Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question Part 1 Question Part 2 Question Part 3 Please do in word file with working notes and don't copy the solution which is already
Question Part 1
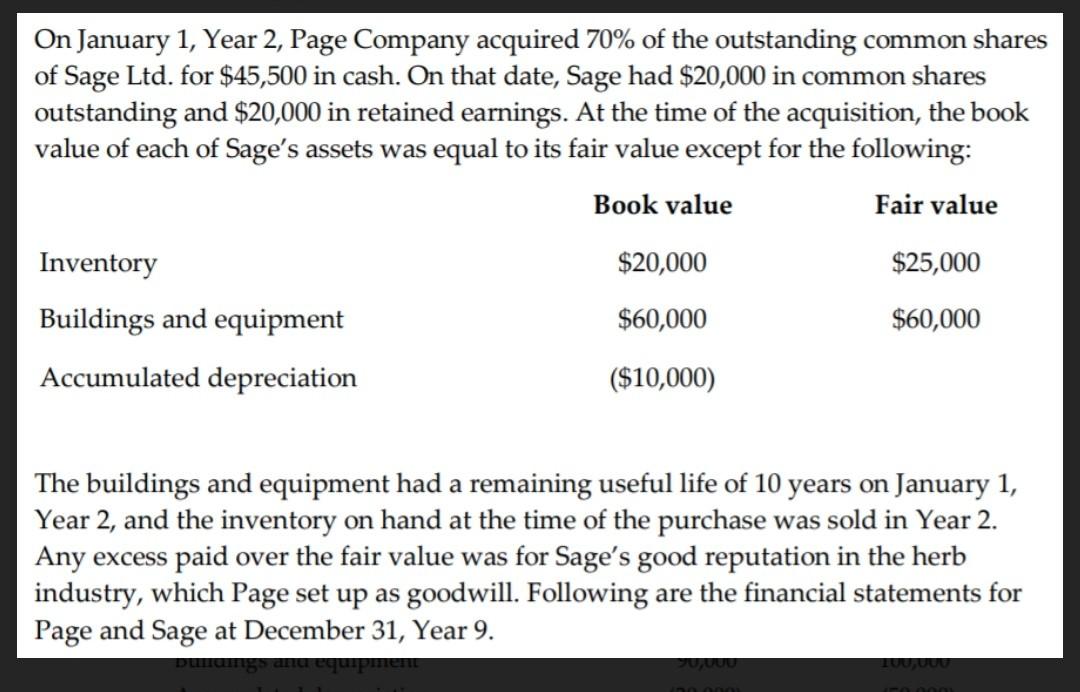
Question Part 2
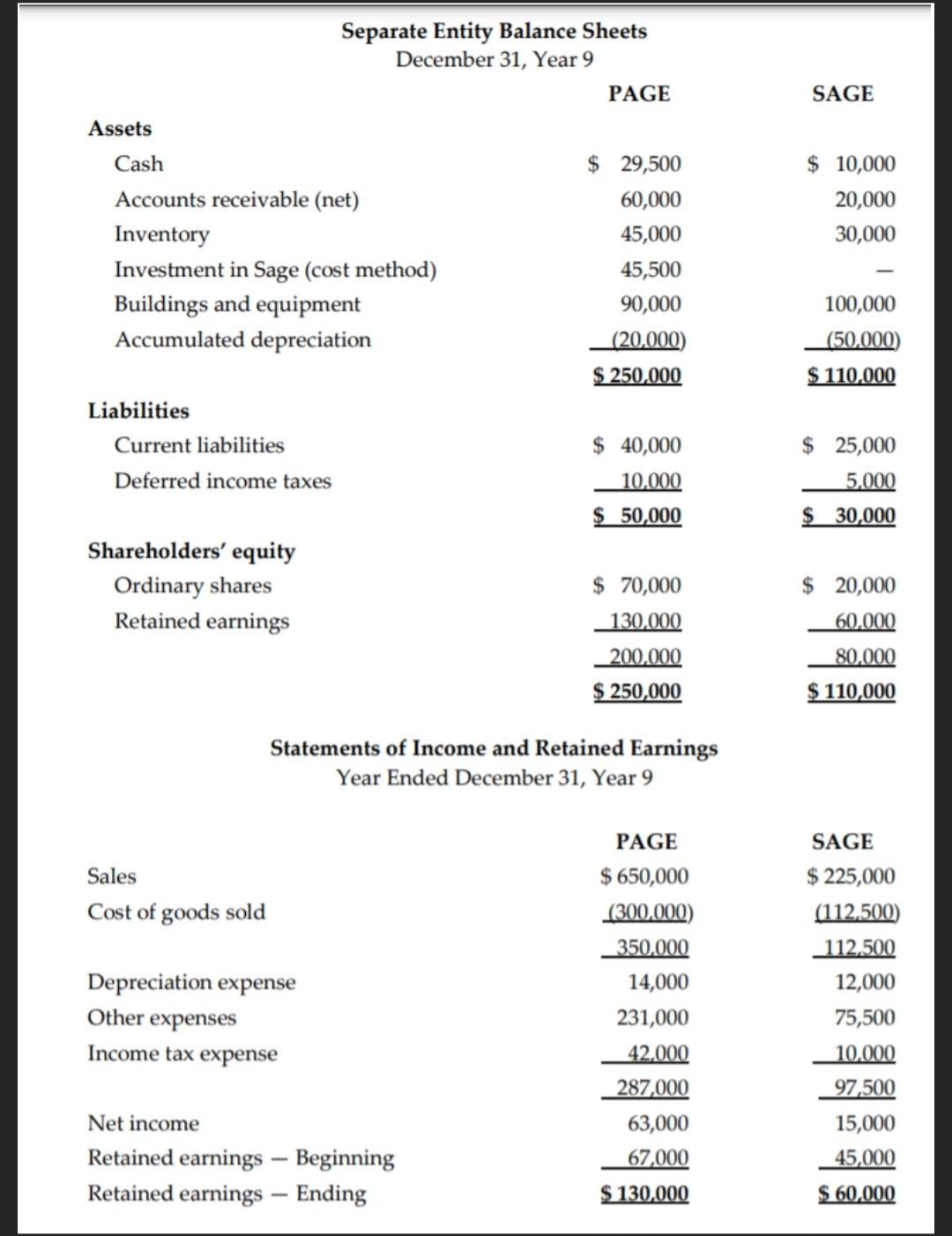
Question Part 3

Please do in word file with working notes and don't copy the solution which is already here on Chegg. Thanks in advance.
On January 1, Year 2, Page Company acquired 70% of the outstanding common shares of Sage Ltd. for $45,500 in cash. On that date, Sage had $20,000 in common shares outstanding and $20,000 in retained earnings. At the time of the acquisition, the book value of each of Sage's assets was equal to its fair value except for the following: Book value Fair value $20,000 $25,000 Inventory Buildings and equipment Accumulated depreciation $60,000 $60,000 ($10,000) The buildings and equipment had a remaining useful life of 10 years on January 1, Year 2, and the inventory on hand at the time of the purchase was sold in Year 2. Any excess paid over the fair value was for Sage's good reputation in the herb industry, which Page set up as goodwill. Following are the financial statements for Page and Sage at December 31, Year 9. Separate Entity Balance Sheets December 31, Year 9 PAGE SAGE Assets Cash Accounts receivable (net) Inventory Investment in Sage (cost method) Buildings and equipment Accumulated depreciation $ 10,000 20,000 30,000 $ 29,500 60,000 45,000 45,500 90,000 (20,000) 100,000 (50,000) $ 250,000 $ 110,000 Liabilities Current liabilities Deferred income taxes $ 40,000 10,000 $ 50,000 $ 25,000 5,000 $ 30,000 Shareholders' equity Ordinary shares Retained earnings $ 20,000 60,000 $ 70,000 130,000 200,000 $ 250,000 80,000 $ 110,000 Statements of Income and Retained Earnings Year Ended December 31, Year 9 Sales Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Other expenses Income tax expense PAGE $ 650,000 (300,000) 350,000 14,000 231,000 42,000 287,000 63,000 67,000 $ 130,000 SAGE $ 225,000 (112,500) 112.500 12,000 75,500 10,000 97,500 15,000 45,000 Net income Retained earnings Beginning Retained earnings Ending $ 60,000 During Year 8 and Year 9, Sage sold merchandise to Page at a price that provides it with a gross profit of 50%. The Year 9 sale was $10,000. Page's December 31, Year 