
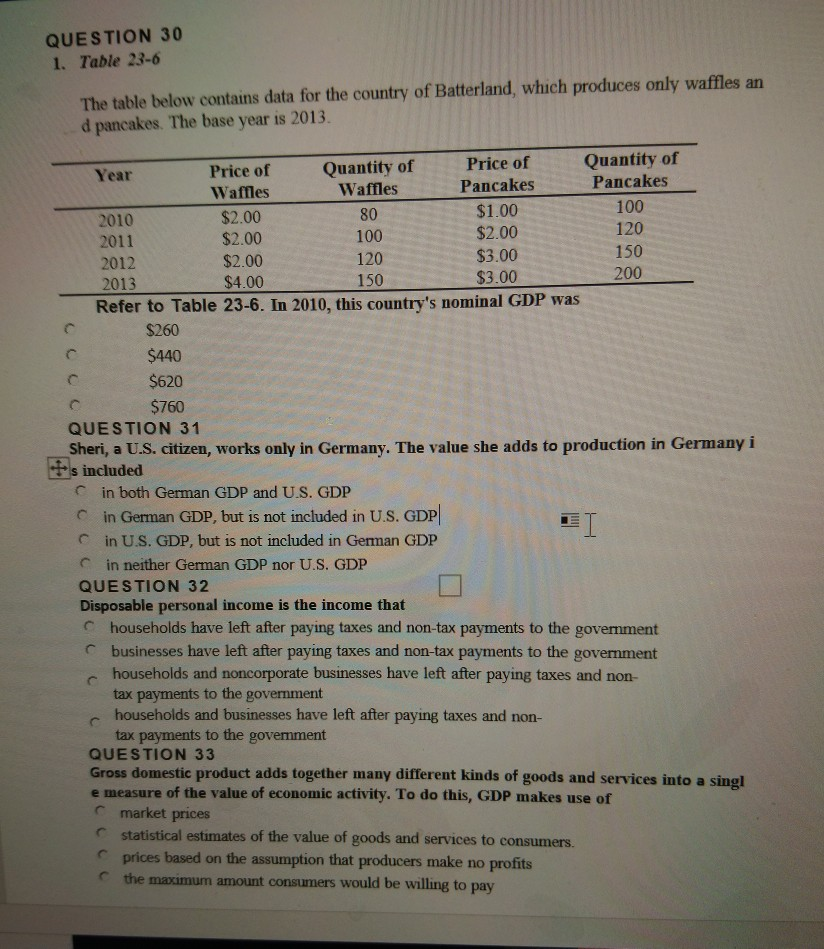


Question:
R v Raverson
Charges under the Liquor License Act of Ontario RSO 1990 c.L.19:
Unlawful purchase of liquor, contrary to s.27
Sell liquor to intoxicated person, contrary to s.29
Sell liquor to person under 19 years old, contrary to ss.30(1) (2)
Draft your submission as the Prosecutor
Raverson is the owner of Tavern Restaurant. He is 50 years old and is the married father of the two young children. He has been married for 9 years and supports one dependent from a previous relationship. He has no criminal record. Tavern Restaurant has been open and changed ownership in 2008.
Tavern Restaurant has been cited numerous times for breaches of municipal by-laws. These convictions include excessive noise complaints, staying open after closing hours, serving under-age and intoxicated patrons on premises. In total, there have been 20 violations of municipal by-laws and Liquor License Act infractions over the period of 2001- 2007
The bottles of alcohol seized by the police in this case are estimated to be worth in excess of $30,000. It is estimated that through the illegal purchase of these products the cost to the province and municipality due to lost revenues if between $10,000-$20,000.
There have also been a lot of concerns that unadulterated alcohol has been found to contain excessive traces of chemicals that preserve their longevity beyond the normal period of time that these products are considered fit for consumption.
At the time of his arrest, there were about 30 persons on the premises. A number of them appears to be obviously intoxicated and impaired. At least one patron appeared to be well under 19 years old. Mr. Raverson was present as well. He spoke to the police while the search warrant was being executed. He was generally uncooperative and did not seem overly concerned for the wellbeing of his patrons.
