Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ed The Engine Guys produces specialized engines for snow climber buses. The company's normal monthly production volume is 2,500 engines, whereas its monthly production
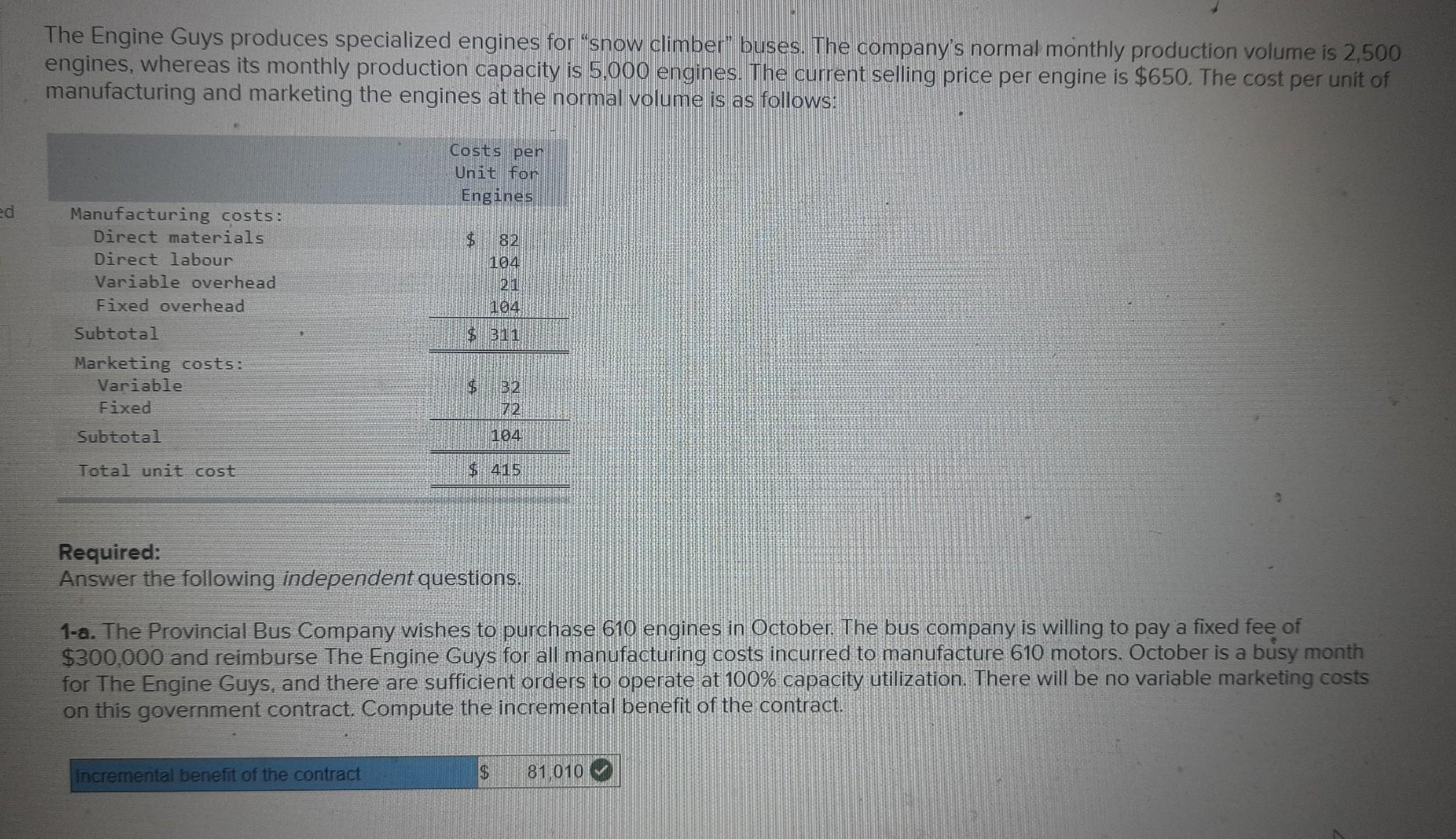
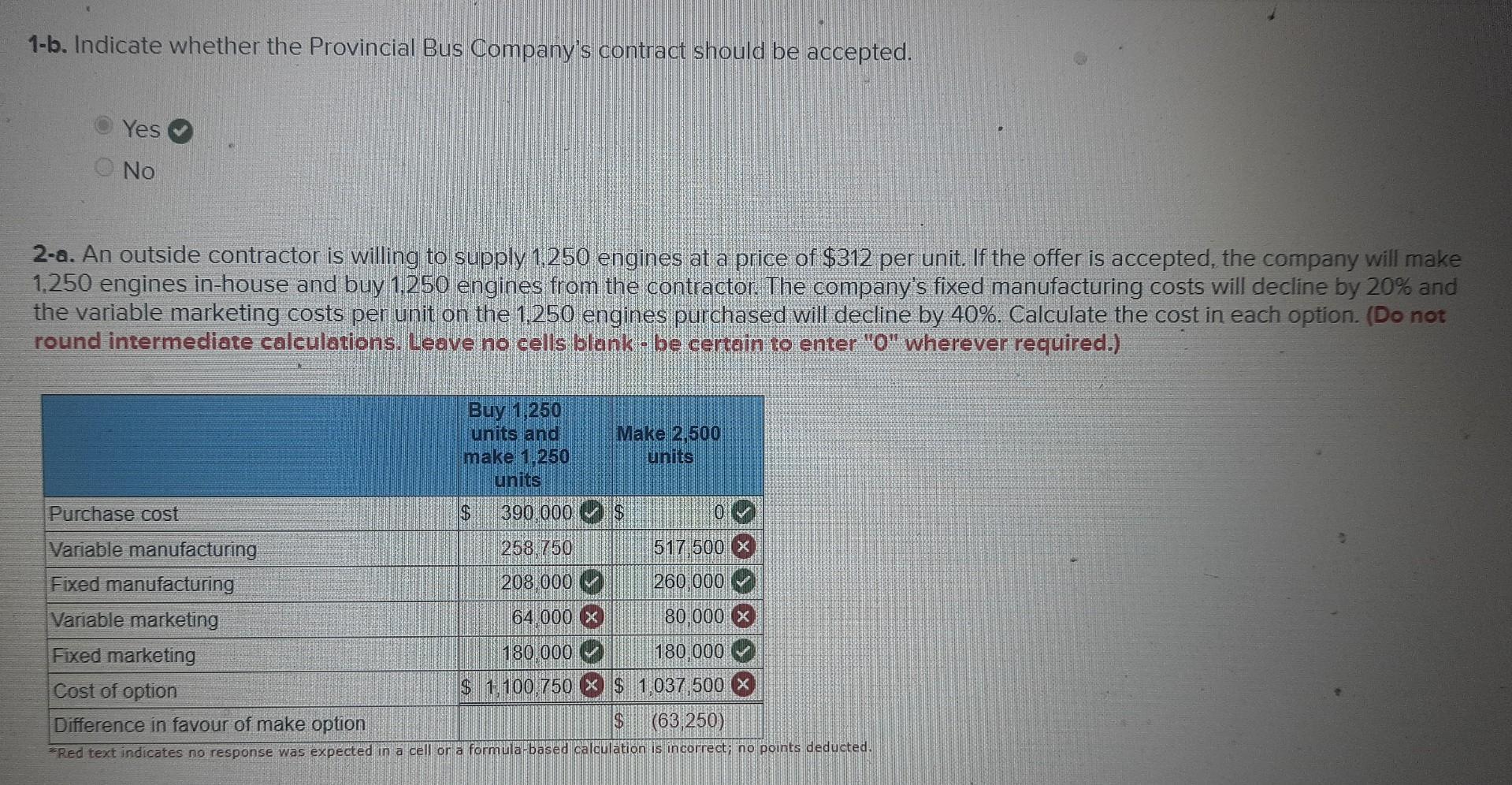
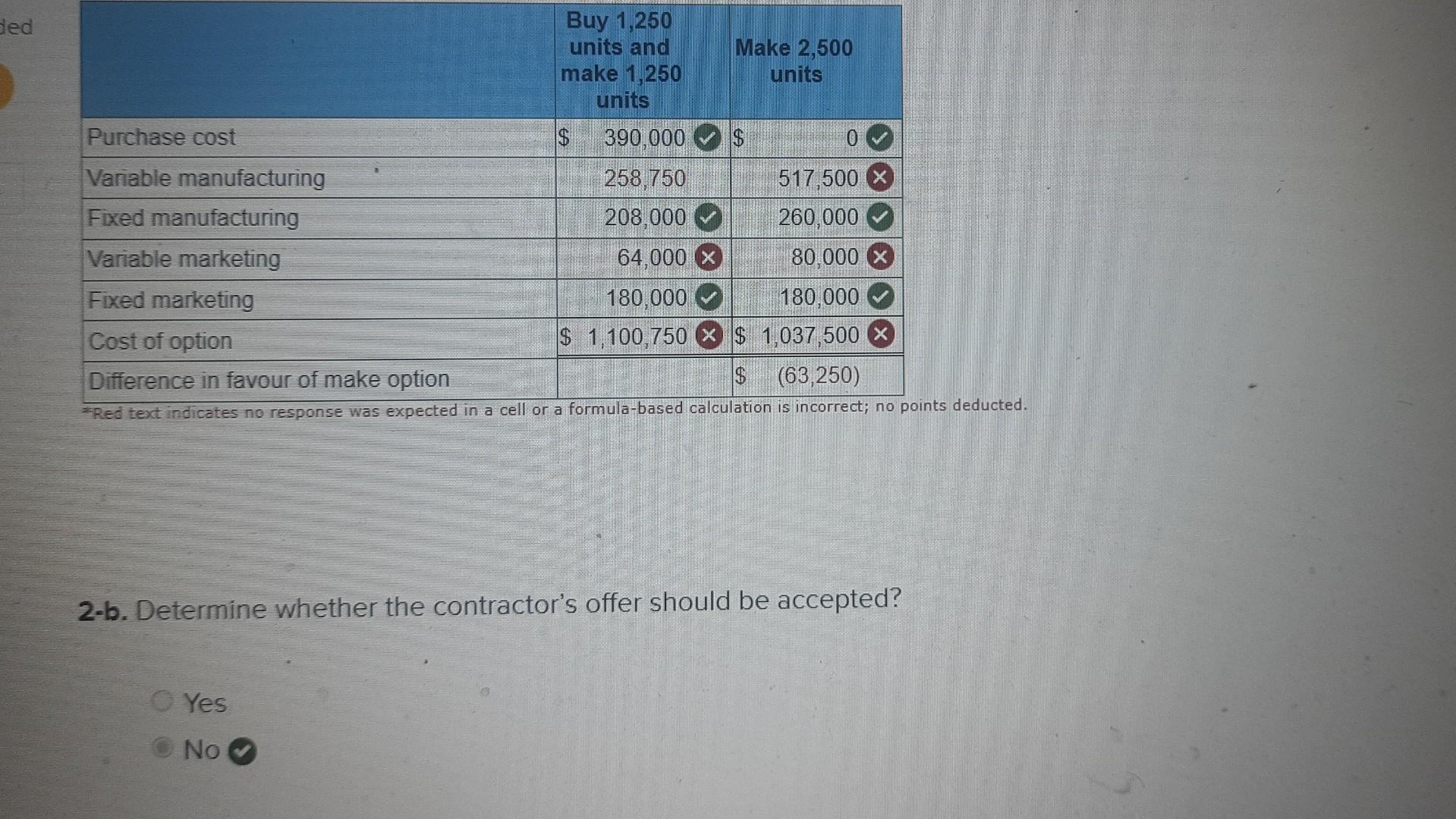
ed The Engine Guys produces specialized engines for "snow climber buses. The company's normal monthly production volume is 2,500 engines, whereas its monthly production capacity is 5,000 engines. The current selling price per engine is $650. The cost per unit of manufacturing and marketing the engines at the normal volume is as follows: Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Subtotal Marketing costs: Variable Fixed Subtotal Total unit cost Costs per Unit for Engines $ Incremental benefit of the contract 82 104 21 104 $ 311 $ B2 72 104 $415 Required: Answer the following independent questions. 1-a. The Provincial Bus Company wishes to purchase 610 engines in October. The bus company is willing to pay a fixed fee of $300,000 and reimburse The Engine Guys for all manufacturing costs incurred to manufacture 610 motors. October is a busy month for The Engine Guys, and there are sufficient orders to operate at 100% capacity utilization. There will be no variable marketing costs on this government contract. Compute the incremental benefit of the contract. $ 81,010 1-b. Indicate whether the Provincial Bus Company's contract should be accepted. Yes No 2-a. An outside contractor is willing to supply 1,250 engines at a price of $312 per unit. If the offer is accepted, the company will make 1,250 engines in-house and buy 1.250 engines from the contractor. The company's fixed manufacturing costs will decline by 20% and the variable marketing costs per unit on the 1,250 engines purchased will decline by 40%. Calculate the cost in each option. