Question
Question1 When a monopoly increases its output and sales, what is the impact of the output effect and the price effect on total revenue? Select
Question1
When a monopoly increases its output and sales, what is the impact of the output effect and the price effect on total revenue?
Select one:
a.Both the output effect and the price effect work to increase total revenue.
b.The output effect works to increase total revenue, and the price effect works to decrease total revenue.
c.The output effect works to decrease total revenue, and the price effect works to increase total revenue.
d.Both the output effect and the price effect work to decrease total revenue.
Question2
What is one method used to control the ability of firms to capture monopoly profit in Canada?
Select one:
a.government purchase of products produced by monopolists
b.government distribution of a monopolist's excess production
c.enforcement of antitrust laws
d.regulation of firms in highly competitive markets
Question3
For a firm to price discriminate, it must
Select one:
a.be a natural monopoly.
b.be regulated by the government.
c.have some market power.
d.have large fixed costs.
Question4
The process of buying a good in one market at a low cost and selling the good in another market for a higher cost to profit from the price difference is called
Select one:
a.sabotage.
b.resale conspiracy.
c.arbitrage.
d.collusion.
Question5
Why does inefficiency arise from a monopoly?
Select one:
a.The monopoly firm earns an excessively large profit.
b.Some buyers will refrain from buying the good, due to the high price.
c.Some sellers will refrain from buying the good, due to the low price.
d.Consumers who buy the goods feel exploited.
Question6
What is the typical market demand curve for a monopolist?
Select one:
a.upward sloping
b.downward sloping
c.horizontal
d.vertical
Question7
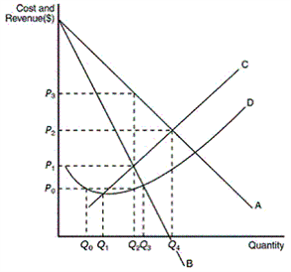
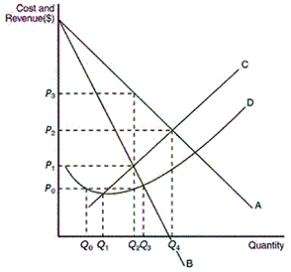
The figure below reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. How does one calculate the profit of a profit-maximizing monopoly?
Select one:
a.P2x Q4
b.P3x Q2
c.(P3- P0) x Q2
d.(P3- P1) x Q2
Question8
In what way does the profit-maximization problem for a monopolist differ from that of a competitive firm?
Select one:
a.A competitive firm maximizes profit at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; a monopolist maximizes profit at the point where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
b.A competitive firm maximizes profit at the point where average revenue equals marginal cost; a monopolist maximizes profit at a point where average revenue exceeds marginal cost.
c.For a competitive firm, marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output is equal to marginal revenue at all other levels of output; for a monopolist, marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output is smaller than it is for larger levels of output.
d.For a profit-maximizing competitive firm, thinking at the margin is much more important than it is for a profit-maximizing monopolist.
Question9
In comparison to the price a competitive firm charges, monopoly pricing has the effect of causing
Select one:
a.a higher level of output.
b.a higher price.
c.a larger consumer surplus.
d.smaller deadweight losses.
Question10
If a social planner were running a monopoly, that planner could achieve an efficient outcome by charging the price that is determined by
Select one:
a.the minimum point on the average-total-cost curve.
b.the minimum point on the average-variable-cost curve.
c.the intersection of the marginal-cost curve and the demand curve.
d.the intersection of the marginal-cost curve and the marginal-revenue curve.
Question11
In which of the following ways do patent and copyright laws benefit society?
Select one:
a.These laws help to keep prices down.
b.These laws help to prevent a single firm from acquiring ownership of a key resource.
c.These laws encourage creative activity.
d.These laws discourage excessive amounts of output of certain products.
Question12
Why do natural monopolies differ from other forms of monopoly?
Select one:
a.They are not subject to barriers to entry.
b.They are not regulated by government.
c.They generally don't make a profit.
d.They are generally not concerned about competition.
Question13
Which of the following statements represents a monopoly firm?
Select one:
a.A monopoly firm is a price taker and has no supply curve.
b.A monopoly firm is a price maker and has no supply curve.
c.A monopoly firm is a price taker and has a downward-sloping demand curve.
d.A monopoly firm is a price maker and has an upward-sloping supply curve.
Question14
How do monopoly firms exert their market power?
