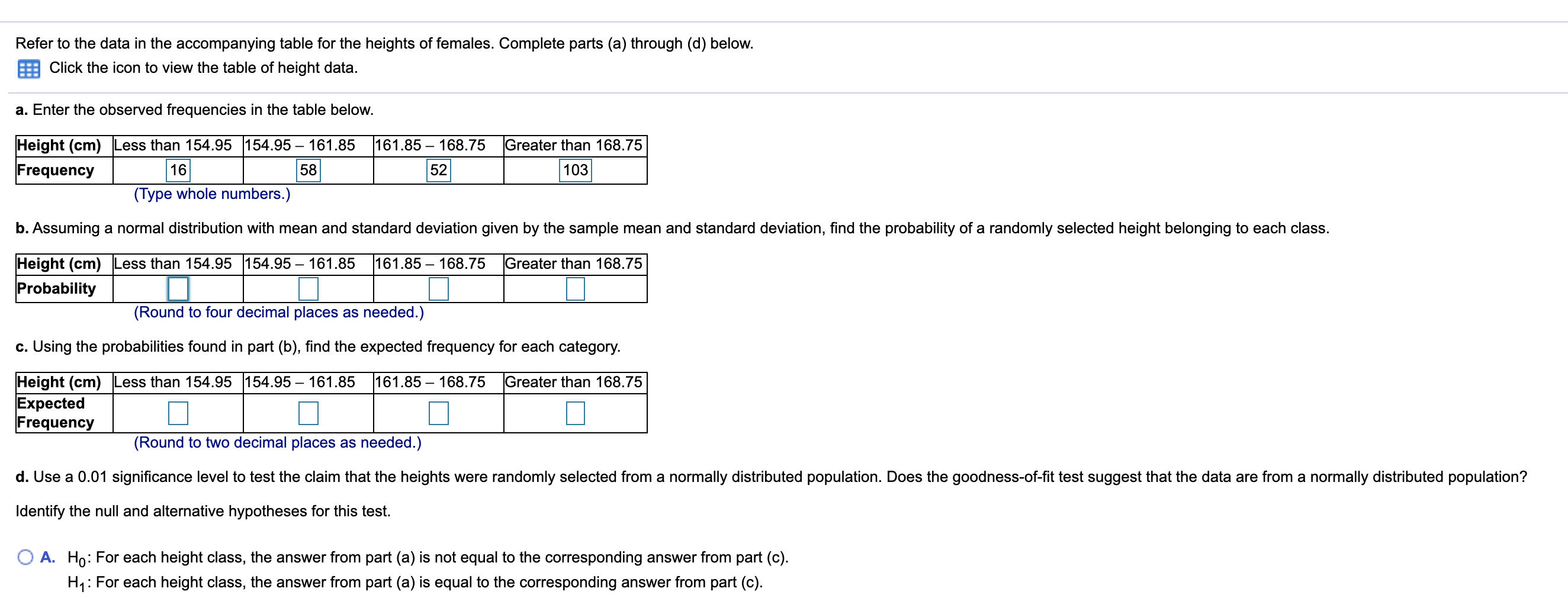
Refer to the data in the accompanying table for the heights of females. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a Click the icon to view the table of height data. a. Enter the observed frequencies in the table below. Height (cm) Less than 154.95 154.95 161.85 161.85 168.75 Greater than 168.75 Frequency 16 58 52 103 (Type whole numbers.) b. Assuming a normal distribution with mean and standard deviation given by the sample mean and standard deviation, nd the probability of a randomly selected height belonging to each class. Height (cm) Less than 154.95 154.95 161.85 161 .85 168.75 Greater than 168.75 Probability D (Round to four decimal places as needed.) 1:. Using the probabilities found in part (b), nd the expected frequency for each category. Height (cm) Less than 154.95 154.95 161.85 161.85 168.75 Greater than 168.75 Expected Frequency D D D D (Round to two decimal places as needed.) d. Use a 0.01 signicance level to test the claim that the heights were randomly selected from a normally distributed population. Does the goodness-of-tit test suggest that the data are from a normally distributed population? Identify the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. 0 A. H : For each height class, the answer from part (a) is not equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). 0 H1: For each height class, the answer from part (a) is equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). d. Use a 0.01 signicance level to test the claim that the heights were randomly selected from a normally distributed population, Does the gccdness-of-tit test suggest that the data are from a normally distributed population? identify the null and altemative hypotheses for this test. 0 A. Ho: For each height class, the answer from part (a) is not equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). H1 : For each height class, the answer from part (a) is equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). O B. Ho: For each height class, the answer from part (a) is equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). H1: For each height class, the answer from part (a) is not equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). O C. Ho: The answers from part (a) for each height class are equal to each other H1 : At least one of the answers from part (a) is not equal to the other answers from part (a). O D. Ho: For each height class, the answer from part (a) is equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). H1 : For at least one height class, the answer from part (a) is not equal to the corresponding answer from part (c). Identify the test statistic. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Identify the Pvalue. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the nal conclusion that addresses the original claim. V Ho. There is l evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the female heights were randomly selected from a normally distributed population