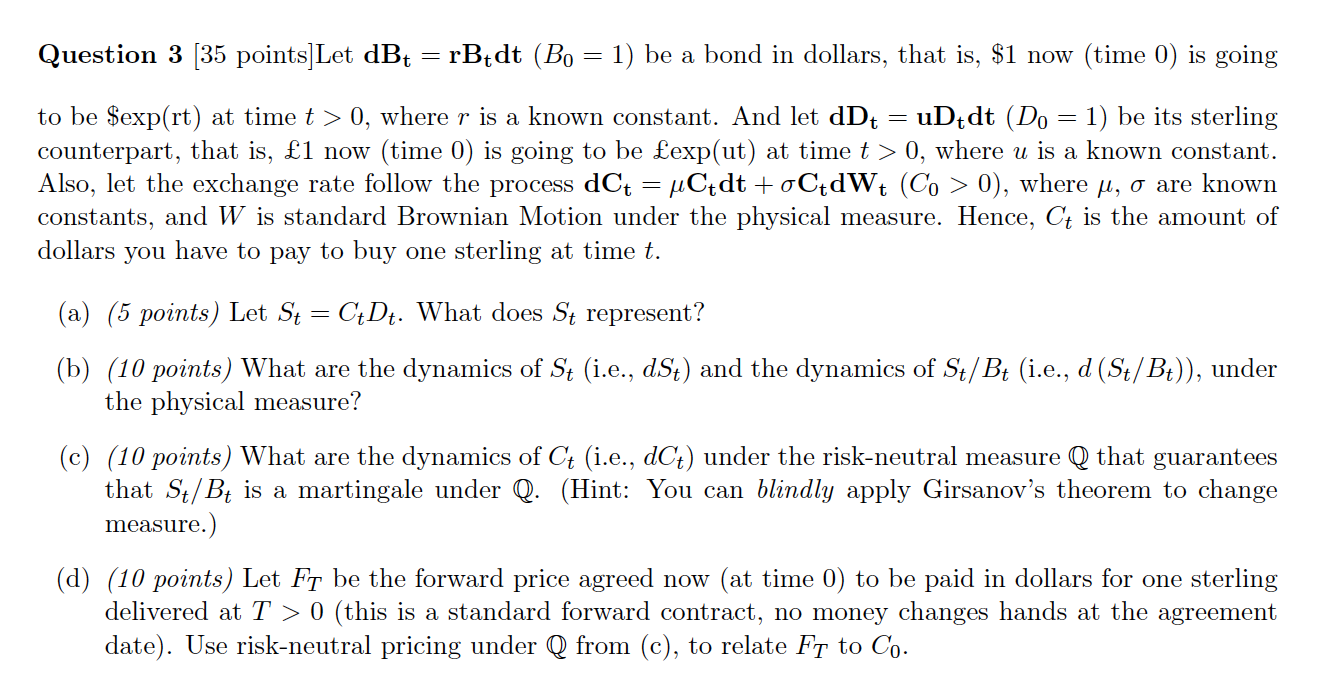
Question 3 [35 points]Let dBt = rBrdt (Bo = 1) be a bond in dollars, that is, $1 now (time 0) is going = - to be $exp(rt) at time t > 0, where r is a known constant. And let dDt = uDtdt (Do = 1) be its sterling counterpart, that is, 1 now (time 0) is going to be exp(ut) at time t > 0, where u is a known constant. Also, let the exchange rate follow the process dCt = uCtdt + oCtdWt (Co > 0), where ui, o are known constants, and W is standard Brownian Motion under the physical measure. Hence, Ct is the amount of dollars you have to pay to buy one sterling at time t. (a) (5 points) Let St = CtDt. What does St represent? (b) (10 points) What are the dynamics of St (i.e., dSt) and the dynamics of St/Bt (i.e., d (St/Bt)), under the physical measure? (c) (10 points) What are the dynamics of Ct (i.e., dCt) under the risk-neutral measure Q that guarantees that St/Bt is a martingale under Q. (Hint: You can blindly apply Girsanov's theorem to change measure.) (d) (10 points) Let Ft be the forward price agreed now (at time 0) to be paid in dollars for one sterling delivered at T > 0 (this is a standard forward contract, no money changes hands at the agreement date). Use risk-neutral pricing under Q from (c), to relate Ft to Co. Question 3 [35 points]Let dBt = rBrdt (Bo = 1) be a bond in dollars, that is, $1 now (time 0) is going = - to be $exp(rt) at time t > 0, where r is a known constant. And let dDt = uDtdt (Do = 1) be its sterling counterpart, that is, 1 now (time 0) is going to be exp(ut) at time t > 0, where u is a known constant. Also, let the exchange rate follow the process dCt = uCtdt + oCtdWt (Co > 0), where ui, o are known constants, and W is standard Brownian Motion under the physical measure. Hence, Ct is the amount of dollars you have to pay to buy one sterling at time t. (a) (5 points) Let St = CtDt. What does St represent? (b) (10 points) What are the dynamics of St (i.e., dSt) and the dynamics of St/Bt (i.e., d (St/Bt)), under the physical measure? (c) (10 points) What are the dynamics of Ct (i.e., dCt) under the risk-neutral measure Q that guarantees that St/Bt is a martingale under Q. (Hint: You can blindly apply Girsanov's theorem to change measure.) (d) (10 points) Let Ft be the forward price agreed now (at time 0) to be paid in dollars for one sterling delivered at T > 0 (this is a standard forward contract, no money changes hands at the agreement date). Use risk-neutral pricing under Q from (c), to relate Ft to Co







