
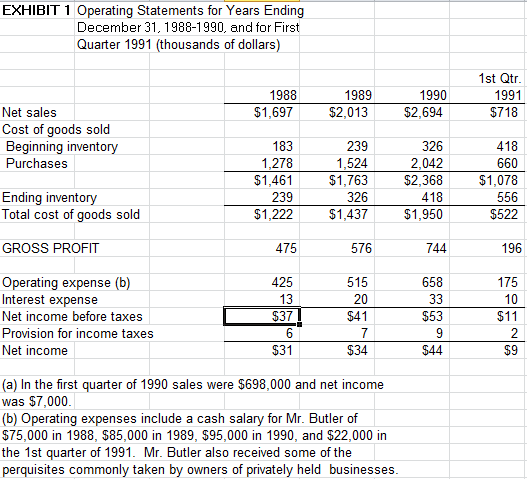
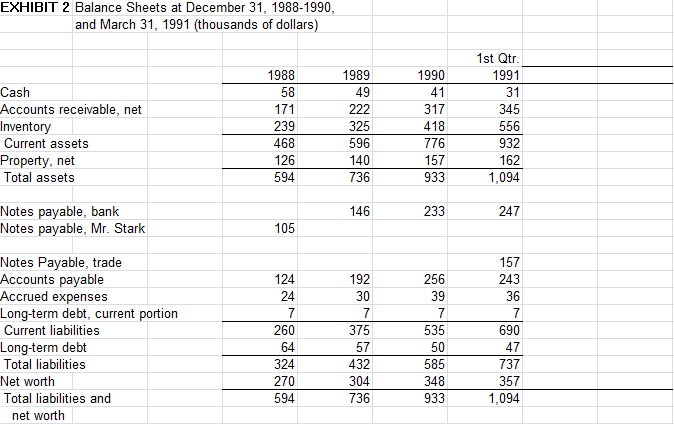
Questions to consider with your groups: You are advisingMr. Butler 1. Why does Mr. Butler have to borrow so much monay to support this profitable businass? Towards assessing Butler's financial health and performance, calculate common financial ratios as3essing the firm's profitability, assat efficiency (espacially working capital), leverage and liquidity. Your text for Business Finance should have a chapter covering thase ratios and your Introductory Accounting text should also have a chapter on financial ratios. You are given, for the years, 1988-1990, and first quarter, 1991, balance shaats and income statemants (operating statemants) for Butler Lumber Co. From thase stataments, produce aCash Flow statement for 1989, 1990 and for first quarter, 1991 What are you able to conclude about Mr. Butler's business? a b. c. 2. Much of Butler's incresad nead for funds has been due to increased levels of Invantory and Accounts Racaivabla. Considering theperiod from end of 1988 to and of 1990, how much of tha increase in Invantories has ben due to siower inentor turms (or, eguaienty longer das yf inventory on hand versus that due to sales growth. Similarly, how much of the increase in Accounts Receivable has ben due to a longer collection period versus that due to sales growth. 3. Do vou agre with Butler's estimate of the company's loan requiremant? How much will he nead in 1991 to finance his expactad expansion in sales? Towards address this quastion, build a pro-forma income statament and balance shaet for 1991 year end. a Assume Butler's 1991 Sales grow to $3.6 million. ii. i. Unlass you have evidance to the contrary, assume that expanse category ratios to sales are the same a in 1990 iii. Intarast expanse should be estimated as a function of the amount of DEBT the company ends up with on the balance shaat. Start out with a guess of $40K for intarest expen32. iv. The net income from 1991 will directly increment the book value of equity from 1990 to 1991 year and (there are no dividands, no rpurchases of stock and no stoc issues in 1991) v. Assume Cash by the and of 1991 is incresad to $60K vi. Forecast AR. Inventory, AP, Accoed Expenses using either %'s of sales or the working capital ratios you got fom #1 above. vii. Assume property, net, will increase to $179K viii. Long term debt will go down by $TK. ix. Back into the New Bank Loan siz2 given the rest of the balance information x. Recalculate interest expanse now, given the loan size youjust calculatad. xi. Iterate. 4. Suppose he can gat the discussed loan from Northrop National Bank. Should he take it? EXHIBIT 1 Operating Statements for Years Ending December 31, 1988-1990, and for First Quarter 1991 (thousands of dollars 1988 $1,697 1989 $2,013 1990 $2,694 1st Qtr 1991 $718 Net sales Cost of goods sold Beginning inventory Purchases 183 1,278 $1,461 239 $1,222 239 1,524 $1,763 326 $1,437 326 2,042 $2,368 418 $1,950 660 $1,078 556 $522 Ending inventory Total cost of goods sold 576 744 658 $53 $44 GROSS PROFIT 475 196 Operating expense (b) Interest expense Net income before taxes Provision for income taxes Net income 425 13 $37 515 20 $41 175 10 $11 $31 $34 $9 (a) In the first quarter of 1990 sales were $698,000 and net income was $7,000 (b) Operating expenses include a cash salary for Mr. Butler of $75,000 in 1988, $85,000 in 1989, $95,000 in 1990, and $22,000 in the 1st quarter of 1991. Mr. Butler also received some of the perquisites commonly taken by owners of privately held businesses EXHIBIT 2 Balance Sheets at December 31, 1988-1990 and March 31, 1991 (thousands of dollars) 1st Qtr 1991 31 345 556 932 162 1,094 1989 49 1990 1988 58 Cash Accounts receivable, net nventory Current assets Property, net lotal assets 239 468 126 594 325 596 140 736 317 418 776 157 933 146 Notes payable, bank Notes payable, Mr. Stark 233 247 105 157 243 36 Notes Payable, trade Accounts pavable Accrued expenses Long-term debt, current portion Current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabliies Net worth Total liabilities and 124 24 192 30 256 39 260 64 324 270 594 375 57 432 304 736 535 50 585 348 933 690 47 737 357 1,094 net worth