As a result of some charges, Tavern Restaurant has had its liquor licence suspended by the municipality and is no longer carrying on business. Mr. Raverson is out of job thereby currently in the process of applying for social assistance. His wife is on medical leave from her employment as a law clerk due to an injury to her hand. Since the charges were laid, Mr. Raverson has experienced depression and has been referred to a therapist. He has acknowledged a long-standing alcohol and substance addiction and expressed a willingness to attend for counselling. It appears that his parents had alcohol ad substance abuse issues while he was a teenager.
As a result of resolution discussions, it is anticipated that the individual defendant, Raverson wants to enter a guilty plea to one count of unlawful purchase of liquor and one count of knowingly selling liquor to a person under the age of 19 years old, contrary to the Liquor Licence Act. The penalty for the unlawful purchase offence is a maximum of $100,000 and/or imprisonment for one year; the penalty for the knowingly selling liquor to a minor is a maximum fine of $200,000 and/or imprisonment for one year. The charge of selling liquor to an intoxicated person against Raverson will be withdrawn at the conclusion of sentencing, and all three charges against the corporate accused, Tavern Restaurant, will also be withdrawn.
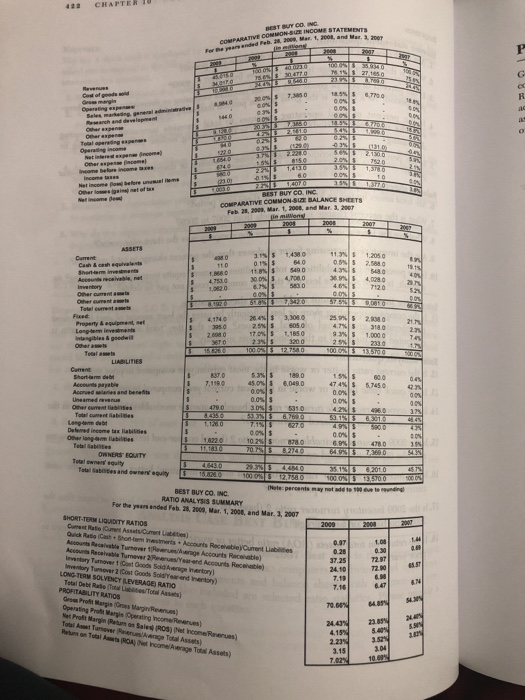
LONG-TERM ASSETS 121 REQUIRED Income statement questions: 1. Are total revenues higher or lower over the three-year period? 2. What is the percent change in total revenues from 2007 to 2009? 3. Is the percent of cost of goods sold to total revenues increasing or decreasing over the three- year period? As a result, is the gross margin percent increasing or decreasing" 4. Is the percent of total operating expenses to total revenues increasing or decreasing over the three-year period? As a result, is the operating income percent increasing or decreasing? 5. Is the percent of net income to total revenue increasing or decreasing over the three-year period? Balance sheet questions: 6. Are total assets higher or lower over the three-year period? 7. What is the percent change in total assets from 2007 to 2009? 8. What are the largest asset investments for the company over the three-year period? 9. Are the inventories increasing faster or slower than the percent change in total revenues? 10. Is the percent of total liabilities to total liabilities + owners' equity increasing or decreasing? As a result, is there more or less risk that the company could not pay its debts? Integrative income statement and balance sheet question: 1 1. Is the company operating more or less efficiently by using the least amount of asset investment to generate a given level of total revenues? Note that the "total asset turnover" ratio is computed and included in the "ratio analysis summary". Ratio analysis questions: 12. Is the current ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 13. Is the quick ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 14. Is the accounts receivable turnover ratio I (based on average receivables) better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 15. Is the 2009 accounts receivable turnover ratio 2 (based on year-end receivables) better or worse than the 2009 ratio based on an average? 16. Is the inventory turnover ratio I (based on average inventory) better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years? 17. Is the 2009 inventory turnover ratio 2 (based on year-end inventory) better or worse than the 2009 ratio based on an average? 