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) Buy 1,250 units and make 1.250 units $ Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option $ (63,250) Difference in favour of make option *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. 390.000 258.750 208.000 Make 2,500 units 64.000 x $ 0 517 500 x 260 000 80,000 x 180.000 180.000 $ 1,100,750 x $1,037,500 x ded Buy 1,250 units and make 1,250 units Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option Difference in favour of make option (63,250) *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. $ Yes No 390,000 258,750 208,000 Make 2,500 units 64,000 x $ 517,500 260,000 80.000 180,000 180,000 $ 1,100,750 x $ 1,037,500 $ 0 69 2-b. Determine whether the contractor's offer should be accepted? ed The Engine Guys produces specialized engines for "snow climber buses. The company's normal monthly production volume is 2,500 engines, whereas its monthly production capacity is 5,000 engines. The current selling price per engine is $650. The cost per unit of manufacturing and marketing the engines at the normal volume is as follows: Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Subtotal Marketing costs: Variable Fixed Subtotal Total unit cost Costs per Unit for Engines $ Incremental benefit of the contract 82 104 21 104 $ 311 $ B2 72 104 $415 Required: Answer the following independent questions. 1-a. The Provincial Bus Company wishes to purchase 610 engines in October. The bus company is willing to pay a fixed fee of $300,000 and reimburse The Engine Guys for all manufacturing costs incurred to manufacture 610 motors. October is a busy month for The Engine Guys, and there are sufficient orders to operate at 100% capacity utilization. There will be no variable marketing costs on this government contract. Compute the incremental benefit of the contract. $ 81,010 1-b. Indicate whether the Provincial Bus Company's contract should be accepted. Yes No 2-a. An outside contractor is willing to supply 1,250 engines at a price of $312 per unit. If the offer is accepted, the company will make 1,250 engines in-house and buy 1.250 engines from the contractor. The company's fixed manufacturing costs will decline by 20% and the variable marketing costs per unit on the 1,250 engines purchased will decline by 40%. Calculate the cost in each option. