
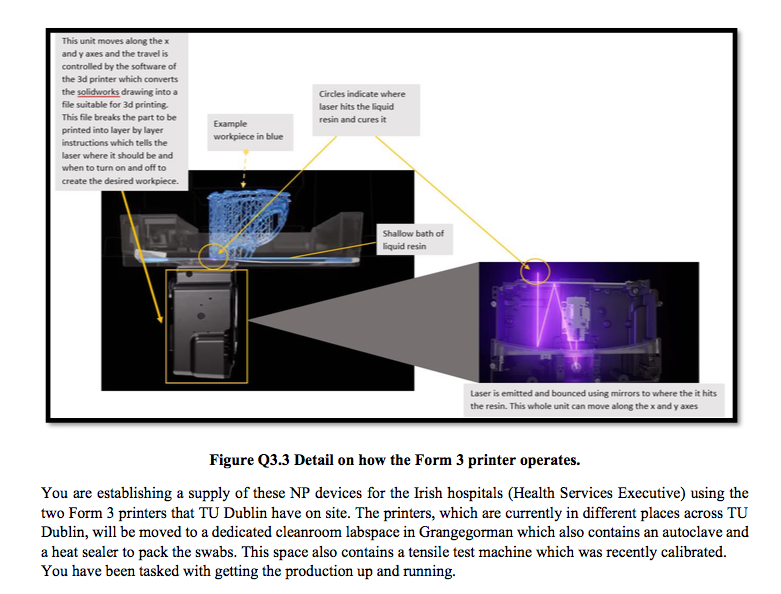

Question There is a worldwide shortage of the Primo nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs which are used to collect samples for COVID-19 testing. NP swabs are single use devices typically used for testing for influenza and other respiratory infections. They are flexible sticks with a bristled end that are inserted into the nose, to the back of the nasal cavity and swept around to collect material that sticks to or wicks in between the bristles. The swab is then placed into a vial that Nasopharyngeal Swabs contains a culture medium (not part of our product, available in clinical setting). Swab formlabs sticks have an intentionally weak point 7-8 cm from the bristled tip, which allows the stick to be broken to the correct length so that the vial can be capped before it is transported to a laboratory for testing. Formlabs have come up with a design for 3d printing of NP swabs (see Figure Q3.1) Figure Q3.1 Example NP swabs developed and packaged by using their 3d SLA printers, specifically the Formlabs Form 3 printer (see Figure Q3.2). Their NP design has been tested to prove its safety and effectiveness. The material the NP swab is printed from is a 3d printing liquid resin that is usually used in dental practices to make surgical guides for drilling into the jawbone, enabling dental implants to be fitted. The material can be autoclaved. In the Form 3 printer, a laser heats and sinters liquid resin into a predetermined shape (see Figure Q3.3). A timer controls the length of time each laser is switched on for. The travel of the laser housing is controlled by motorised lead screw, and x, y coordinates and again, the timer controls travel speed. Figure Q3.2 Formlabs Form 3 printer- this is the printer recommended for printing of NP swabs. This unit moves along the x and yaxes and the travel is controlled by the software of the 3d printer which converts the solidworks drawing into a file suitable for 3d printing. This file breaks the part to be printed into layer by layer instructions which tells the laser where it should be and when to turn on and off to create the desired workpiece. Circles indicate where laser hits the liquid resin and cures it Example workpiece in blue Shallow bath of liquid resin Laser is emitted and bounced using mirrors to where the it hits the resin. This whole unit can move along the x and y axes Figure Q3.3 Detail on how the Form 3 printer operates. You are establishing a supply of these NP devices for the Irish hospitals (Health Services Executive) using the two Form 3 printers that TU Dublin have on site. The printers, which are currently in different places across TU Dublin, will be moved to a dedicated cleanroom labspace in Grangegorman which also contains an autoclave and a heat sealer to pack the swabs. This space also contains a tensile test machine which was recently calibrated. You have been tasked with getting the production up and running. Please answer the following questions: i. 'Their NP design has been tested to prove its safety and effectiveness. What tests would have had to be carried out to prove safety of the device. (Go into detail here.) Who would give approval for these NP swabs to be used in Irish hospitals? ii. iii. Write a high level checklist for the main tests to be carried out on the Form 3 printers as part of their IQ validation. Include a) what general checks need to be run on the printers b) what calibration needs have these specific printers. (Please detail any assumptions you make.) iv. Assuming your company has a QMS, what specific documentation would be needed for the entire validation? V. Should the NP swabs be sealed into their pouches (seen in image Q3.1) before or after autoclaving? Give your reason why vi. Why do the NP swabs need to be sterilised if they are made in a cleanroom? vii. What other types of sterilisation may be suitable for these NP swabs? Explain any risks or disadvantages associated with the methods you mention. viii. What end of batch testing should be completed for each run of product? ix. Discuss incoming inspections that would need