Question
Ratios from Comparative and Common-Size Data Consider the following financial statements for Waverly Company. During 2013, management obtained additional bond financing to enlarge its production
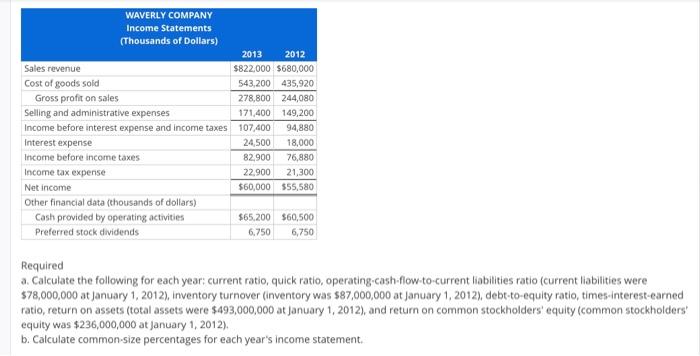
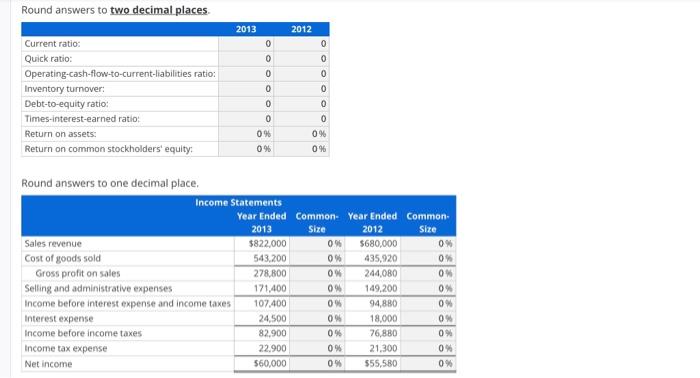
Ratios from Comparative and Common-Size Data Consider the following financial statements for Waverly Company. During 2013, management obtained additional bond financing to enlarge its production facilities. The company faced higher production costs during the year for such things as fuel, materials, and freight. Because of temporary government price controls, a planned price increase on products was delayed several months. As a holder of both common and preferred stock, you decide to analyze the financial statements: WAVERLY COMPANY Assets Balance Sheets (Thousands of Dollars) Dec. 31, 2013 Dec. 31, 2012 Cash and cash equivalents $20,000 $14,000 Accounts receivable (net) 57,000 45,000 Inventory 122,000 107,000 Prepaid expenses 20,000 14,000 Plant and other assets (net) 471,000 411,000 Total Assets $690,000 $591,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities $92,000 $84,000 10% Bonds payable 227,000 162,000 9% Preferred stock, $50 Par Value 77,000 77,000 Common stock, $10 Par Value 200,000 200,000 Retained earnings 94,000 68,000 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $690,000 $591,000 WAVERLY COMPANY Income Statements (Thousands of Dollars) Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Gross profit on sales Selling and administrative expenses Income before interest expense and income taxes Interest expense Income before income taxes 2013 2012 $822,000 $680,000 543,200 435,920 278,800 244,080 171,400 149,200 107,400 94,880 24,500 18,000 82,900 76,880 Income tax expense 22,900 21,300 Net income $60,000 $55,580 Other financial data (thousands of dollars) Cash provided by operating activities Preferred stock dividends $65,200 $60,500 6,750 6,750 Required a. Calculate the following for each year: current ratio, quick ratio, operating-cash-flow-to-current liabilities ratio (current liabilities were $78,000,000 at January 1, 2012), inventory turnover (inventory was $87,000,000 at January 1, 2012), debt-to-equity ratio, times-interest-earned ratio, return on assets (total assets were $493,000,000 at January 1, 2012), and return on common stockholders' equity (common stockholders' equity was $236,000,000 at January 1, 2012). b. Calculate common-size percentages for each year's income statement. Round answers to two decimal places. 2013 2012 Current ratio: 0 Quick ratio: Operating-cash-flow-to-current-liabilities ratio: 0 0 0 0 Inventory turnover: 0 Debt-to-equity ratio: 0 0 Times-interest-earned ratio: 0 0 Return on assets: 0% 0% Return on common stockholders' equity: 0% 0% Round answers to one decimal place. Income Statements Year Ended Common- Year Ended Common- Sales revenue 2013 $822,000 Size 2012 Size 0% $680,000 0% Cost of goods sold 543,200 0% 435,920 0% Gross profit on sales 278,800 0% 244,080 0% Selling and administrative expenses 171,400 0% 149,200 0% Income before interest expense and income taxes 107,400 0% 94,880 0% Interest expense 24,500 0% 18,000. 0% Income before income taxes 82,900 0% 76,880 0% Income tax expense 22,900 0% 21.300 0% Net income $60,000 0% $55,580 0%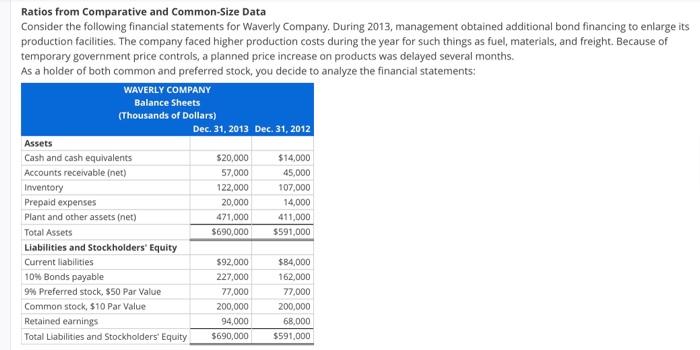
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