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) Buy 1,250 units and make 1.250 units $ Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option $ (63,250) Difference in favour of make option *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. 390.000 258.750 208.000 Make 2,500 units 64.000 x $ 0 517 500 x 260 000 80,000 x 180.000 180.000 $ 1,100,750 x $1,037,500 x ded Buy 1,250 units and make 1,250 units Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option Difference in favour of make option (63,250) *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. $ Yes No 390,000 258,750 208,000 Make 2,500 units 64,000 x $ 517,500 260,000 80.000 180,000 180,000 $ 1,100,750 X $ 1,037,500 $ 0 69 2-b. Determine whether the contractor's offer should be accepted? ed The Engine Guys produces specialized engines for "snow climber buses. The company's normal monthly production volume is 2,500 engines, whereas its monthly production capacity is 5,000 engines. The current selling price per engine is $650. The cost per unit of manufacturing and marketing the engines at the normal volume is as follows: Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Subtotal Marketing costs: Variable Fixed Subtotal Total unit cost Costs per Unit for Engines $ Incremental benefit of the contract 82 104 21 104 $ 311 $ B2 72 104 $415 Required: Answer the following independent questions. 1-a. The Provincial Bus Company wishes to purchase 610 engines in October. The bus company is willing to pay a fixed fee of $300,000 and reimburse The Engine Guys for all manufacturing costs incurred to manufacture 610 motors. October is a busy month for The Engine Guys, and there are sufficient orders to operate at 100% capacity utilization. There will be no variable marketing