to carried out. Question There is a worldwide shortage of the Primo nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs which are used to collect samples for COVID-19 testing. NP swabs are single use devices typically used for testing for influenza and other respiratory infections. They are flexible sticks with a bristled end that are inserted into the nose, to the back of the nasal cavity and swept around to collect material that sticks to or wicks in between the bristles. The swab is then placed into a vial that Nasopharyngeal Swabs contains a culture medium (not part of our product, available in clinical setting). Swab formlabs sticks have an intentionally weak point 7-8 cm from the bristled tip, which allows the stick to be broken to the correct length so that the vial can be capped before it is transported to a laboratory for testing. Formlabs have come up with a design for 3d printing of NP swabs (see Figure Q3.1) Figure Q3.1 Example NP swabs developed and packaged by using their 3d SLA printers, specifically the Formlabs Form 3 printer (see Figure Q3.2). Their NP design has been tested to prove its safety and effectiveness. The material the NP swab is printed from is a 3d printing liquid resin that is usually used in dental practices to make surgical guides for drilling into the jawbone, enabling dental implants to be fitted. The material can be autoclaved. In the Form 3 printer, a laser heats and sinters liquid resin into a predetermined shape (see Figure Q3.3). A timer controls the length of time each laser is switched on for. The travel of the laser housing is controlled by motorised lead screw, and x, y coordinates and again, the timer controls travel speed. Figure Q3.2 Formlabs Form 3 printer- this is the printer recommended for printing of NP swabs. This unit moves along the x and yaxes and the travel is controlled by the software of the 3d printer which converts the solidworks drawing into a file suitable for 3d printing. This file breaks the part to be printed into layer by layer instructions which tells the laser where it should be and when to turn on and off to create the desired workpiece. Circles indicate where laser hits the liquid resin and cures it Example workpiece in blue Shallow bath of liquid resin Laser is emitted and bounced using mirrors to where the it hits the resin. This whole unit can move along the x and y axes Figure Q3.3 Detail on how the Form 3 printer operates. You are establishing a supply of these NP devices for the Irish hospitals (Health Services Executive) using the two Form 3 printers that TU Dublin have on site. The printers, which are currently in different places across TU Dublin, will be moved to a dedicated cleanroom labspace in Grangegorman which also contains an autoclave and a heat sealer to pack the swabs. This space also contains a tensile test machine which was recently calibrated. You have been tasked with getting the production up and running. Please answer the following questions: i. 'Their NP design has been tested to prove its safety and effectiveness. What tests would have had to be carried out to prove safety of the device. (Go into detail here.) Who would give approval for these NP swabs to be used in Irish hospitals? ii. iii. Write a high level checklist for the main tests to be carried out on the Form 3 printers as part of their IQ validation. Include a) what general checks need to be run on the printers b) what calibration needs have these specific printers. (Please detail any assumptions you make.) iv. Assuming your company has a QMS, what specific documentation would be needed for the entire validation? V. Should the NP swabs be sealed into their pouches (seen in image Q3.1) before or after autoclaving? Give your reason why vi. Why do the NP swabs need to be sterilised if they are made in a cleanroom? vii. What other types of sterilisation may be suitable for these NP swabs? Explain any risks or disadvantages associated with the methods you mention. viii. What end of batch testing should be completed for each run of product? ix. Discuss incoming inspections that would need to carried out









