A differential amplifier circuit is used to generate an amplitude modulated (AM) signal. The modulation signal is a 100 Hz sine wave with zero

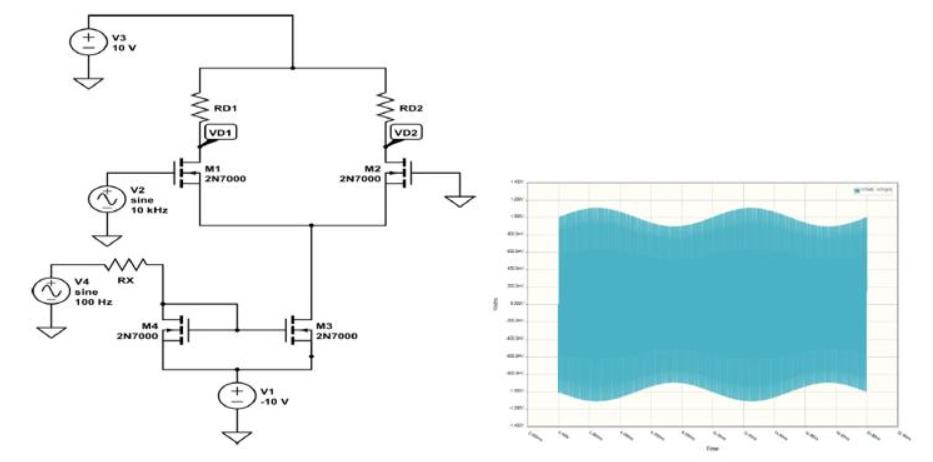
A differential amplifier circuit is used to generate an amplitude modulated (AM) signal. The modulation signal is a 100 Hz sine wave with zero mean, and the amplitude of this signal cannot be larger than 5 V peak. The output voltage amplitude can only vary between 0.9 V and 1.1 V, while having minimal (ideally zero) D.C. shift. 1. Assuming the 10 kHz carrier has a 25 mVpk amplitude, generate a differential-mode gain of 40 V/V (which is a specific depth of modulation on the carrier), or an output amplitude of 1 Vpk at the carrier frequency, before modulation is applied to the circuit. Use the differential output v = vc1-vc2. This can be done by modifying resistor values. V3 $. 10 V $ V4 sine 100 Hz V2 sine 10 kHz RX M4 2N7000 VD1 M1 2N7000 V1 $. -10 V ww M2 2N7000 M3 2N7000 RD2 VD2 ww C
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To achieve a differentialmode gain of 40 VV and an outp...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