costs on this government contract. Compute the incremental benefit of the contract. $ 81,010 1-b. Indicate whether the Provincial Bus Company's contract should be accepted. Yes No 2-a. An outside contractor is willing to supply 1,250 engines at a price of $312 per unit. If the offer is accepted, the company will make 1,250 engines in-house and buy 1.250 engines from the contractor. The company's fixed manufacturing costs will decline by 20% and the variable marketing costs per unit on the 1,250 engines purchased will decline by 40%. Calculate the cost in each option. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) Buy 1,250 units and make 1.250 units $ Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option $ (63,250) Difference in favour of make option *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. 390.000 258.750 208.000 Make 2,500 units 64.000 x $ 0 517 500 x 260 000 80,000 x 180.000 180.000 $ 1,100,750 x $1,037,500 x ded Buy 1,250 units and make 1,250 units Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option Difference in favour of make option (63,250) *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. $ Yes No 390,000 258,750 208,000 Make 2,500 units 64,000 x $ 517,500 260,000 80.000 180,000 180,000 $ 1,100,750 x $ 1,037,500 $ 0 69 2-b. Determine whether the contractor's offer should be accepted? ed The Engine Guys produces specialized engines for "snow climber buses. The company's normal monthly production volume is 2,500 engines, whereas its monthly production capacity is 5,000 engines. The current selling price per engine is $650. The cost per unit of manufacturing and marketing the engines at the normal volume is as follows: Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead Subtotal Marketing costs: Variable Fixed Subtotal Total unit cost Costs per Unit for Engines $ Incremental benefit of the contract 82 104 21 104 $ 311 $ B2 72 104 $415 Required: Answer the following independent questions. 