Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
QUESTIONS: NOTE: Before you answer the questions below read the treasury policies reading file available on the blackboard 1. Comment on the firm's loan maturity

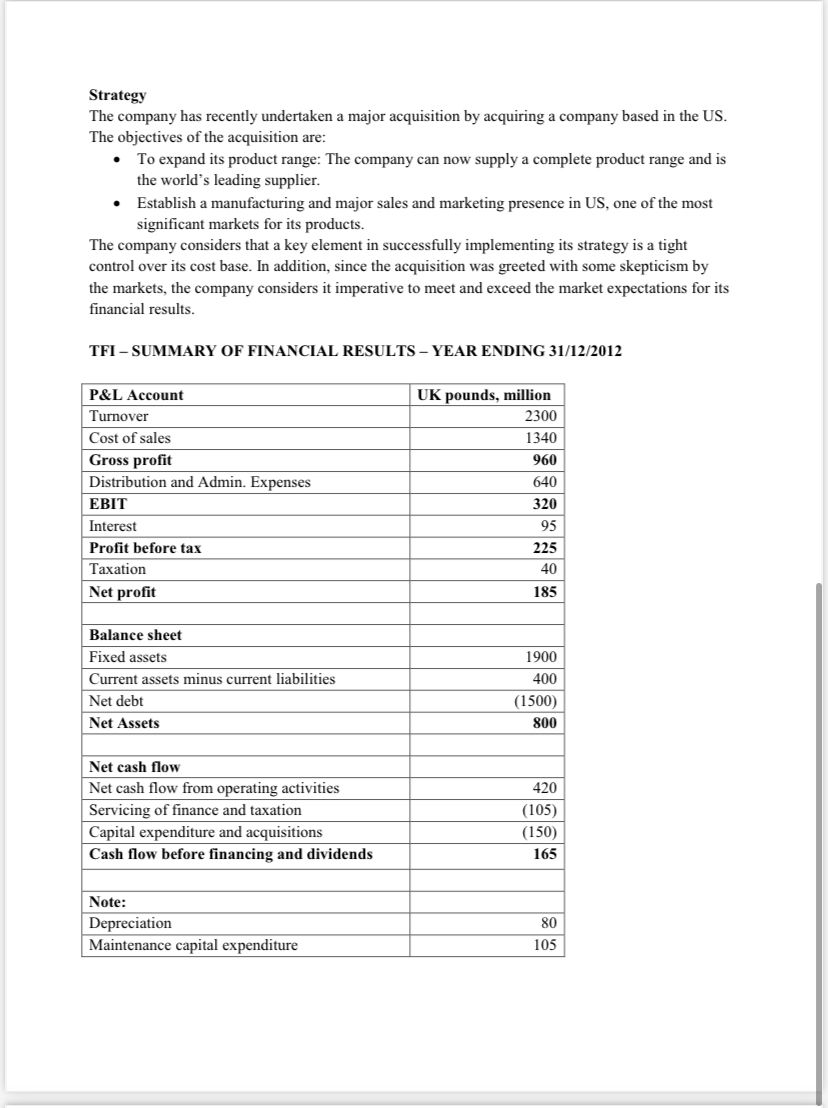
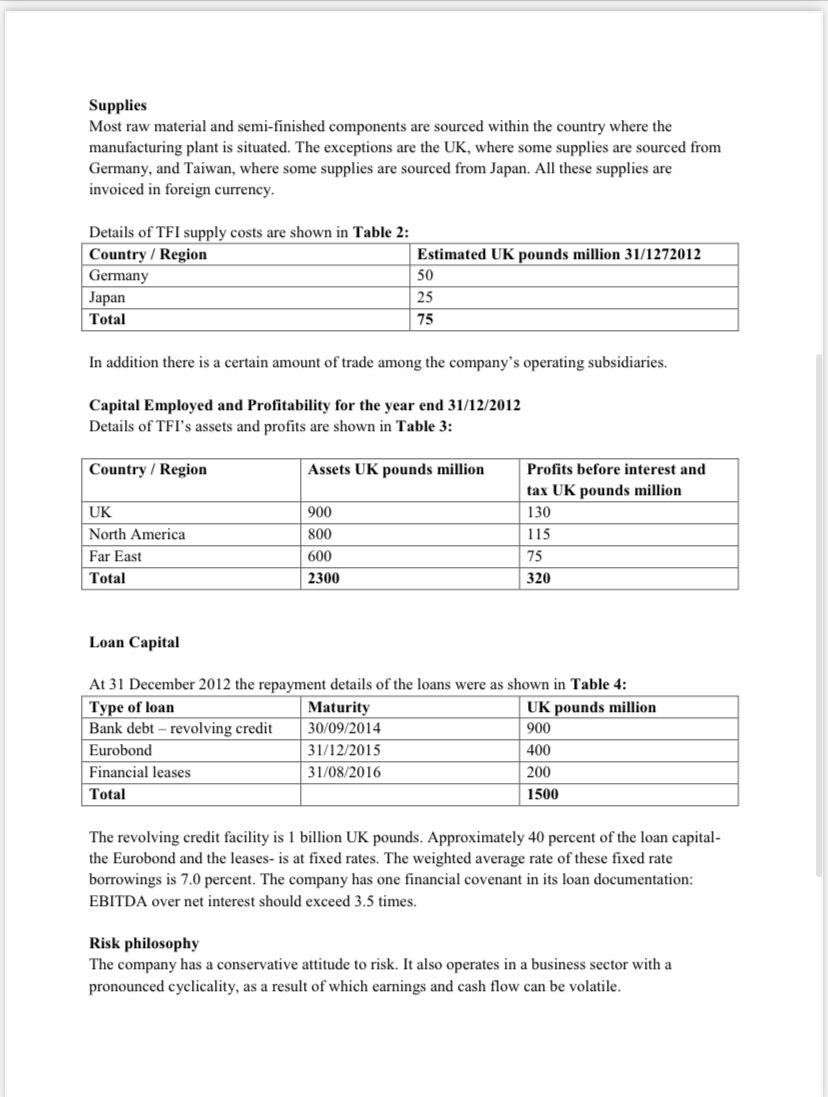
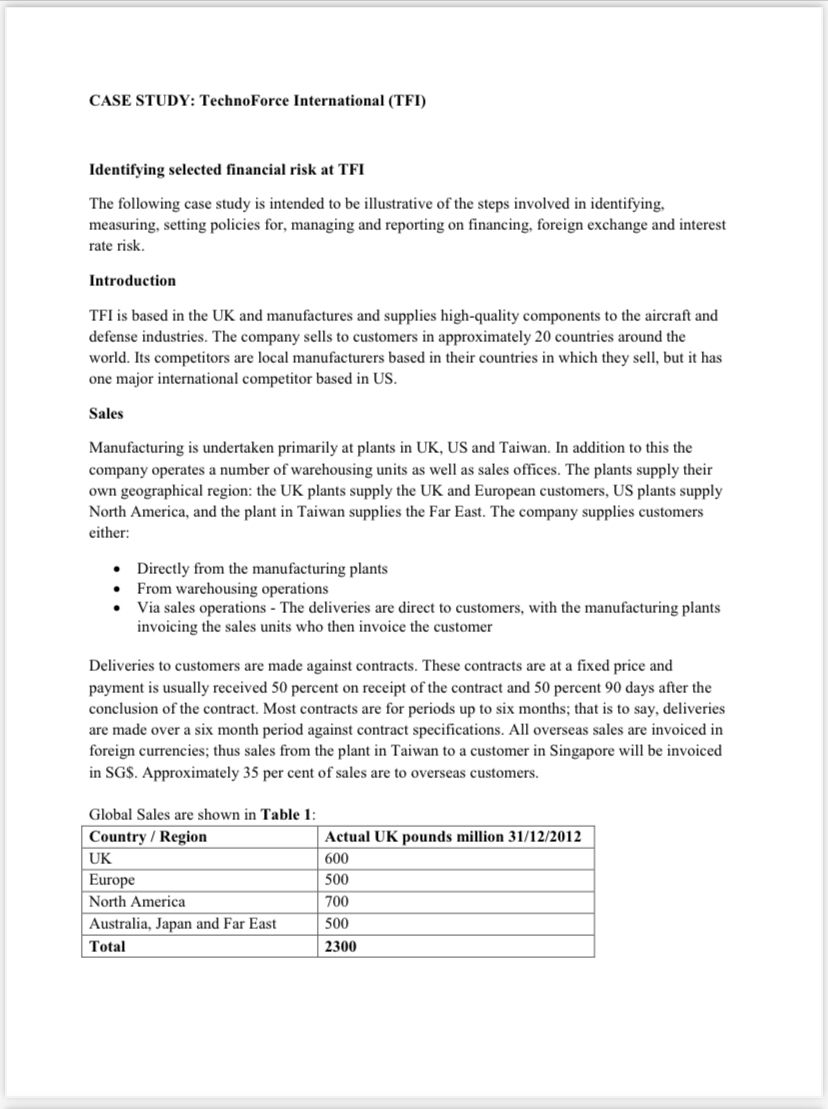
QUESTIONS: NOTE: Before you answer the questions below read the "treasury policies reading" file available on the blackboard 1. Comment on the firm's loan maturity profile. Is it safe? 2. Check the debt markets the company borrows from. Calculate the head room. Is it sufficient? Comment. 3. What are the loan covenant(s) for the firm? Does it satisfy them? What are your estimations for the future performance of the firm with respect to this criterion? 4. Based on your findings from the above questions provide a summary and conclusions on the company's financing risk and the interest rate risk 5. Measure the transaction exposure of the firm and comment on the results. How the firm can reduce exposure to transaction risk. Explain 6. Explain what is the Pre transaction risk and translation risk of the firm and suggest ways to reduce the risk exposure of the firm. Strategy The company has recently undertaken a major acquisition by acquiring a company based in the US. The objectives of the acquisition are: - To expand its product range: The company can now supply a complete product range and is the world's leading supplier. - Establish a manufacturing and major sales and marketing presence in US, one of the most significant markets for its products. The company considers that a key element in successfully implementing its strategy is a tight