Question: Question entre 1.00 Atch 3 GLASI Moving to another question will save this response. Question 4 Frequency is a defining characteristic of many physical phenomena
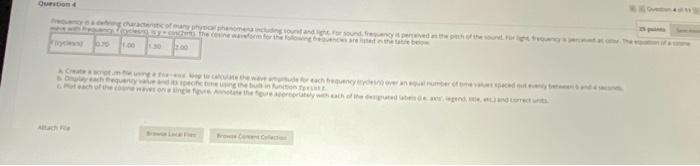

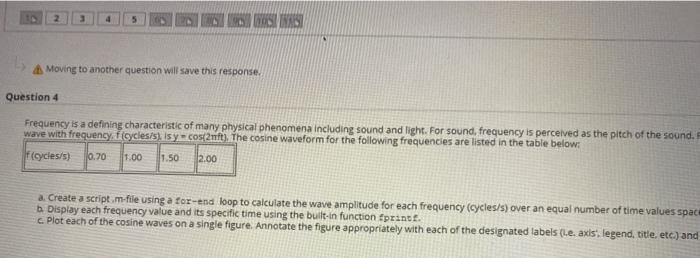
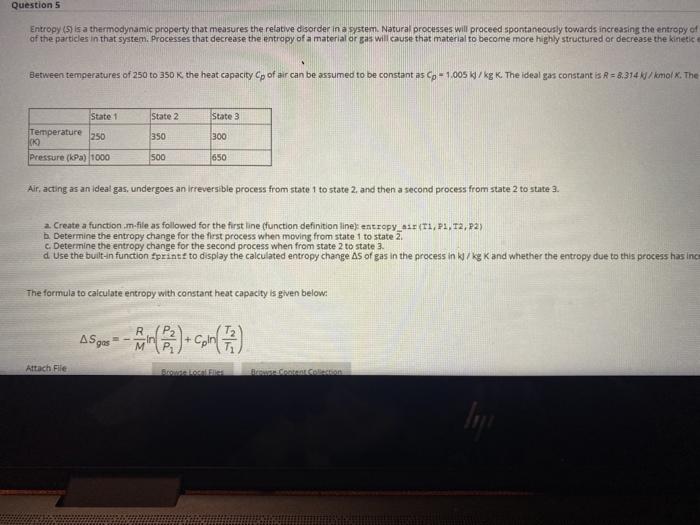
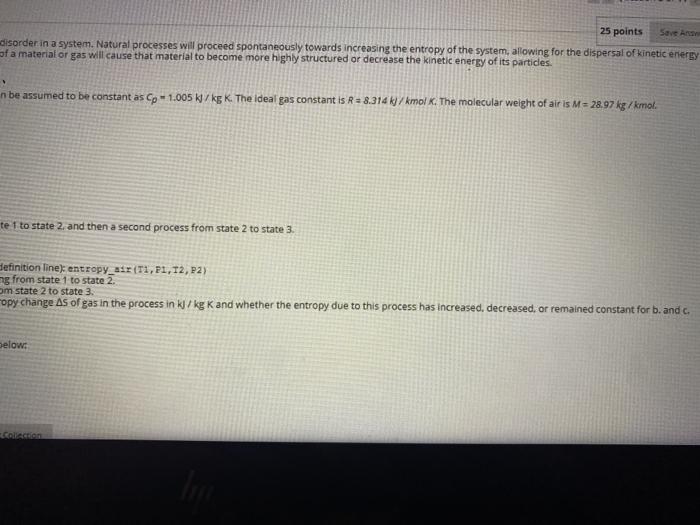
Question entre 1.00 Atch 3 GLASI Moving to another question will save this response. Question 4 Frequency is a defining characteristic of many physical phenomena including sound and light. For sound, frequency is perceived as the pitch of the sound. wave with frequency, ficycles/s) Isy = CO2nft). The cosine waveform for the following frequencies are listed in the table below: fcycles/s) 0.70 1.00 11.50 12.00 a. Create a script.m-file using a for-end loop to calculate the wave amplitude for each frequency (cycles/s) over an equal number of time values spac b Display each frequency value and its specific time using the built-in function fprint. c. Plot each of the cosine waves on a single figure. Annotate the figure appropriately with each of the designated labels (.e. axis, legend, title, etc.) and Question 5 Entropy (S) is a thermodynamic property that measures the relative disorder in a system. Natural processes will proceed spontaneously towards increasing the entropy of of the particles in that system. Processes that decrease the entropy of a material or gas will cause that material to become more highly structured or decrease the kinetic Between temperatures of 250 to 350 K the heat capacity Cp of air can be assumed to be constant as Cp-1.005 W/kg K The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314/kmolx. The State 2 State 1 Temperature 250 100 Pressure (kPa) 1000 State 3 300 350 500 650 Air, acting as an ideal gas, undergoes an irreversible process from state 1 to state 2. and then a second process from state 2 to state 3. a. Create a function.m.file as followed for the first line (function definition line entropyTI,P1, T2,22) b. Determine the entropy change for the first process when moving from state 1 to state 2. c. Determine the entropy change for the second process when from state 2 to state 3. d Use the built-in function fprintf to display the calculated entropy change As of gas in the process in W/kg Kand whether the entropy due to this process has inc The formula to calculate entropy with constant heat capacity is given below: AS gas e no Con (12) Attach File 25 points Save A disorder in a system. Natural processes will proceed spontaneously towards increasing the entropy of the system, allowing for the dispersal of kinetic energy of a material or gas will cause that material to become more highly structured or decrease the kinetic energy of its particles. n be assumed to be constant as Cp - 1.005 kJ/kg K. The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 kJ/kmol K. The molecular weight of air is M = 28.97 kg /kmol. te 1 to state 2 and then a second process from state 2 to state 3. Definition line) entropy_air (11,11,12, P2) ng from state 1 to state 2. om state 2 to state 3. opy change As of gas in