Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Regal Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. For June 2017 each suit is budgeted to take 4 labor-hours. The budgeted number of suits to
Regal Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. For June 2017 each suit is budgeted to take 4 labor-hours. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1,180. Regal Clothing allocates fixed manufacturing overhead to each suit using budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit.
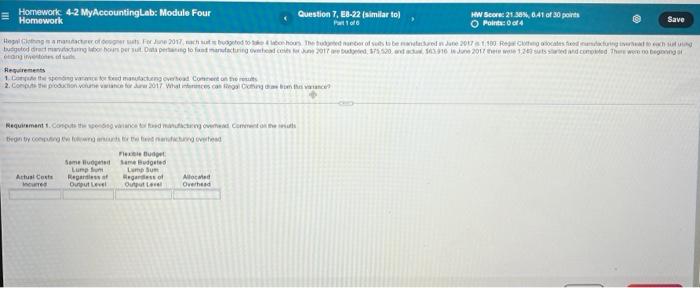


Regal Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 4 labor-hours. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1,180. Regal Clothing allocated foxed manufacturing overhead to each suit using budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. Data pertaining to fixed manufacturing overhead costs for June 2017 are budgeted $75,520 and actual $63,916. In June 2017 1,240 suits were started and completed. 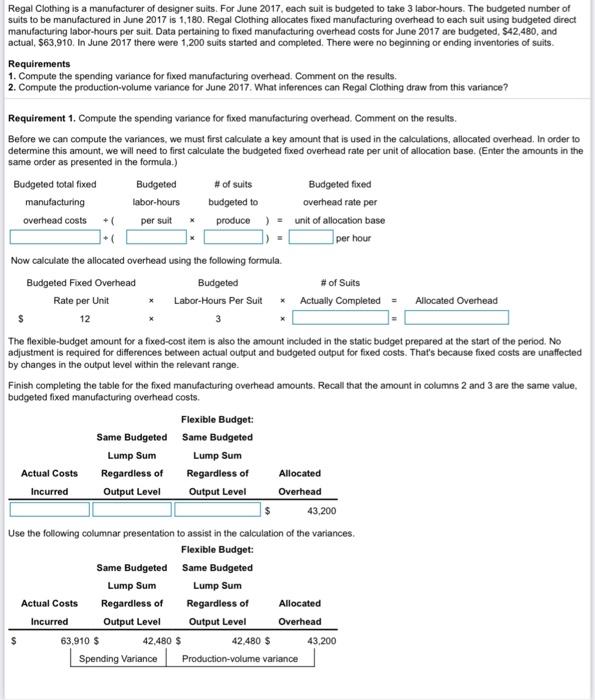

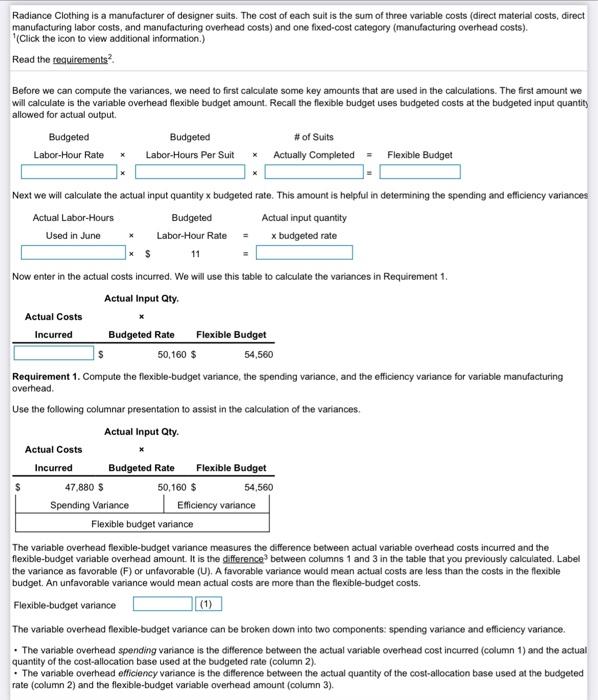
Homework 4-2 My AccountingLab: Module Four HW Score 21.30 041 of 30 points Question 7. EB-22 similar to) Homework Save Part 10 Points: 0014 Hepalsam 2017 bodo menor statements et a Roces feed to med det tager hon perut Oua pengo litructuring of consumed 1350 0.0 Jo 2017 12 dood The tegeng Rewirements 1. Contactangover Connect on the 2. Como pouchon one 2017 Watces can also Requirement 1. Compostweg walance and much as Content on the Bron by competence Bul Some Home Budgeted Lumpu Lumum Attual Costs Regar eers of Allowed Ince Out Out Owheed Now compute the spending variance Label the vanance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (UL A favorable variance would mean actual costs in column 1 are less than the costs in column 2, the labor-hour rate is less than budgeted. An unfavorable variance would mean the actual costs in column 1 are more than the costs in column 2 the labor-hour rate is more than budgeted. Spending variance (2) Finally, compute the efficiency variance Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) A favorable variance would mean the costs in column 2 are less than the flexible budget costs in column 3, we have used less inout quantity. An unfavorable variance would mean the costs in column 2 are more than the flexible budget costs in column 3 we have used more input quantity Eficiency variance (3) Requirement 2. Comment on the results, If Radiance has a favorable spending variance this would mean that the actual overhead rate per labor-hour is less than budgeted. They have spent less on labor than anticipated. If the spending variance is unfavorable then the actual overhead rate per labor-hour is more than budgeted. Radiance would have spent more on labor than anticipated. A favorable efficiency variance would mean that each suit produced averaged fewer labor-hous to make than was planned (budgeted). Thus, an unfavorable efficiency variance is the result of each suit produced averaging more labor hours to make than was planned 1: More Info Variable manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to each sut on the basis of budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 4 labor-hours. Budgeted variable manufacturing overhead cost per labor-hour is $11. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1.200. Actual variable manufacturing overhead costs in June 2017 were $47.880 for 1.240 suls staned and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits. Actual direct manufacturing labor-hours for June were 4560 2. Requirements 1. Compute the flexible-budget variance, the spending variance, and the efficiency variance for variabile manufacturing overhead. 2. Comment on the results 3. Definition $47.880 - $54,560 4: Definition 547.880 - $50,160 5: Definition $50, 160 - $54,560 ? (2) ) (1) O OU F F OU (3) O OU F Radiance Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. The cost of each suit is the sum of three variable costs (direct material costs, direct manufacturing labor costs, and manufacturing overhead costs) and one fixed-cost category (manufacturing overhead costs). (Click the icon to view additional information.) Read the requirements Before we can compute the variances, we need to first calculate some key amounts that are used in the calculations. The first amount we will calculate is the variable overhead flexible budget amount. Recall the flexible budget uses budgeted costs at the budgeted input quantity allowed for actual output Budgeted Budgeted # of Suits Labor-Hour Rate * Labor-Hours Per Suit Actually completed - Flexible Budget Next we will calculate the actual input quantity x budgeted rate. This amount is helpful in determining the spending and efficiency variances Actual Labor-Hours Budgeted Actual input quantity Used in June * Labor-Hour Rate * budgeted rate * $ 11 Now enter in the actual costs incurred. We will use this table to calculate the variances in Requirement 1. Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred Budgeted Rate Flexible Budget 50,160 $ 54,560 Requirement 1. Compute the flexible-budget variance, the spending variance, and the efficiency variance for variable manufacturing overhead. Use the following columnar presentation to assist in the calculation of the variances Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred Budgeted Rate Flexible Budget 47,880 $ 50,160 $ 54,560 Spending Variance Efficiency variance Flexible budget variance The variable overhead flexible-budget variance measures the difference between actual variable overhead costs incurred and the flexible-budget variable overhead amount. It is the difference between columns 1 and 3 in the table that you previously calculated. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable variance would mean actual costs are less than the costs in the flexible budget. An unfavorable variance would mean actual costs are more than the flexible-budget costs. Flexible-budget variance (1) The variable overhead flexible-budget variance can be broken down into two components: spending variance and efficiency variance. The variable overhead spending variance is the difference between the actual variable overhead cost incurred (column 1) and the actual quantity of the cost-allocation base used at the budgeted rate (column 2). . The variable overhead efficiency variance is the difference between the actual quantity of the cost-allocation base used at the budgeted rate (column 2) and the flexible-budget variable overhead amount (column 3). Variable manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to each suit on the basis of budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 5 labor-hours. Budgeted variable manufacturing overhead cost per labor-hour is $14. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1.100 Actual variable manufacturing overhead costs in June 2017 were $67,800 for 1,040 suits started and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits. Actual direct manufacturing labor-hours for June were 4,520. Regal Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 3 labor-hours. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1,180. Regal Clothing allocates fixed manufacturing overhead to each suit using budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. Data pertaining to fixed manufacturing overhead costs for June 2017 are budgeted, 542,480, and actual $63,910, In June 2017 there were 1,200 suits started and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits Requirements 1. Compute the spending variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Comment on the results. 2. Compute the production-volume variance for June 2017. What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? per suit Requirement 1. Compute the spending variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Comment on the results. Before we can compute the variances, we must first calculate a key amount that is used in the calculations, allocated overhead. In order to determine this amount, we will need to first calculate the budgeted fixed overhead rate per unit of allocation base(Enter the amounts in the same order as presented in the formula.) Budgeted total fixed Budgeted # of suits Budgeted fixed manufacturing labor-hours budgeted to overhead rate per overhead costs + produce unit of allocation base per hour Now calculate the allocated overhead using the following formula Budgeted Fixed Overhead Budgeted # of Suits Rate per Unit Labor-Hours Per Suit * Actually completed Allocated Overhead 12 3 The flexible-budget amount for a fixed-cost item is also the amount included in the static budget prepared at the start of the period. No adjustment is required for differences between actual output and budgeted output for fixed costs. That's because fixed costs are unaffected by changes in the output level within the relevant range. Finish completing the table for the fixed manufacturing overhead amounts. Recall that the amount in columns 2 and 3 are the same value, budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Flexible Budget: Same Budgeted Same Budgeted Lump Sum Lump Sum Actual Costs Regardless of Regardless of Allocated Incurred Output Level Output Level Overhead 43,200 Use the following columnar presentation to assist in the calculation of the variances Flexible Budget Same Budgeted Same Budgeted Lump Sum Lump Sum Actual Costs Regardless of Regardless of Allocated Incurred Output