Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
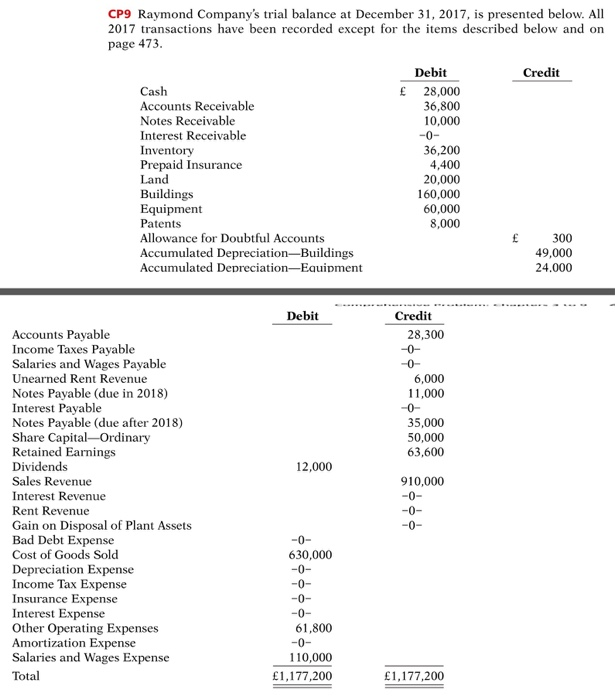
Questions: (a) Without narrations, or cross references, prepare journal entries for events 1 - 14 in the text, but incorporate the following: i. For event
Questions:
(a) Without narrations, or cross references, prepare journal entries for events 1 - 14 in the text, but incorporate the following:
i. For event #1, assume that the "sales taxes" consist of non-refundable import taxes.
ii. For event #8, assume that the company has decided to switch to the declining balance method using a rate of 30%.
iii. For event 10, you may credit Patents. (Note that events 4-14 are AJEs.)
(b) In addition to events 1 -14 above, prepare journal entries for events 15 and 16 below. Note that these new accounts were created for the general ledger: Inventory Write-down Loss; OCI Gain/Loss on Revaluation, Land; OCI Gain/Loss on Revaluation, Building; Gain/Loss on Revaluation, Land; Gain/Loss on Revaluation, Building, and Revaluation Reserve.
15) The Revaluation Model was adopted for the Land, which was re-valued to $30,000, and for the Building, which was revalued to $100,000.
16) The $36,200 of Merchandise Inventory includes several classes of merchandise. One of these classes, with a cost of $12,000, has suffered a loss in market value such that its net realizable value is now estimated at $10,000. This "class" was not part of the inventory sold in event #3.
(c) A Statement of Comprehensive Income for the year, in the form and format prescribed in this course. Even though a GL is not required, make sure that all of your balances are updated prior to preparing your financial statements.
(d) A Balance Sheet as at 31 December 2017, also in the form and format prescribed in this course. Even though closing entries are not required, assume that they were journalised and posted so that the general ledger balances are correct for the Balance Sheet.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


