Question one.
Answer and explain each.
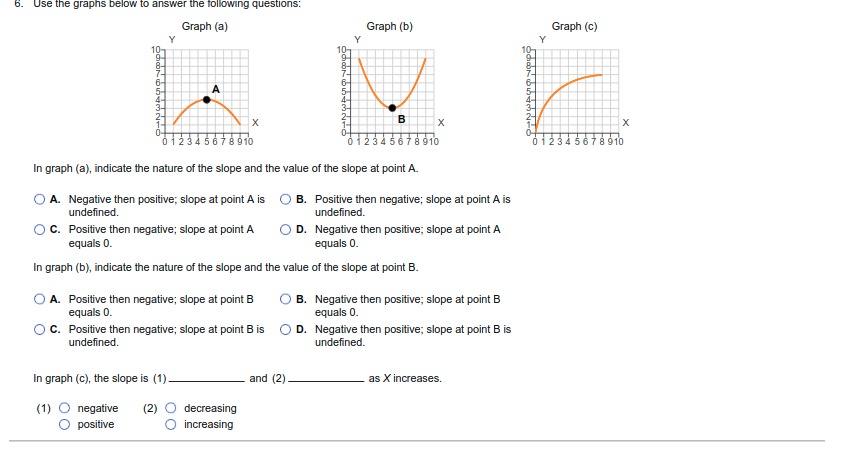
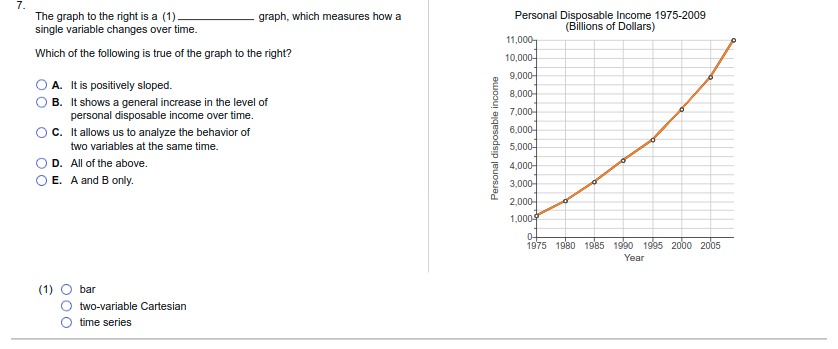
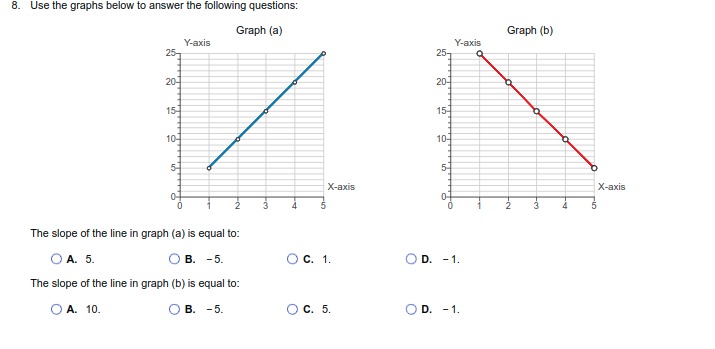
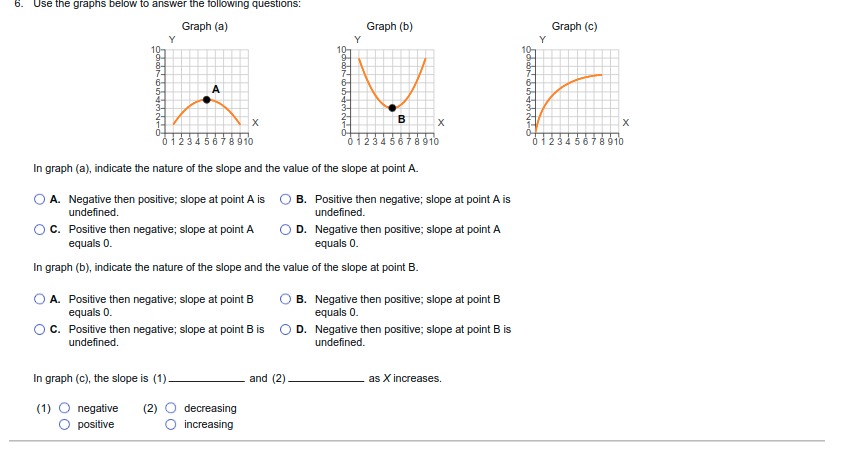
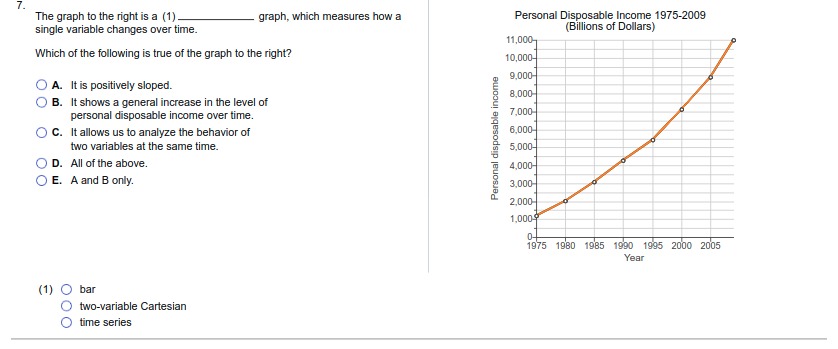
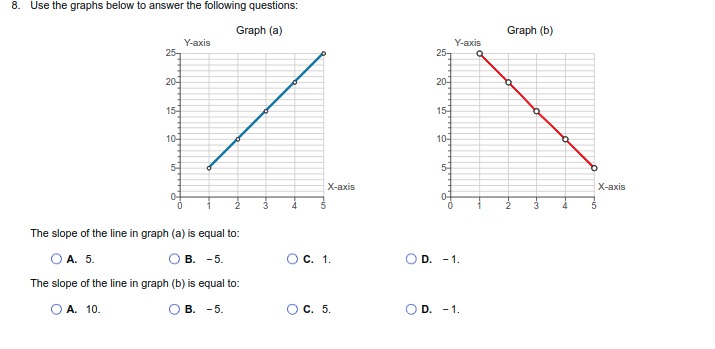
1. For each of the following situations, identify the full cost (opportunity cost)' involved: Monique quits her $75,000 per-year job as an accountant to become a full-time volunteer at a women's shelter. O A. The opportunity cost of volunteering at the shelter is the wages she gave up. O B. The opportunity cost of Monique's decision is the value of the next-best alternative not chosen. O C. The opportunity cost of Monique's decision is the time she can spend on other activities. O D. None of the above. O E. All of the above. The Agrizone Corporation invests $10.5 million in a new inventory tracking system. O A. The opportunity cost of Agrizone's decision is the value of the other investments it is pursuing at the same time. O B. The opportunity cost of Agrizone's decision is the value of leaving the money unutilized. O C. The opportunity cost of investing in a new inventory tracking system is any other projects Agrizone could have invested in. O D. All of the above. O E. None of the above. Taylor receives $100 from his grandmother for his birthday and uses it all to buy shares of stock in Harley-Davidson, Inc. O A. The opportunity cost of buying the Harley Davidson shares is the price of the shares that could have been spent on other goods and services O B. The opportunity cost of Taylor's decision is the value of the next-best alternative not chosen. O C. The opportunity cost of buying shares is the value of the time Taylor might have spent researching the stock market. O D. A and B only. O E. All of the above. Hector decides to spend the summer backpacking across Europe after he graduates from Harvard University. O A. The opportunity cost of Hector's decision is the wage he could earn if he decided to get a job. O B. The opportunity cost of backpacking across Europe is the time Hector could have spent on other activities. O C. The opportunity cost of Hector's decision is the next-best alternative to backpacking across EuropeAfter receiving her master's degree, Molly chooses to enter the doctoral program in Behavioral Science at the University of Texas. O A. The opportunity cost of entering a doctoral program is the time Molly could have spent on other activities. O B. The opportunity cost of Molly's decision is not being able to have a family. O C. The opportunity cost of Molly's decision is the price of any other doctoral program she could have chosen to enter. O D. All of the above. O E. None of the above. Sanjay chooses to use his vacation time to paint the exterior of