the process in kJ/kg K and whether the entropy due to this process has increased decreased, or remained constant for b. and c. below: LARAR Question entre 1.00 Atch 3 GLASI Moving to another question will save this response. Question 4 Frequency is a defining characteristic of many physical phenomena including sound and light. For sound, frequency is perceived as the pitch of the sound. wave with frequency, ficycles/s) Isy = CO2nft). The cosine waveform for the following frequencies are listed in the table below: fcycles/s) 0.70 1.00 11.50 12.00 a. Create a script.m-file using a for-end loop to calculate the wave amplitude for each frequency (cycles/s) over an equal number of time values spac b Display each frequency value and its specific time using the built-in function fprint. c. Plot each of the cosine waves on a single figure. Annotate the figure appropriately with each of the designated labels (.e. axis, legend, title, etc.) and Question 5 Entropy (S) is a thermodynamic property that measures the relative disorder in a system. Natural processes will proceed spontaneously towards increasing the entropy of of the particles in that system. Processes that decrease the entropy of a material or gas will cause that material to become more highly structured or decrease the kinetic Between temperatures of 250 to 350 K the heat capacity Cp of air can be assumed to be constant as Cp-1.005 W/kg K The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314/kmolx. The State 2 State 1 Temperature 250 100 Pressure (kPa) 1000 State 3 300 350 500 650 Air, acting as an ideal gas, undergoes an irreversible process from state 1 to state 2. and then a second process from state 2 to state 3. a. Create a function.m.file as followed for the first line (function definition line entropyTI,P1, T2,22) b. Determine the entropy change for the first process when moving from state 1 to state 2. c. Determine the entropy change for the second process when from state 2 to state 3. d Use the built-in function fprintf to display the calculated entropy change As of gas in the process in W/kg Kand whether the entropy due to this process has inc The formula to calculate entropy with constant heat capacity is given below: AS gas e no Con (12) Attach File 25 points Save A disorder in a system. Natural processes will proceed spontaneously towards increasing the entropy of the system, allowing for the dispersal of kinetic energy of a material or gas will cause that material to become more highly structured or decrease the kinetic energy of its particles. n be assumed to be constant as Cp - 1.005 kJ/kg K. The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 kJ/kmol K. The molecular weight of air is M = 28.97 kg /kmol. te 1 to state 2 and then a second process from state 2 to state 3. Definition line) entropy_air (11,11,12, P2) ng from state 1 to state 2. om state 2 to state 3. opy change As of gas in the process in kJ/kg K and whether the entropy due to this process has increased decreased, or remained constant for b. and c. below: LARAR
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


