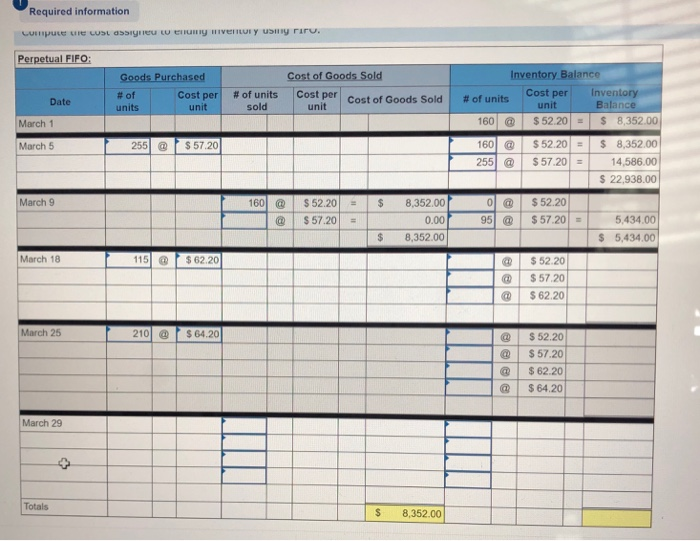
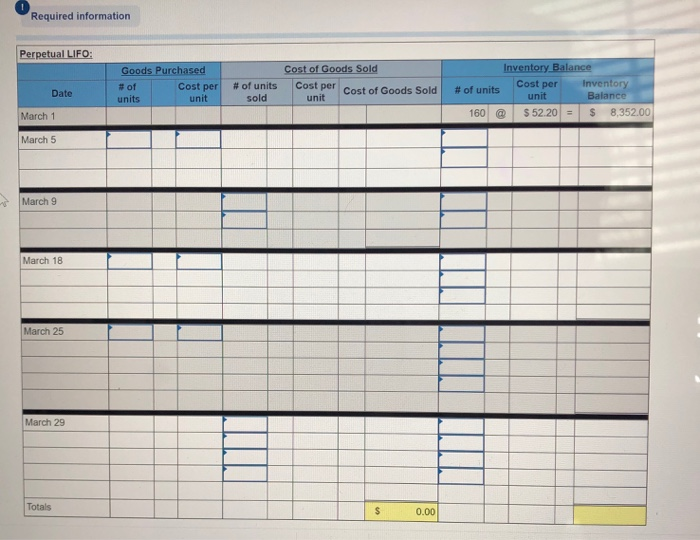
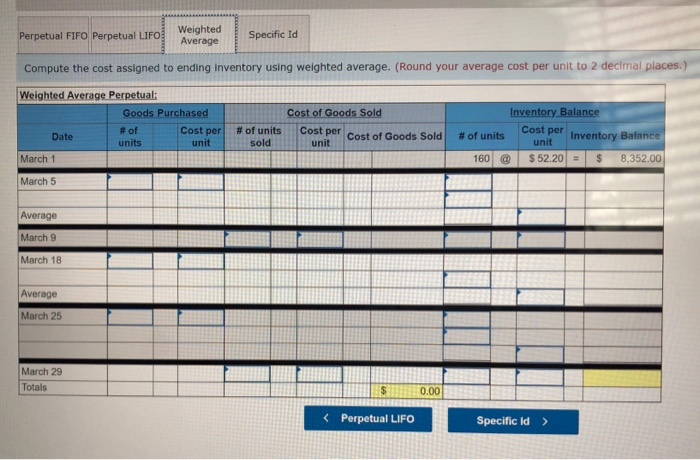
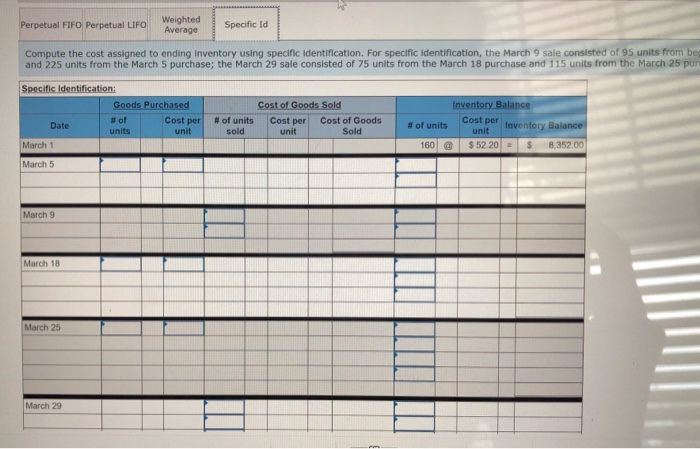
Question 6 only the blue boxes need to be filled in. Also question 1 at the end please.
