Questions 29 through 39. Let me write the calculation
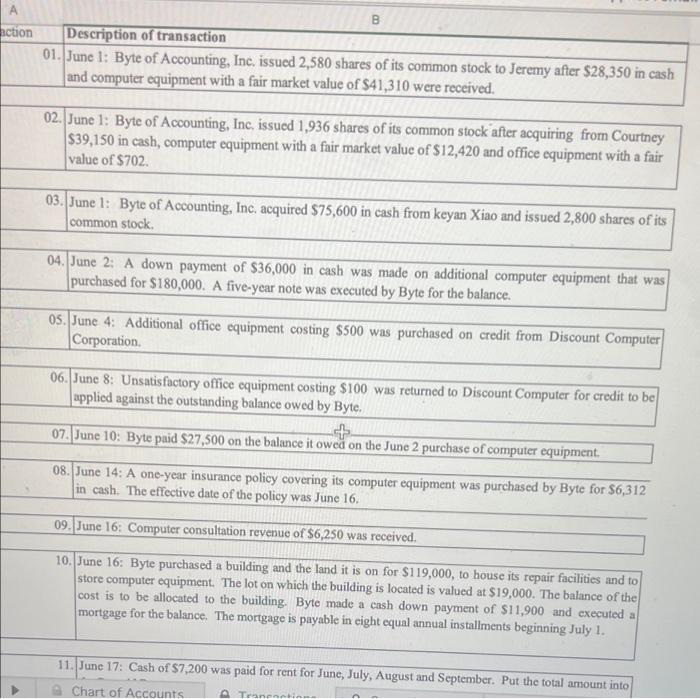
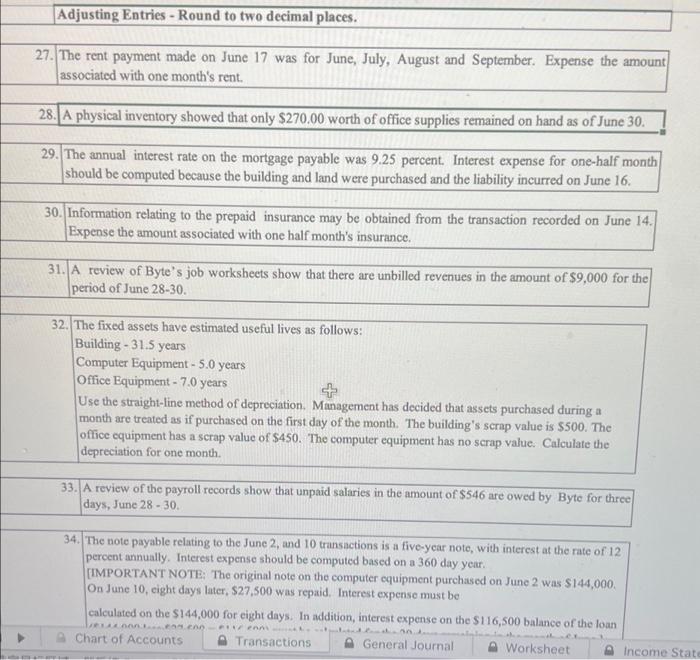
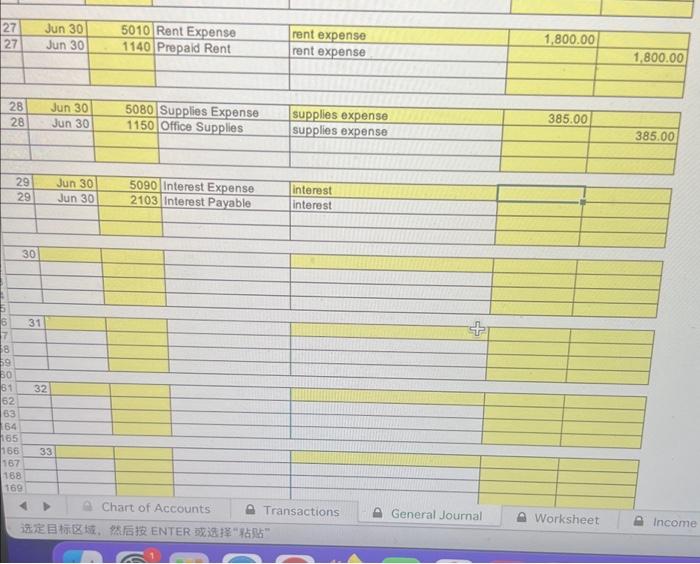
Chart of Accounts 11. June 17: Cash of \$7,200 was paid for rent for June, July, August and September. Put the total amount into the Prepaid Rent account. 12. June 17: Received a bill of $300 from the local newspaper for advertising. 13. June 21: Billed various miscellaneous local customers $4,200 for consulting services performed. 14. June 21: A fax machine for the office was purchased for $775cash. 15. June 21: Accounts payable in the amount of $400 were paid. 16. June 22: Paid the advertising bill that was received on June 17. 17. June 22: Received a bill for $1,190 from Computer Parts and Repair Co. for repairs to the computer equipment. 18. June 22: Paid salaries of $910 to equipment operators for the week ending June 18. 19. June 23: Cash in the amount of $3,365 was received on billings. 20. June 23: Purchased office supplies for $655 on credit. Record the purchase as an increase to the assets. 21. June 28: Billed $5,805 to miscellaneous customers for services performed to June 25 . 22. June 29: Cash in the amount of $5,500 was received for billings. 23. June 29: Paid the bill received on June 22, from Computer Parts and Repairs Co. 24. June 29: Paid salaries of $910 to equipment operators for the week ending June 25. 25. June 30: Received a bill for the amount of 5865 from O \& G Oil and Gas Co0 26. June 30: Paid a cash dividend of $0.20 per share to the three shareholders of Byte. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The number of shares of capital stock outstanding can be determined from the first three transactions.] Chart of Accounts Adjusting Entries - Round to two decimal places. 27. The rent payment made on June 17 was for June, July, August and September. Expense the amount associated with one month's rent. 28. A physical inventory showed that only $270.00 worth of office supplies remained on hand as of June 30 . 29. The annual interest rate on the mortgage payable was 9.25 percent. Interest expense for one-half month should be computed because the building and land were purchased and the liability incurred on June 16. 30. Information relating to the prepaid insurance may be obtained from the transaction recorded on June 14. Expense the amount associated with one half month's insurance. 31. A review of Byte's job worksheets show that there are unbilled revenues in the amount of $9,000 for the period of June 28-30. 32. The fixed assets have estimated useful lives as follows: Building - 31.5 years Computer Equipment 5.0 years Office Equipment - 7.0 years Use the straight-line method of depreciation. Management has decided that assets purchased during a month are treated as if purchased on the first day of the month. The building's scrap value is $500. The office cquipment has a scrap value of $450. The computer equipment has no scrap value. Calculate the depreciation for one month. 