18. Is the return on total assets (ROA) ratio better or worse in the most current year compared to prior years?CHAPTER BEST BUT CO. ING. COMPARATIVE COMMON-BUT INCOME STATEMENTS I De pearsended Feb. H Hop, Mar 1, Itg), and Her. $. For God of ponds gold Be march ind developrant 1131 0 213010 8150 1, 370 BEST BUY CO INC COMPARATIVE COMMON-BUT BALANCE SHEETS Feb. 21, 1903, Mar. 1, 2908, and Mar. J. NOT in miWongi ASSETS Current 11.8 9 30 04 4.024 0 Insuntory 10130 TIZO Oner cumnl itabs Talal commit ain't Fond Property A equipment, Fit 4.7% 318 0 1. 185 0 Invinny bles I poodail 1.0010 100 03 5 13 7910 LIABILITIES Short-form that 7. 178.0 8,049.0 47AN 30%$ 531.0 2710 4 79 On lined Income tax listitnon 1.4220 10 2% OWNERS EQUITY Total camps' equity Foul Nabilities and careers equity 314 5 63010 10ON 8 12 7580 100.05 4 1275100 BEST BUY CO. INC IHole- percents may not add to The hat to RATIO ANALYSIS SUMMARY For the yours anded Fab. 28, 2009, Mar, 1, 2010, and Mar. 3, 3907 SHORT-TEAM LIQUIDITY RATIOS 2080 Quick Ratio Cinch + Shortom Insulmints + Account Rych biel Curent Liabilities 1.09 Ancouch Recaleable Turnover 1 Haverun Average Accounts Recunable] /Yearend Accounts Reophable) 37.25 Inwwwtory Turnover 2 [Cost Goods Bold/fair-and Inantory) LONG-TERM SOLVENCY (LEVERAGE) RATIO 7.1 Total Debt Rule (Toul Libifyou Tool Anmetal 7.10 PROFITABILITY RATIOS Grow Prof Bugin (Crops Magin Revrun) Operating Profit Margin Operating Income Revenues Net Profit Margin [Barn on Sales) (803) [het hcome Revenues) 24.AJK Tokill Anget Turnover Pierces/Average Total Assets) 4.15% Butum on Total Arts (RCA) (Net heamalAwrage Total Assets) 2.23% 3.15 1.04 7.02% 10 89QUESTION 30 1. Table 23-6 The table below contains data for the country of Batterland, which produces only waffles an d pancakes. The base year is 2013. Year Price of Quantity of Price of Quantity of Waffles Waffles Pancakes Pancakes 2010 $2.00 80 $1.00 100 2011 $2.00 100 $2.00 120 2012 $2.00 120 $3.00 150 2013 $4.00 150 $3.00 200 Refer to Table 23-6. In 2010, this country's nominal GDP was $260 $440 $620 $760 QUESTION 31 Sheri, a U.S. citizen, works only in Germany. The value she adds to production in Germany i +'s included in both German GDP and U.S. GDP in German GDP, but is not included in U.S. GDP ET C in U.S. GDP, but is not included in German GDP in neither German GDP nor U.S. GDP QUESTION 32 Disposable personal income is the income that "households have left after paying taxes and non-tax payments to the government businesses have left after paying taxes and non-tax payments to the government households and noncorporate businesses have left after paying taxes and non- tax payments to the government households and businesses have left after paying taxes and non- tax payments to the government QUESTION 33 Gross domestic product adds together many different kinds of goods and services into a singl e measure of the value of economic activity. To do this, GDP makes use of C market prices " statistical estimates of the value of goods and services to consumers. prices based on the assumption that producers make no profits the maximum amount consumers would be willing to payQUESTION 20 Discretionary fiscal policy refers to O A. Policy undertaken at the sole discretion of Congress which cannot be vetoed by the President. OB. Policy conducted discretely as to not attract undue attention, O C. Policy that takes effect automatically when an economy slides into a recession. O D. Policy in which Congress and the President take explicit legislative action to change government spending or taxes.E. One month Question 5: An increase in real wealth in India will . Select all that apply. Choose one or more: A. increase Indian aggregate demand B. decrease Indian aggregate demand C. increase U.S. aggregate demand D. decrease U.S. aggregate demand Question 6: Choose the right answer: Net exports will increase/decrease/stay the same when the value of the dollar result, the aggregate demand curve will shift left/increase. ECON 1204-001 Principles of Macro Spring 2019 Question 7
