his house. O A. The opportunity cost of Sanjay's decision is the price of the paint that he could have spent on other goods and activities O B. The opportunity cost of Sanjay's decision is the next-best alternative to painting the exterior of his house. O C. The opportunity cost of Sanjay's decision is the time he could have spent on other activities. O D. None of the above. O E. All of the above. After a night of karaoke, Tiffany forgets to set her alarm and sleeps through her Chemistry final exam. O A. The opportunity cost of Tiffany's decision is a poor grade on the exam. O B. The opportunity cost of Tiffany's decision is a better grade on the exam. O C. The opportunity cost of Tiffany's decision is the value of everything she could have done instead of staying out late O D. The opportunity cost of Tiffany's decision is the price to retake the exam. O E. All of the above.2. Determine whether each of the following is covered by microeconomics? or macroeconomics Number of employees in the steel industry: (1) _ Changes in the aggregate price level (inflation): (2) The price of gasoline: (3). The unemployment rate: (4). 2: Definition Microeconomics: The study of how individual households and individual firms make choices and how they interact in markets. 3: Definition Macroeconomics: The study of the economy as a whole, or aggregate, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, national income, and national output. (1) O Microeconomics (2) O Microeconomics (3) O Macroeconomics (4) O Microeconomics O Macroeconomics O Macroeconomics O Microeconomics O Macroeconomics3. Indicate whether the following statements are examples of positive economic analysis* or normative economic analysis". A devaluation of the U.S. dollar would increase exports from the United States: (1) Increasing the federal tax on gasoline would cause shipping costs in the United States to increase: (2) Florida should devote all revenues from its state lottery to improving public education: (3) Eliminating the trade embargo with Cuba would increase the number of Cuban cigars available in the United States: (4). As a public safety measure, the state of Texas should not pass legislation that allows people with concealed handgun permits to carry concealed weapons on college campuses: (5) 4: Definition Positive economic analysis: Describes what exists and how it works without making judgments about whether or not something is good or bad. 5: Definition Normative economic analysis: Involves judgments and prescriptions for courses of action. (1) O Positive (2) O Positive (3) O Positive (4) O Normative (5) O Normative O Normative O Normative O Normative O Positive O Positive4. A formal statement of theory, usually a mathematical statement of a presumed relationship between two or more