33. A review of the payroll records show that unpaid salaries in the amount of $546 are owed by Byte for three days, June 2830 34. The note payable relating to the Junc 2 , and 10 transactions is a five-ycar note, with interest at the rate of 12 percent annually. Interest expense should be computed based on a 360 day year. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The original note on the computer equipment purchased on June 2 was $144,000. On June 10, eight days later, $27,500 was repaid. Interest expense must be calculated on the $144,000 for eight days. In addition, interest expense on the $116,500 balance of the loan Chart of Accounts - Transactions General Journal 34. The note payable relating to the June 2 , and 10 transactions is a five-year note, with interest at the rate of 12 percent annually. Interest expense should be computed based on a 360 day year. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The original note on the computer equipment purchased on June 2 was $144,000. On June 10 , eight days later, $27,500 was repaid. Interest expense must be calculated on the $144,000 for eight days. In addition, interest expense on the $116,500 balance of the loan ($144,000 less $27,500=$116,500) must be calculated for the 20 days remaining in the month of June.] \begin{tabular}{|l|r|r|l|l|l|} \hline 29 & Jun 30 & 5090 & Interest Expense & interest & \\ \hline 29 & Jun 30 & 2103 & Interest Payable & interest & \\ \hline & & & & \\ \hline & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} 33. 4 Chart of Accounits: Transactions Chart of Accounts 11. June 17: Cash of \$7,200 was paid for rent for June, July, August and September. Put the total amount into the Prepaid Rent account. 12. June 17: Received a bill of $300 from the local newspaper for advertising. 13. June 21: Billed various miscellaneous local customers $4,200 for consulting services performed. 14. June 21: A fax machine for the office was purchased for $775cash. 15. June 21: Accounts payable in the amount of $400 were paid. 16. June 22: Paid the advertising bill that was received on June 17. 17. June 22: Received a bill for $1,190 from Computer Parts and Repair Co. for repairs to the computer equipment. 18. June 22: Paid salaries of $910 to equipment operators for the week ending June 18. 19. June 23: Cash in the amount of $3,365 was received on billings. 20. June 23: Purchased office supplies for $655 on credit. Record the purchase as an increase to the assets. 21. June 28: Billed $5,805 to miscellaneous customers for services performed to June 25 . 22. June 29: Cash in the amount of $5,500 was received for billings. 23. June 29: Paid the bill received on June 22, from Computer Parts and Repairs Co. 24. June 29: Paid salaries of $910 to equipment operators for the week ending June 25. 25. June 30: Received a bill for the amount of 5865 from O \& G Oil and Gas Co0 26. June 30: Paid a cash dividend of $0.20 per share to the three shareholders of Byte. