Question: Read the Google Chaptercase at the end of Chapter 11, and then answer the following three questions in an initial post to express your original,
Read the Google Chaptercase at the end of Chapter 11, and then answer the following three questions in an initial post to express your original, relevant analyses and observations from the case:
Why did Google restructure itself and create Alphabet? What is it hoping to accomplish? For additional in-sights, see Larry Pages post announcing the restructuring at https://abc.xyz/.
Do you think the reorganization is beneficial for Alphabets moon shots, now housed in their own business unit with profit-and-loss responsibility? Why, or why not? Explain.
Why has Google failed to develop other profitable businesses? Is Googles strategy process of planned emergence to blame? Why or why not? Will Alphabets new structure with independent SBUs enable the company to innovate more and to find the next highly profitable business beyond online search and advertising?
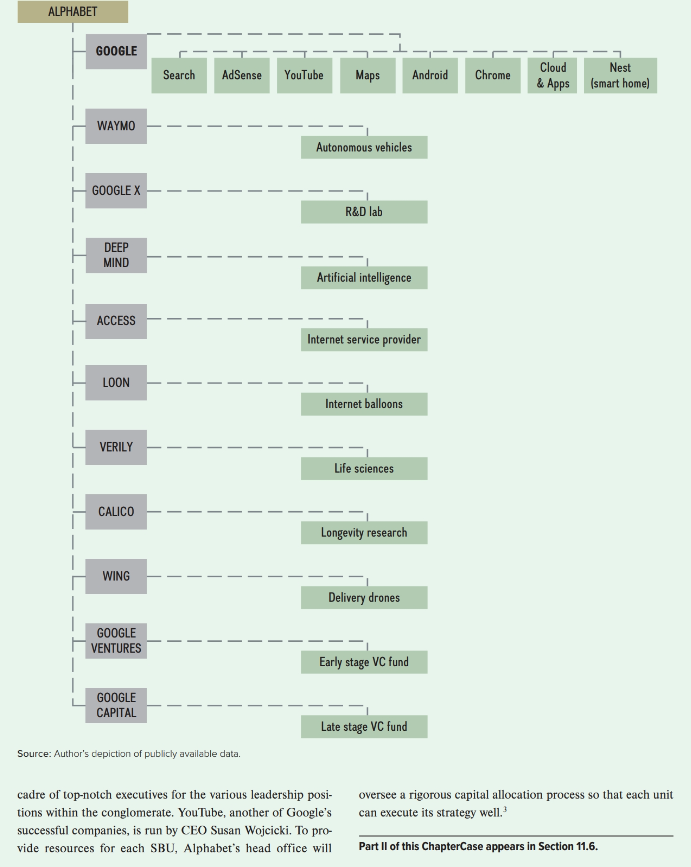

"A" Is for Alphabet and "6" IS Google X (R\&D lab), Deep Mind (artificial intelligence), for Google Access (internet service provider), Loon (internet balloons), Calico (longevity research), Wing (delivery drones), Google Ventures (early-stage VC fund), and "GOOGLE IS NOT A conventional company. We do not inGoogle Capital (late-stage VC fund). (See Exhibit 11.1.) tend to become one, H1 wrote founders Larry Page and Sergey _ This sweeping restructuring allowed the company to sepBrin in 2004 for the company's initial public offering (IPO). arate its highly profitable search and advertising business These computer science graduate students turned entreprefrom its moon shots, for example, wireless internet connecneurs, best known for cretivity via high-altitude balating the world's most loons and contact lenses successful online search that double as a computer engine, also indicated monitor, providing realtime information to the they would make "smaller wearer. Furthermore, it bets in areas that might seem very speculative or created greater financial even strange when compared to our current businesses." 2 Some of these smaller bets seemed transparency and accountability. Perhaps the most notable outcome of Google's restructuring is crazy at the time, but resulted in Google Maps, its pursuit of business opYouTube, Chrome, and portunities that went far Android-all of which Pawel Kopczynski/Reuters beyond Google's roots in have more than 1 billion users today. To say that Google has online search-opportunities potentially worth billions of been hugely successful is an understatement. Since listing on dollars. In his letter to shareholders announcing the restructhe stock market, this online search and advertising company turing, Larry Page stated that the new structure would premanaged to outperform the tech-heavy NASDAQ-100 index vent Alphabet from becoming complacent and encourage by more than 1,700 percentage points. And in 2019, Google the firm to take a long-term view in pursuing ambitious albeit reached a market cap of more than $850 billion, becoming uncertain projects. One of Page's major goals was to one of the three most valuable companies globally, along ensure that Google would continue to pursue radical innovawith Microsoft and Apple. tion, rather than to remain satisfied with incremental innovaGoogle proved it was not a conventional company as is common among other incumbent firms. In again when it split itself into keeping with this goal, Alphabet spent over $21 billion in rebusiness une search and development (R\&D) in 2018, second only to the business units (SBUs in 2015). As Google's structure $23 billion that Amazon spent. grew increasingly complex and its number of business Alphabet's CEO is Larry Page and its president is Serlines grew increasingly unrelated (think online search gey Brin. Alphabet's core business unit, Google, is led by and longevity research), it felt the need to transition from CEO Sundar Pichai. Although slimmer and more focused, a functional structure to a multidivisional structure. It thus Google continues to generate 99 percent of Alphabet's revformed Alphabet, a new corporate entity, to act as the enues, garnering \$140 billion in 2019. Currently, Google's parent company in charge of overseeing these varied business lines include online search and advertising, YouSBUs, each of which had its own CEO and profit-and- Tube, maps, Android, Chrome, cloud and apps services, loss responsibilities. Page said he modeled Alphabet's and the reintegrated Nest, a smart-home company. new organizational structure after that of Berkshire Ha- Alphabet houses a number of SBUs that are run by inthaway, a conglomerate led by Warren Buffett. Page had dependent CEOs. Besides creating financial transparency long admired Buffet for effectively managing a set of un- and accountability for each SBU, this new organizational related businesses. Alphabet's business units, in addition structure also allows Alphabet to retain and develop a to Google, included Waymo (autonomous vehicles). cadre of top-notch executives for the various leadership posi- oversee a rigorous capital allocation process so that each unit tions within the conglomerate. YouTube, another of Google's can execute its strategy well. 3 successful companies, is run by CEO Susan Wojcicki. To provide resources for each SBU, Alphabet's head office will Part II of this ChapterCase appears in Section 11.6. AS OF 2019, Alphabet remains a one-trick pony, with Facebook's more than 