control over its cost base. In addition, since the acquisition was greeted with some skepticism by the markets, the company considers it imperative to meet and exceed the market expectations for its financial results. TFI - SUMMARY OF FINANCIAL RESULTS - YEAR ENDING 31/12/2012 Supplies Most raw material and semi-finished components are sourced within the country where the manufacturing plant is situated. The exceptions are the UK, where some supplies are sourced from Germany, and Taiwan, where some supplies are sourced from Japan. All these supplies are invoiced in foreign currency. Details of TFI supply costs are shown in Table 2 : In addition there is a certain amount of trade among the company's operating subsidiaries. Capital Employed and Profitability for the year end 31/12/2012 Details of TFI's assets and profits are shown in Table 3: Loan Capital At 31 December 2012 the repayment details of the loans were as shown in Table 4: The revolving credit facility is 1 billion UK pounds. Approximately 40 percent of the loan capitalthe Eurobond and the leases- is at fixed rates. The weighted average rate of these fixed rate borrowings is 7.0 percent. The company has one financial covenant in its loan documentation: EBITDA over net interest should exceed 3.5 times. Risk philosophy The company has a conservative attitude to risk. It also operates in a business sector with a pronounced cyclicality, as a result of which earnings and cash flow can be volatile. CASE STUDY: TechnoForce International (TFI) Identifying selected financial risk at TFI The following case study is intended to be illustrative of the steps involved in identifying, measuring, setting policies for, managing and reporting on financing, foreign exchange and interest rate risk. Introduction TFI is based in the UK and manufactures and supplies high-quality components to the aircraft and defense industries. The company sells to customers in approximately 20 countries around the world. Its competitors are local manufacturers based in their countries in which they sell, but it has one major international competitor based in US. Sales Manufacturing is undertaken primarily at plants in UK, US and Taiwan. In addition to this the company operates a number of warehousing units as well as sales offices. The plants supply their own geographical region: the UK plants supply the UK and European customers, US plants supply North America, and the plant in Taiwan supplies the Far East. The company supplies customers either: - Directly from the manufacturing plants - From warehousing operations - Via sales operations - The deliveries are direct to customers, with the manufacturing plants invoicing the sales units who then invoice the customer Deliveries to customers are made against contracts. These contracts are at a fixed price and payment is usually received 50 percent on receipt of the contract and 50 percent 90 days after the conclusion of the contract. Most contracts are for periods up to six months; that is to say, deliveries are made over a six month period against contract specifications. All overseas sales are invoiced in foreign currencies; thus sales from the plant in Taiwan to a customer in Singapore will be invoiced in SG\$. Approximately 35 per cent of sales are to overseas customers. Global Sales are shown in Table 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