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The number of shares of capital stock outstanding can be determined from the first three transactions.] Chart of Accounts Adjusting Entries - Round to two decimal places. 27. The rent payment made on June 17 was for June, July, August and September. Expense the amount associated with one month's rent. 28. A physical inventory showed that only $270.00 worth of office supplies remained on hand as of June 30 . 29. The annual interest rate on the mortgage payable was 9.25 percent. Interest expense for one-half month should be computed because the building and land were purchased and the liability incurred on June 16. 30. Information relating to the prepaid insurance may be obtained from the transaction recorded on June 14. Expense the amount associated with one half month's insurance. 31. A review of Byte's job worksheets show that there are unbilled revenues in the amount of $9,000 for the period of June 28-30. 32. The fixed assets have estimated useful lives as follows: Building - 31.5 years Computer Equipment 5.0 years Office Equipment - 7.0 years Use the straight-line method of depreciation. Management has decided that assets purchased during a month are treated as if purchased on the first day of the month. The building's scrap value is $500. The office cquipment has a scrap value of $450. The computer equipment has no scrap value. Calculate the depreciation for one month. 33. A review of the payroll records show that unpaid salaries in the amount of $546 are owed by Byte for three days, June 2830 34. The note payable relating to the Junc 2 , and 10 transactions is a five-ycar note, with interest at the rate of 12 percent annually. Interest expense should be computed based on a 360 day year. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The original note on the computer equipment purchased on June 2 was $144,000. On June 10, eight days later, $27,500 was repaid. Interest expense must be calculated on the $144,000 for eight days. In addition, interest expense on the $116,500 balance of the loan Chart of Accounts - Transactions General Journal 34. The note payable relating to the June 2 , and 10 transactions is a five-year note, with interest at the rate of 12 percent annually. Interest expense should be computed based on a 360 day year. [IMPORTANT NOTE: The original note on the computer equipment purchased on June 2 was $144,000. On June 10 , eight days later, $27,500 was repaid. Interest expense must be calculated on the $144,000 for eight days. In addition, interest expense on the $116,500 balance of the loan ($144,000 less $27,500=$116,500) must be calculated for the 20 days remaining in the month of June.] \begin{tabular}{|l|r|r|l|l|l|} \hline 29 & Jun 30 & 5090 & Interest Expense & interest & \\ \hline 29 & Jun 30 & 2103 & Interest Payable & interest & \\ \hline & & & & \\ \hline & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} 33. 4 Chart of Accounits: Transactions