Level Output Level Overhead 63.910 $ 42,480 $ 42.480 $ 43,200 Spending Variance Production-volume variance The variable overhead flexible-budget variance is subdivided into a spending variance and an efficiency variance. There is not an efficiency variance for fixed overhead costs. That's because a given lump sum of fixed overhead costs will be unaffected by how efficiently machine-hours are used to produce output in a given budget period. Because there is no efficiency variance, the fixed overhead spending variance is the same amount as the fixed overhead flexible-budget variance. The fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance is the difference between columns 1 and 2 of the table you completed above. Compute the spending variance and label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable variance would mean actual costs are less than the budgeted costs. An unfavorable variance would mean actual costs are more than the budgeted costs. Spending variance (1) Comment on the results. If the spending variance is favorable, Regal will have spent below the budgeted amount for fixed costs. If the spending variance is unfavorable, they will have spent above the budgeted amount. Requirement 2. Compute the production-volume variance for June 2017. What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? The production-volume variance is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead and fixed overhead allocated on the basis of actual output produced (columns 3 and 4 of the table completed above). This variance will only arise for faced costs and is due to the difference between the budgeted production and actual production. Compute the production-volume variance Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable vanance would mean the flexible budget costs are less than the allocated overhead costs. An unfavorable variance would mean the flexible budget costs are more than the allocated overhead costs. Production-volume variance (2) What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? A favorable production-volume variance would arise because the actual production of suits is more than the budgeted production. Regal Clothing may then want to consider if the market is growing, are they increasing market share, and/or will they need to add capacity to keep up with demand. In contrast, an unfavorable production-volume variance would arise because the actual production of suits is less than the budgeted production. With an unfavorable variance Regal may need to look into whether the market is shrinking or if they are losing market share. 1: Definition $63,910 - 542,480 = ? 2: Definition Also referred to as the denominator-level variance. 3: Definition 542,480 - 543,200 = ? (1) U F C U Homework 4-2 My AccountingLab: Module Four HW Score 21.30 041 of 30 points Question 7. EB-22 similar to) Homework Save Part 10 Points: 0014 Hepalsam 2017 bodo menor statements et a Roces feed to med det tager hon perut Oua pengo litructuring of consumed 1350 0.0 Jo 2017 12 dood The tegeng Rewirements 1. Contactangover Connect on the 2. Como pouchon one 2017 Watces can also Requirement 1. Compostweg walance and much as Content on the Bron by competence Bul Some Home Budgeted Lumpu Lumum Attual Costs Regar eers of Allowed Ince Out Out Owheed Now compute the spending variance Label the vanance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (UL A favorable variance would mean actual costs in column 1 are less than the costs in column 2, the labor-hour rate is less than budgeted. An unfavorable variance would mean the actual costs in column 1 are more than the costs in column 2 the labor-hour rate is more than budgeted. Spending variance (2) Finally, compute the efficiency variance Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) A favorable variance would mean the costs in column 2 are less than the flexible budget costs in column 3, we have used less inout quantity. An unfavorable variance would mean the costs in column 2 are more than the flexible budget costs in column 3 we have used more input quantity Eficiency variance (3) Requirement 2. Comment on the results, If Radiance has a favorable spending variance this would mean that the actual overhead rate per labor-hour is less than budgeted. They have spent less on labor than anticipated. If the spending variance is unfavorable then the actual overhead rate per labor-hour is more than budgeted. Radiance would have spent more on labor than anticipated. A favorable efficiency variance would mean that each suit produced averaged fewer labor-hous to make than was planned (budgeted). Thus, an unfavorable efficiency variance is the result of each suit produced averaging more labor hours to make than was planned 1: More Info Variable manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to each sut on the basis of budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 4 labor-hours. Budgeted variable manufacturing overhead cost per labor-hour is $11. