Question
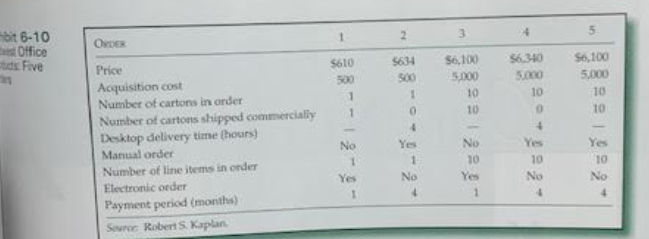
Question: Using this capacity cost rate information, calculate the cost and profitability of the five orders in exhibit 6-10 (below). What explains the variation in
Question: Using this capacity cost rate information, calculate the cost and profitability of the five orders in exhibit 6-10 (below). What explains the variation in profitability across the five orders?
Question: Using this capacity cost rate information, calculate the cost and profitability of the five orders in exhibit 6-10 (below). What explains the variation in profitability across the five orders?
Below is the answer A)
A)
The cost of processing cartons through the facility
To calculate the cost of processing cartons through the facility we need to first subtract the truck drivers expenses from the personnel expenses as it includes both warehouse and truck drivers expense and then we need to add warehouse expenses (excluding personnel) to it.
Cost of processing = ($2,570,000 - $250,000) + $2,000,000
= $4,320,000
Capacity that could be handled = 80,000 cartons
Cost per carton = $4,320,000/80,000 = $54 per carton
This scenario is solved by assuming all the cartons used for processing are of the same size, arrived and stored in the facility for the same amount of time. Otherwise, the calculations will be complex, and a detailed ABC cost system should be used to solve it.
The cost of entering electronic and manual customer orders
As mentioned, Midwest employed 16 order entry operators with annual expenses of $840,000 which includes salaries, supervision and equipment costs and other benefits for the operators.
Order entry expenses = $840,000
Number of employees employed = 16
Each employee works for average of 1,500 productive hours per year after removing vacations, breaks and holidays
Capacity of resources = 1500 x 16 = 24,000 hours
Cost of manual order entry = $35/hour.
Time taken to enter a customer order manually = Time taken to enter basic information +
Additional time taken to enter each line item on the order
= 0.15 hour + 0.075 hour = 0.225 hour
Total cost to entering manual customer order = 0.225hr x $35/ hour = $7.875 per entry
Operator spends an average of 0.10 hour to verify electronic order information and it requires no additional time for line item.
Cost for verifying information on electronic customer order = 0.10 hour x $35/ hour = $3.5 per entry
The main assumption when calculating the cost of order entry is that the complexity of all electronic orders requires the same amount of time to validate or verify, and all manual orders take the same amount of time to enter the basic information (except line items)
The cost of shipping cartons on commercial carriers
Assuming that each carton shipped by commercial carrier costs around the same, whatever the weight or distance, we can estimate the cost per carton using the total freight expenses and the total number of cartons shipped by commercial freight.
Cost of commercial freight = $450,000
Number of cartons shipped = 75,000
Shipping cost of each carton = $450,000/75,000 = $6 per carton
The cost per hour for desktop deliveries
Midwest leased 4 trucks and hired 4 drivers for desktop delivery services.
Each truck driver worked for a max of 1500 hours and the maximum available time for each truck is 1500 hours after service and maintenance.
Therefore, hours available for desktop delivery = 1500 hours x 4 = 6000hrs
Based on Time-Driven approach we can calculate the delivery cost per hour for desktops
Delivery resources cost is calculated by adding delivery truck expenses and truck driver compensation = $200,000 + $250,000 = $450,000
Cost per hour to deliver desktops = $450,000/6000 = $75/ hour
Please use the above to answer B)

it should look like this:
[Correct way to solve
(b) Order 1 Gross Margin = Sales cost of items purchased = 610 - 500 = $110
Number of cartons is 1, so cost for Processing carton = $54 per carton (as per 1 of (a))
Cost for shipping the cartons commercially = $ 6 (as per 3 of (a))
No desktop delivery = 0
No manual order processing or line items = 0
Electronic order yes = $3.50 (as per 2 of (a))
Interest per month is 1% hence interest on sales amount = 1% of $610 = 6.10
Hence Interest on receivable = $6.10
Total processing cost = $ 54 + 6 + 3.50 + 6.10 = $69.60
Order profitability = $110 - $69.60 = $40.40]
bit \\( 6-10 \\) Office atdr Five Required (a) Based on the interviews and the data in the case, estimate the following: (1) The cost of processing cartons through the facility (2) The cost of entering electronic and manual customet orders (3) The cost of shipping cartons on commercial carriers (4) The cost per hour for desktop deliveries. (b) Using this capacity cost rate information, calculate the cost and profitability of the five orders in Exhibit 6-10. What explains the variation in protitability across the five onders? (c) On the basis of your analysis, what actions should John Malone take to improve Midwest's profitability? Include suggestions for managing customer profitability. (d) Suppose that currently. Midwest processes 40,000 manual orders per year, with a total of 200,000 line items entered, and 30,000 electronic orders. (1) How much unused practical capacity does the company have? (2) If the company's efforts to encourage customers who order manually to change to electronic ordering results in 20,000 manual orders per year ( 100,000 line items entered) and 50,000 electronic orders, how many order entry operators will the company require? if order entry resource costs can be reduced in proportion to the number of employees, what will be the cost savings from the changes? (3) Returning to the original information in part \\( d \\), if the company's process improvement efforts result in a \20 reduction in time to perform each of the three order entry activities, how many order entry operators will the company require? If order entry resource costs can be reduced in proportion to the number of employees, what will be the cost savings from the process improvements? bit \\( 6-10 \\) Office atdr Five Required (a) Based on the interviews and the data in the case, estimate the following: (1) The cost of processing cartons through the facility (2) The cost of entering electronic and manual customet orders (3) The cost of shipping cartons on commercial carriers (4) The cost per hour for desktop deliveries. (b) Using this capacity cost rate information, calculate the cost and profitability of the five orders in Exhibit 6-10. What explains the variation in protitability across the five onders? (c) On the basis of your analysis, what actions should John Malone take to improve Midwest's profitability? Include suggestions for managing customer profitability. (d) Suppose that currently. Midwest processes 40,000 manual orders per year, with a total of 200,000 line items entered, and 30,000 electronic orders. (1) How much unused practical capacity does the company have? (2) If the company's efforts to encourage customers who order manually to change to electronic ordering results in 20,000 manual orders per year ( 100,000 line items entered) and 50,000 electronic orders, how many order entry operators will the company require? if order entry resource costs can be reduced in proportion to the number of employees, what will be the cost savings from the changes? (3) Returning to the original information in part \\( d \\), if the company's process improvement efforts result in a \20 reduction in time to perform each of the three order entry activities, how many order entry operators will the company require? If order entry resource costs can be reduced in proportion to the number of employees, what will be the cost savings from the process improvementsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