Select one:
a.by charging a price that is above average revenue
b.by charging a price that is below average total cost
c.by charging a price that is above marginal cost
d.by charging a price that is below marginal cost
Question15
Which of the following is a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist able to do?
Select one:
a.maximize profit, and produce a socially optimal level of output
b.maximize profit, but not produce a socially optimal level of output
c.produce a socially optimal level of output, but not maximize profit
d.produce a socially optimal level of output, and minimize the total cost
Question16
Consider the following: the profit-maximizing price charged for goods produced is $19. The intersection of the marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves occurs where output is 12 units and marginal cost is $9. Average total cost for 12 units of output is $7. What is the monopolist's profit under these conditions?
Select one:
a.$24
b.$80
c.$108
d.$144
Question17
Consider a profit-maximizing monopoly pricing under the following conditions: the profit-maximizing price charged for goods produced is $14; the intersection of the marginal-revenue and marginal-cost curves occurs where output is 10 units and marginal cost is $8; and the socially efficient level of production is 12 units. The demand curve and marginal-cost curves are linear. What is the deadweight loss?
Select one:
a.$4
b.$6
c.$12
d.$16
Question18
How do competitive firms and monopolists differ?
Select one:
a.A competitive firm cannot choose its level of output; a monopolist chooses its level of output.
b.A competitive firm's short-run profit is always zero; a monopolist can have a positive short-run profit.
c.A competitive firm's marginal-revenue curve is horizontal; a monopolist's marginal-revenue curve is downward sloping.
d.A competitive firm sets price equal to marginal cost; a monopolist sets price equal to marginal revenue.
Question19
Economists assume that monopolists behave as
Select one:
a.cost minimizers.
b.profit maximizers.
c.price maximizers.
d.output maximizers.
Question20
A monopoly firm can sell 200 units of output for $36.00 per unit. Alternatively, it can sell 201 units of output for $35.50 per unit. What is the marginal revenue of the 201st unit of output?
Select one:
a.-$35.50
b.-$64.50
c.$64.50
d.$35.50
Question21
What is the main social problem caused by monopoly?
Select one:
a.an inefficiently low quantity of output
b.an inefficiently high value of marginal cost
c.excessive monopoly profits
d.excessive producer surplus
Question22
What is generally the case for a monopolist's average revenue?
Select one:
a.It is equal to marginal revenue.
b.It is less than marginal revenue.
c.It is equal to the price of its product.
d.It is less than the price of its product.
Question23
Supply curves tell us how much producers are willing to supply at any given price. What type of supply curves will monopoly firms have?
Select one:
a.vertical supply curves
b.steeper supply curves than competitive firms
c.upward-sloping supply curves
d.no supply curves
Question24
Since natural monopolies have a declining average-cost curve, regulating natural monopolies by setting price equal to marginal cost would
Select one:
a.cause the monopolist to operate at a loss.
b.result in a less than optimal total surplus.
c.maximize producer surplus.
d.encourage research in order to recoup lost profits.
Question25
What can measure the economic inefficiency of a monopolist?
Select one:
a.the number of consumers who are unable to purchase the product because of its high price
b.the excess profit generated by monopoly firms
c.the loss of producer surplus by monopoly firms
d.the deadweight loss
Question26
If a monopolist sells 100 units at $8 per unit and realizes an average total cost of $5 per unit, what is the monopolist's profit?
Select one:
a.$200
b.$300
c.$600
d.$800
Question27
When does a natural monopoly arise?
Select one:
a.when there are constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output
b.when there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output
c.when one firm owns a key natural resource
d.when the government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce a particular good or service
Question28
When does a government-created monopoly arise?
Select one:
a.when government spending in a certain industry gives rise to monopoly power
b.when the government exercises its market control by encouraging competition among sellers
c.when the government gives a firm the exclusive right to sell some good or service
d.when the government imposes a sales tax so high that competitors are discouraged from entry
Question29
If a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a downward-sloping market demand curve, what do we know?
Select one:
a.Its average revenue is less than the price of the product.
b.Its average revenue equals marginal revenue.
c.Its marginal revenue equals total revenue.
d.Its marginal revenue is less than the price of the product.
Question30
Patent and copyright laws are major sources of
Select one:
a.natural monopolies.
b.government-created monopolies.
c.resource monopolies.
d.product monopolies.
Question 7:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