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1.200. Actual variable manufacturing overhead costs in June 2017 were $47.880 for 1.240 suls staned and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits. Actual direct manufacturing labor-hours for June were 4560 2. Requirements 1. Compute the flexible-budget variance, the spending variance, and the efficiency variance for variabile manufacturing overhead. 2. Comment on the results 3. Definition $47.880 - $54,560 4: Definition 547.880 - $50,160 5: Definition $50, 160 - $54,560 ? (2) ) (1) O OU F F OU (3) O OU F Radiance Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. The cost of each suit is the sum of three variable costs (direct material costs, direct manufacturing labor costs, and manufacturing overhead costs) and one fixed-cost category (manufacturing overhead costs). (Click the icon to view additional information.) Read the requirements Before we can compute the variances, we need to first calculate some key amounts that are used in the calculations. The first amount we will calculate is the variable overhead flexible budget amount. Recall the flexible budget uses budgeted costs at the budgeted input quantity allowed for actual output Budgeted Budgeted # of Suits Labor-Hour Rate * Labor-Hours Per Suit Actually completed - Flexible Budget Next we will calculate the actual input quantity x budgeted rate. This amount is helpful in determining the spending and efficiency variances Actual Labor-Hours Budgeted Actual input quantity Used in June * Labor-Hour Rate * budgeted rate * $ 11 Now enter in the actual costs incurred. We will use this table to calculate the variances in Requirement 1. Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred Budgeted Rate Flexible Budget 50,160 $ 54,560 Requirement 1. Compute the flexible-budget variance, the spending variance, and the efficiency variance for variable manufacturing overhead. Use the following columnar presentation to assist in the calculation of the variances Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred Budgeted Rate Flexible Budget 47,880 $ 50,160 $ 54,560 Spending Variance Efficiency variance Flexible budget variance The variable overhead flexible-budget variance measures the difference between actual variable overhead costs incurred and the flexible-budget variable overhead amount. It is the difference between columns 1 and 3 in the table that you previously calculated. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable variance would mean actual costs are less than the costs in the flexible budget. An unfavorable variance would mean actual costs are more than the flexible-budget costs. Flexible-budget variance (1) The variable overhead flexible-budget variance can be broken down into two components: spending variance and efficiency variance. The variable overhead spending variance is the difference between the actual variable overhead cost incurred (column 1) and the actual quantity of the cost-allocation base used at the budgeted rate (column 2). . The variable overhead efficiency variance is the difference between the actual quantity of the cost-allocation base used at the budgeted rate (column 2) and the flexible-budget variable overhead amount (column 3). Variable manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to each suit on the basis of budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 5 labor-hours. Budgeted variable manufacturing overhead cost per labor-hour is $14. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1.100 Actual variable manufacturing overhead costs in June 2017 were $67,800 for 1,040 suits started and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits. Actual direct manufacturing labor-hours for June were 4,520. Regal Clothing is a manufacturer of designer suits. For June 2017, each suit is budgeted to take 3 labor-hours. The budgeted number of suits to be manufactured in June 2017 is 1,180. Regal Clothing allocates fixed manufacturing overhead to each suit using budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. Data pertaining to fixed manufacturing overhead costs for June 2017 are budgeted, 542,480, and actual $63,910, In June 2017 there were 1,200 suits started and completed. There were no beginning or ending inventories of suits Requirements 1. Compute the spending variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Comment on the results. 