9, inventory contained $2,000 worth of these purchases from Sage, while the December 31, Year 8, inventory contained $1,000 worth of intercompany merchandise. At the end of Year 9, Page owed Sage $500 for merchandise inventory purchased on account. This liability is non-interest bearing. On December 31, Year 6, Page sold equipment having a cost of $5,000 and accumulated depreciation of $1,000 to Sage for $5,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment at the time of the sale was 10 years. In Year 5 the goodwill impairment test resulted in a $5,000 loss, and for Year 9, goodwill was further impaired by $714. Neither company paid dividends during Year 9. Both companies have a 40% tax rate. Page accounts for Sage using the FVE and cost methods. Required: 1. Prepare preliminary calculations as noted below: a) Calculation of goodwill using fair values b) Calculation and allocation of acquisition differential and calculation of goodwill, and calculation of initial NCI c) Acquisition differential amortization and goodwill impairment table d) Table of realized and unrealized intercompany inventory profits e) Table of intercompany profits in capital assets and other eliminations f) Calculation of consolidated net income and NCI-I/S g) Calculation of consolidated beginning of Year 9 retained earnings h) Calculation of end of Year 9 NCI-B/S On January 1, Year 2, Page Company acquired 70% of the outstanding common shares of Sage Ltd. for $45,500 in cash. On that date, Sage had $20,000 in common shares outstanding and $20,000 in retained earnings. At the time of the acquisition, the book value of each of Sage's assets was equal to its fair value except for the following: Book value Fair value $20,000 $25,000 Inventory Buildings and equipment Accumulated depreciation $60,000 $60,000 ($10,000) The buildings and equipment had a remaining useful life of 10 years on January 1, Year 2, and the inventory on hand at the time of the purchase was sold in Year 2. Any excess paid over the fair value was for Sage's good reputation in the herb industry, which Page set up as goodwill. Following are the financial statements for Page and Sage at December 31, Year 9. Separate Entity Balance Sheets December 31, Year 9 PAGE SAGE Assets Cash Accounts receivable (net) Inventory Investment in Sage (cost method) Buildings and