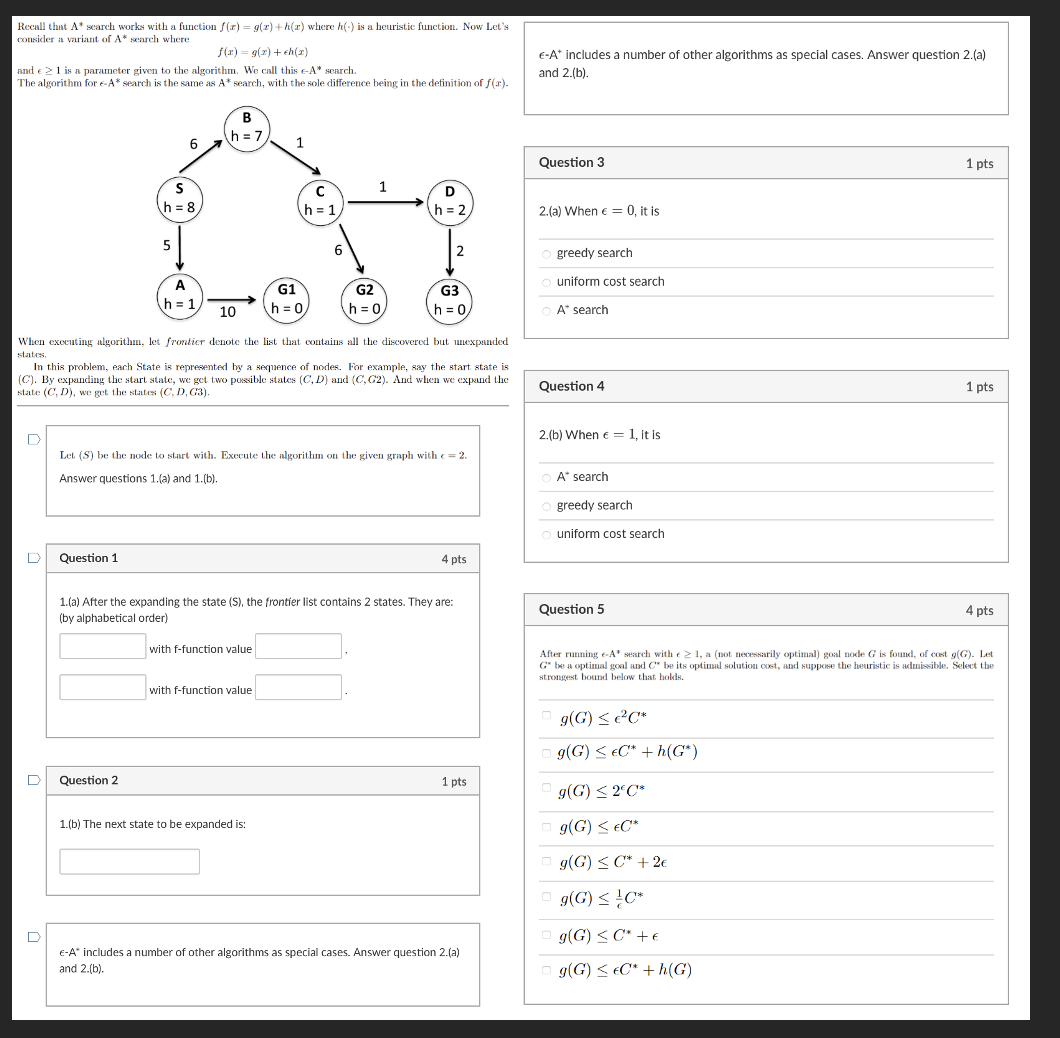
Question: Recall that * * scarch works with a function f ( x ) = g ( x ) + h ( x ) where h
Recall that scarch works with a function where is a heuristic function. Now Let's
consider a variant of search where
and is a parameter given to the algorithm. We call this search.
The algorithm for search is the same as search, with the sole difference being in the definition of
When executing algorithm, let frontier denote the list that contains all the discovered but unexpunded
states,
In this problem, each State is represented by a sexpuence of nodes. For example, say the start state is
By expending the start state, we get two porsible states and And when we expand the
state we get the states
Let be the node to start with. Exceute the algorithm on the given graph with
Answer questions a and b
Question
pts
a After the expanding the state S the frontier list contains states. They are:
by alphabetical order
with ffunction value
with ffunction value
Question
b The next state to be expanded is:
includes a number of other algorithms as special cases. Answer question a
and b
includes a number of other algorithms as special cases. Answer question a
and b
Question
a When it is
greedy search
uniform cost search
search
Question
b When it is
search
greedy search
uniform cost search
Question
After running search with a not necessarily optimal goal node is found, of cost Let
be a optimal goal and be its optimal solution cost, and suppose the heuristic is admissible. Select the
strongest bound below that holds.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