1 billion Google's online search and advertising business bringing in users worldwide at the time. basically all the profits ( 99 percent). Yet, competition in the Why did Google fumble its online advertising space is heating up because Facebook has lead over Facebook? Google become a viable alternative to Google, and it's growing fast. had a huge opportunity to become the leader in social networkIn addition, Amazon-a newcomer to the digital ad space-is ing because Myspace imploded after it was acquired by News making strong inroads. Alphabet's profit sanctuary may be Corp. Despite initial support, Google's top executives felt that under threat. With its new organizational structure, Alphabet social networking did not fit its vision to organize the world's inforCEO Larry Page hopes for more radical innovation that will mation and make it universally accessible and useful. Google relied turn into highly profitable businesses like Google. on highly complex and proprietary algorithms to organize the Before its reorganization from a functional to M-form knowledge available on the internet and serve up targeted search structure, implemented to manage a set of unrelated busi- ads. Social networking software, in comparison, is fairly pedesnesses, Google had developed many of its most well-known trian. Additionally, Page and Brin, both exceptional computer products and services through planned emergence, wherein scientists, looked down on social networking. They felt their Pagethe impetus for strategic initiatives emerges from the bottom Rank algorithm that accounts for hundreds of variables and conup through autonomous actions by lower-level employ- siders all available websites was far superior in providing objective ees. Google organized the work of its engineers according to recommendations to users' search queries than subjective ena 70-20-10 rule. The majority of the engineers' time (70 per- dorsements by someone's online friends. As a consequence, they cent) focused on its main business-search and ads. One day snubbed social networking. Moreover, given the many different a week ( 20 percent) was spent developing ideas of their own projects Google was pursuing at that time, Orkut was ranked as a choosing, and the remainder ( 10 percent) on total wild cards low priority by Google's top executives. Starved of further resuch as Project Loon, an envisioned network of high-altitude sources, the social networking site withered and was eventually balloons that travel on the edge of space to provide wireless shut down in 2014, making Facebook the undisputed leader. internet services to the two-thirds of the world's population In yet another effort to catch up with Facebook, Google that do not yet have internet access-primarily those in rural launched Google Plus in 2011. This social networking site inteand remote areas. (Loon is now a standalone unit in the new grated all of Google's services-Gmail, YouTube, Chrome, and Alphabet structure.) Google has reported that half of its new others-into one user interface. It required users to sign into its products came from the 20 percent rule, including Gmail, portal, even if they were using just one Google product. After a Google Maps, Google News, Orkut, and AdSense. AdSense data breach, Google Plus was shut down unceremoniously in started as an experiment by two Google engineers: They at- 2019. Meanwhile, Facebook has over 2 billion active users on tempted to match Gmail content with targeted ads based on its platform-and Google is unable to access any of the inforthat content. Today, AdSense enables creators of content mation tied to these users. Not being able to access Facebook sites in its network, such as Google bloggers, to serve online users' activities limits Google's ability to serve targeted ads, ads that are targeted to the site's content. which, in turn, cuts directly into its main line of business. 86 Although Google has a stellar track record for strategy pro- Questions cess as planned emergence, it has fumbled its social networking endeavors multiple times. These missteps left the space open to 1. Why did Google restructure itself and create Alphabet? Facebook, now Google's fiercest competitor in the digital ad What is it hoping to accomplish? For additional inspace. Google's first attempt in social networking goes back to sights, see Larry Page's post announcing the restructur2002, two years (eons in internet time) before Facebook was ing at https://abc.xyz/. founded. Google engineer Orkut Buyukkokten had developed a 2. Do you think the reorganization is beneficial for Alphabet's social network, called Orkut, using his 20 percent discretionary moon shots, now housed in their own business unit with time. Marissa Mayer, then Google's vice president in charge of profit-and-loss responsibility? Why, or why not? Explain. the project, liked what she saw and provided initial support. 3. Why has Google "failed" to develop other profitable More engineers were eventually added to further Orkut's develbusinesses? Is Google's strategy process of planned opment. Google was astonished at Orkut's early success: emergence to blame? Why or why not? Will Alphabet's Within the first month after its release, hundreds of thousands new structure with independent SBUs enable the comof people signed up. By 2014, Orkut had 30 million users pany to innovate more and to find the next highly profmostly in Brazil and India. But this paled in comparison to itable business beyond online search and advertising
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


