk-aversion and moral hazard. (3 points) Explanation