2. Compute the production-volume variance for June 2017. What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? per suit Requirement 1. Compute the spending variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Comment on the results. Before we can compute the variances, we must first calculate a key amount that is used in the calculations, allocated overhead. In order to determine this amount, we will need to first calculate the budgeted fixed overhead rate per unit of allocation base(Enter the amounts in the same order as presented in the formula.) Budgeted total fixed Budgeted # of suits Budgeted fixed manufacturing labor-hours budgeted to overhead rate per overhead costs + produce unit of allocation base per hour Now calculate the allocated overhead using the following formula Budgeted Fixed Overhead Budgeted # of Suits Rate per Unit Labor-Hours Per Suit * Actually completed Allocated Overhead 12 3 The flexible-budget amount for a fixed-cost item is also the amount included in the static budget prepared at the start of the period. No adjustment is required for differences between actual output and budgeted output for fixed costs. That's because fixed costs are unaffected by changes in the output level within the relevant range. Finish completing the table for the fixed manufacturing overhead amounts. Recall that the amount in columns 2 and 3 are the same value, budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Flexible Budget: Same Budgeted Same Budgeted Lump Sum Lump Sum Actual Costs Regardless of Regardless of Allocated Incurred Output Level Output Level Overhead 43,200 Use the following columnar presentation to assist in the calculation of the variances Flexible Budget Same Budgeted Same Budgeted Lump Sum Lump Sum Actual Costs Regardless of Regardless of Allocated Incurred Output Level Output Level Overhead 63.910 $ 42,480 $ 42.480 $ 43,200 Spending Variance Production-volume variance The variable overhead flexible-budget variance is subdivided into a spending variance and an efficiency variance. There is not an efficiency variance for fixed overhead costs. That's because a given lump sum of fixed overhead costs will be unaffected by how efficiently machine-hours are used to produce output in a given budget period. Because there is no efficiency variance, the fixed overhead spending variance is the same amount as the fixed overhead flexible-budget variance. The fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance is the difference between columns 1 and 2 of the table you completed above. Compute the spending variance and label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable variance would mean actual costs are less than the budgeted costs. An unfavorable variance would mean actual costs are more than the budgeted costs. Spending variance (1) Comment on the results. If the spending variance is favorable, Regal will have spent below the budgeted amount for fixed costs. If the spending variance is unfavorable, they will have spent above the budgeted amount. Requirement 2. Compute the production-volume variance for June 2017. What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? The production-volume variance is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead and fixed overhead allocated on the basis of actual output produced (columns 3 and 4 of the table completed above). This variance will only arise for faced costs and is due to the difference between the budgeted production and actual production. Compute the production-volume variance Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). A favorable vanance would mean the flexible budget costs are less than the allocated overhead costs. An unfavorable variance would mean the flexible budget costs are more than the allocated overhead costs. Production-volume variance (2) What inferences can Regal Clothing draw from this variance? A favorable production-volume variance would arise because the actual production of suits is more than the budgeted production. Regal Clothing may then want to consider if the market is growing, are they increasing market share, and/or will they need to add capacity to keep up with demand. In contrast, an unfavorable production-volume variance would arise because the actual production of suits is less than the budgeted production. With an unfavorable variance Regal may need to look into whether the market is shrinking or if they are losing market share. 1: Definition $63,910 - 542,480 = ? 2: Definition Also referred to as the denominator-level variance. 3: Definition 542,480 - 543,200 = ? (1) U F C U Compute the spending variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Comment
Compute the production-volume variance. what inference can be drawn?


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