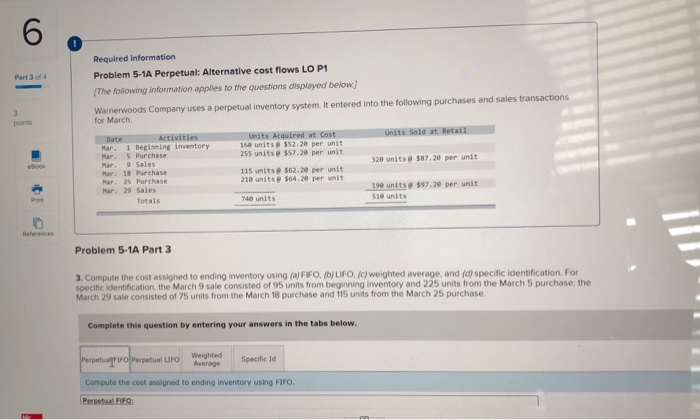
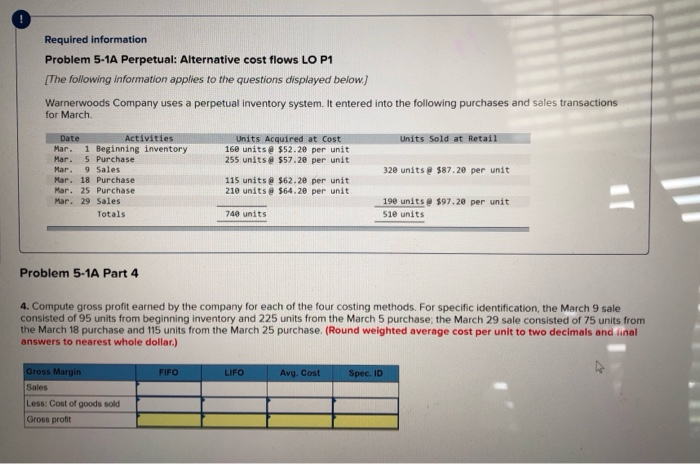
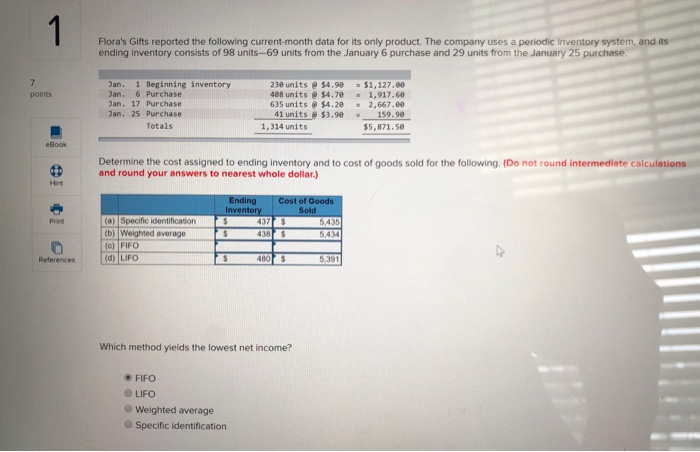
Required information Problem 5-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows LO P1 Part 3 of 4 (The following information applies to the questions displayed below Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. 3 points Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 16e units@ 552,20 per unit 255 units@ $57,20 per unit Activities Date 1 Beginning inventory S Purchase 9 Sales Mar. Mar. 320 units @ $87.20 per unit Mar. eook 115 units $62.20 per unit 210 units $64.28 per unit Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales 190 units# $97.20 per unit 51e units Pint 740 units Totals References Problem 5-1A Part 3 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 95 units from beginning inventory and 225 units from the March 5 purchase, the March 29 sale consisted of 75 units from the March 18 purchase and 115 units from the March 25 purchase. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Weighted Average Perpetualf IFO Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using FIFO. Perpetual FIFO Required information Compute ure cost assigneu tU eIuny nIvenur y usiny riru Perpetual FIFO Inventory Balance Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance # of Cost per unit Cost per unit Cost per unit # of units cost of Goods Sold # of units Date units sold $ 52.20 S8,352.00 160 March 1 $ 8,352.00 160@ $52.20 255 March 5 $57.20 $57.20 @ 14,586.00 255 $ 22,938.00 March 9 160@ $52.20 8,352.00 $52.20 95@ $57.20 0.00 5,434.00 $57.20 $ 5,434.00 8,352.00 March 18 115@ $62.20 $52.20 $57.20 $62.20 March 25 210 @ $64.20 $52.20 $57.20 $62.20 $ 64.20 March 29 Totals S 8.352.00 Required information Perpetual LIFO: Inventory Balance Cost of Goods Sold Goods Purchased Cost per Inventory Balance Cost percost of Goods Sold # of Cost per unit # of units sold # of units Date unit unit units 8.352.00 $ 52.20 $ 160 March 1 March 5 March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 Totals 0.00 Weighted Average Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using weighted average. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Weighted Average Perpetual: Inventory Balance Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold #of units Cost per Inventory Balance unit Cost per Cost per cost of Goods Sold unit # of # of units Date units unit sold March 1 8.352.00 160 @ $52.20 March 5 Average March 9 March 18 Average March 25 March 29 Totals $ 0.00 Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Weighted Average Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using specific identification. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 95 units from beg and 225 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of 75 units from the March 18 purchase and 115 units from the March 25 pur Specific Identification: Inventory Balance Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold Cost per tventory Balance unit # of units Cost per # of units Cost per unit Cost of Goods Date # of units unit sold Sold 160@ March 1 $52.20 8.352.00 March 5 March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 co Required information Problem 5-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows LO P1 The following information applies to the questions displayed below Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Activities Date Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail 1 Beginning inventory 5 Purchase 9 Sales 160 units $52.20 per unit 255 units $57.20 per unit Mar. Mar. Mar. 320 units $87.20 per unit Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 115 units@ $62.20 per unit 210 units $64.20 per unit 25 Purchase 190 units $97.20 per unit Mar. 29 Sales 740 units 51e units Totals Problem 5-1A Part 4 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 95 units from beginning inventory and 225 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of 75 units from the March 18 purchase and 115 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) Gross Margin FIFO LIFO Avg. Cost Spec. ID Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit 1 Flora's Gifts reported the following current-month data for its only product. The company uses a periodic Inventory system, and its ending inventory consists of 98 units-69 units from the January 6 purchase and 29 units from the January 25 purchase. 7 Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 230 units @ $4.98 4e8 units @ $4,70- 635 units $4.28 41 units@ $3.90 $1,127.00 1,917.60 points Jan. 6 Purchase Jan. 17 Purchase Jan. 25 Purchase 2,667.00 159.90 Totals 1,314 units $5,871.50 eBook Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold for the following. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to nearest whole dollar.) Hint Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold (a) Specific identification (b) Weighted average (c) FIFO 5,435 Print 437 438 5,434 $ 5,391 (d) LIFO 480 References Which method yields the lowest net income? FIFO LIFO Weighted average Specific identification