1-a. The Provincial Bus Company wishes to purchase 610 engines in October. The bus company is willing to pay a fixed fee of $300,000 and reimburse The Engine Guys for all manufacturing costs incurred to manufacture 610 motors. October is a busy month for The Engine Guys, and there are sufficient orders to operate at 100% capacity utilization. There will be no variable marketing costs on this government contract. Compute the incremental benefit of the contract. $ 81,010 1-b. Indicate whether the Provincial Bus Company's contract should be accepted. Yes No 2-a. An outside contractor is willing to supply 1,250 engines at a price of $312 per unit. If the offer is accepted, the company will make 1,250 engines in-house and buy 1.250 engines from the contractor. The company's fixed manufacturing costs will decline by 20% and the variable marketing costs per unit on the 1,250 engines purchased will decline by 40%. Calculate the cost in each option. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) Buy 1,250 units and make 1.250 units $ Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option $ (63,250) Difference in favour of make option *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. 390.000 258.750 208.000 Make 2,500 units 64.000 x $ 0 517 500 x 260 000 80,000 x 180.000 180.000 $ 1,100,750 x $1,037,500 x ded Buy 1,250 units and make 1,250 units Purchase cost Variable manufacturing Fixed manufacturing Variable marketing Fixed marketing Cost of option Difference in favour of make option (63,250) *Red text indicates no response was expected in a cell or a formula-based calculation is incorrect; no points deducted. $ Yes No 390,000 258,750 208,000 Make 2,500 units 64,000 x $ 517,500 260,000 80.000 180,000 180,000 $ 1,100,750 X $ 1,037,500 $ 0 69 2-b. Determine whether the contractor's offer should be accepted?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To calculate the incremental benefit of the contract we need to compare the additional revenue from ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