equipment Accumulated depreciation $ 10,000 20,000 30,000 $ 29,500 60,000 45,000 45,500 90,000 (20,000) 100,000 (50,000) $ 250,000 $ 110,000 Liabilities Current liabilities Deferred income taxes $ 40,000 10,000 $ 50,000 $ 25,000 5,000 $ 30,000 Shareholders' equity Ordinary shares Retained earnings $ 20,000 60,000 $ 70,000 130,000 200,000 $ 250,000 80,000 $ 110,000 Statements of Income and Retained Earnings Year Ended December 31, Year 9 Sales Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Other expenses Income tax expense PAGE $ 650,000 (300,000) 350,000 14,000 231,000 42,000 287,000 63,000 67,000 $ 130,000 SAGE $ 225,000 (112,500) 112.500 12,000 75,500 10,000 97,500 15,000 45,000 Net income Retained earnings Beginning Retained earnings Ending $ 60,000 During Year 8 and Year 9, Sage sold merchandise to Page at a price that provides it with a gross profit of 50%. The Year 9 sale was $10,000. Page's December 31, Year 9, inventory contained $2,000 worth of these purchases from Sage, while the December 31, Year 8, inventory contained $1,000 worth of intercompany merchandise. At the end of Year 9, Page owed Sage $500 for merchandise inventory purchased on account. This liability is non-interest bearing. On December 31, Year 6, Page sold equipment having a cost of $5,000 and accumulated depreciation of $1,000 to Sage for $5,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment at the time of the sale was 10 years. In Year 5 the goodwill impairment test resulted in a $5,000 loss, and for Year 9, goodwill was further impaired by $714. Neither company paid dividends during Year 9. Both companies have a 40% tax rate. Page accounts for Sage using the FVE and cost methods. Required: 1. Prepare preliminary calculations as noted below: a) Calculation of goodwill using fair values b) Calculation and allocation of acquisition differential and calculation of goodwill, and calculation of initial NCI c) Acquisition differential amortization and goodwill impairment table d) Table of realized and unrealized intercompany inventory profits e) Table of intercompany profits in capital assets and other eliminations f) Calculation of consolidated net income and NCI-I/S g) Calculation of consolidated beginning of Year 9 retained earnings h) Calculation of end of Year 9 NCI-B/SStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


