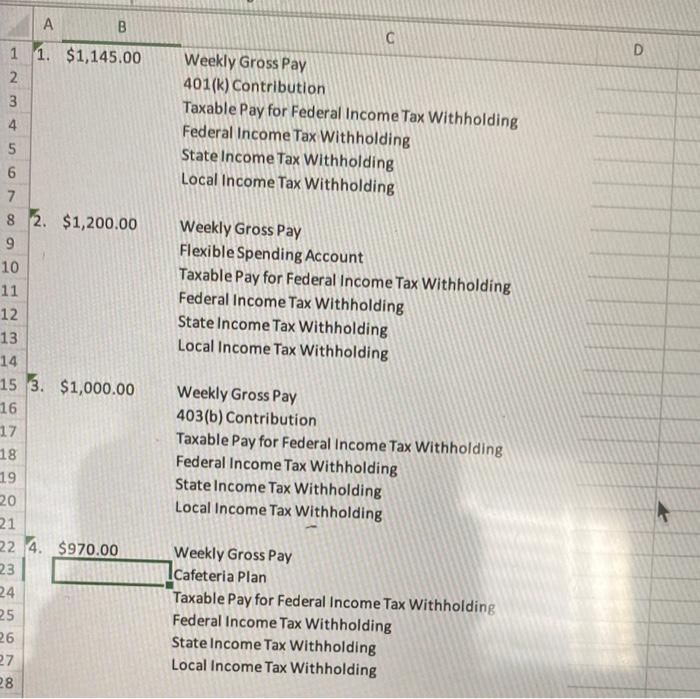
Refer to the Federal Tax Tables in Appendix A. For each employee listed, use the wage-bracket method to calculate federal withholding tax. Then calculate both estate withholding tax (assuming a state tax rate of 5% of taxable pay , with taxable pay being the same for federal and state income tax withholding) and the local withholding tax. 1. Jay Monroe (single; two federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,145. For each period, he makes a 401(k) retirement plan contribution of 12% of gross pay. The city in which he works (he lives elsewhere) levies a tax of 2% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 1.7% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. 2. Gus Damon (married, nine federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,200. He contributed $125 to a flexible spending account during the period. The city in which he lives and works levies a tax of 3% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 0.4% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. 3. Kenneth Riley (single; no federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,000. For each period, he makes a 403(b) retirement plan contribution of 5% of gross pay. The city in which he lives and works levies a tax of 1.7% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on both residents and nonresidents. 4. Ross McMichael (married; two federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $970. He paid $60 to a cafeteria plan during the period. The city in which he works levies a tax of $8/week on employees who work within city limits. A B 1 1. $1,145.00 D 2 3 3 Weekly Gross Pay 401(k) Contribution Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 4 5 6 7 8 2. $1,200.00 9 9 10 11 Weekly Gross Pay Flexible Spending Account Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 12 13 14 15 3. $1,000.00 16 17 18 Weekly Gross Pay 403(b) Contribution Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 19 20 21 22 4. $970.00 23 24 Weekly Gross Pay 1cafeteria Plan Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 25 26 27 28 Refer to the Federal Tax Tables in Appendix A. For each employee listed, use the wage-bracket method to calculate federal withholding tax. Then calculate both estate withholding tax (assuming a state tax rate of 5% of taxable pay , with taxable pay being the same for federal and state income tax withholding) and the local withholding tax. 1. Jay Monroe (single; two federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,145. For each period, he makes a 401(k) retirement plan contribution of 12% of gross pay. The city in which he works (he lives elsewhere) levies a tax of 2% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 1.7% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. 2. Gus Damon (married, nine federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,200. He contributed $125 to a flexible spending account during the period. The city in which he lives and works levies a tax of 3% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 0.4% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. 3. Kenneth Riley (single; no federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,000. For each period, he makes a 403(b) retirement plan contribution of 5% of gross pay. The city in which he lives and works levies a tax of 1.7% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on both residents and nonresidents. 4. Ross McMichael (married; two federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $970. He paid $60 to a cafeteria plan during the period. The city in which he works levies a tax of $8/week on employees who work within city limits. A B 1 1. $1,145.00 D 2 3 3 Weekly Gross Pay 401(k) Contribution Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 4 5 6 7 8 2. $1,200.00 9 9 10 11 Weekly Gross Pay Flexible Spending Account Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 12 13 14 15 3. $1,000.00 16 17 18 Weekly Gross Pay 403(b) Contribution Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 19 20 21 22 4. $970.00 23 24 Weekly Gross Pay 1cafeteria Plan Taxable Pay for Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal Income Tax Withholding State Income Tax Withholding Local Income Tax Withholding 25 26 27 28