variables, is called a (1) A (2) can change over time or across observations. The importance of the ceteris paribus" assumption when using models is that: O A. it eliminates the need for abstraction or simplification. O B. it converts normative analysis into positive analysis. O C. it allows researcher to isolate the effect of one event on another without the influence of outside variables. O D. it allows researcher to analyze the effect of all potential influences on a particular event. 6: Definition Ceteris paribus: "All else equal." To isolate the impact of one single variable, we use the ceferis paribus assumption. (1) O model (2) O model O hypothesis O variable 5. In economics, the concept of equity is rarely debated as most people agree as to what is and what is not equitable. O A. False O B. True All of the following are criteria frequently applied in judging economic outcomes except O A. profitability. O B. stability. O C. efficiency. O D. growth.6. Use the graphs below to answer the following questions: Graph (a) Graph (b) Graph (c) Y Y Y X B X X 01234 567 8910 01 234 56 7 8 910 01234567 8910 In graph (a), indicate the nature of the slope and the value of the slope at point A. O A. Negative then positive; slope at point A is O) B. Positive then negative; slope at point A is undefined. undefined O C. Positive then negative; slope at point A O D. Negative then positive; slope at point A equals 0. equals 0. In graph (b), indicate the nature of the slope and the value of the slope at point B. O A. Positive then negative; slope at point B O B. Negative then positive; slope at point B equals 0. equals 0. O C. Positive then negative; slope at point B is O) D. Negative then positive; slope at point B is undefined. undefined. In graph (c), the slope is (1) and (2) as X increases. (1) O negative (2) O decreasing positive O increasing7. The graph to the right is a (1) graph, which measures how a Personal Disposable Income 1975-2009 single variable changes over time. (Billions of Dollars) 11,000- Which of the following is true of the graph to the right? 10,000- 9.000- O A. It is positively sloped. 8,000 O B. It shows a general increase in the level of personal disposable income over time. 7,000 O C. It allows us to analyze the behavior of 6,000 Personal disposable income two variables at the same time. 5,000- O D. All of the above. 4,000- O E. A and B only. 3,000- 2,000- 1,0009 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Year (1) O bar O two-variable Cartesian O time series8. Use the graphs below to answer the following questions: Graph (a) Graph (b) Y-axis Y-axis 25- 25- 20- X-axis X-axis The slope of the line in graph (a) is equal to: O A. 5. OB. -5. O C. 1. OD. - 1. The slope of the line in graph (b) is equal to: O A. 10. O B. -5. O C. 5. OD. - 1