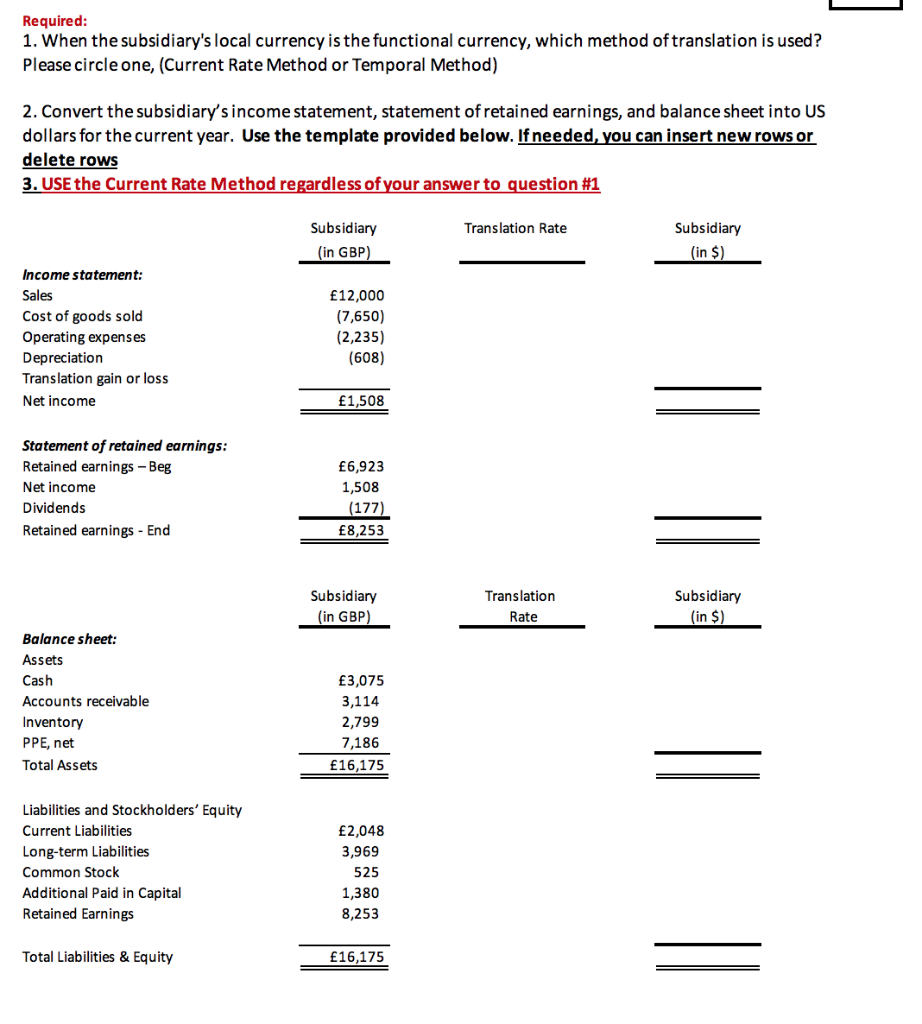
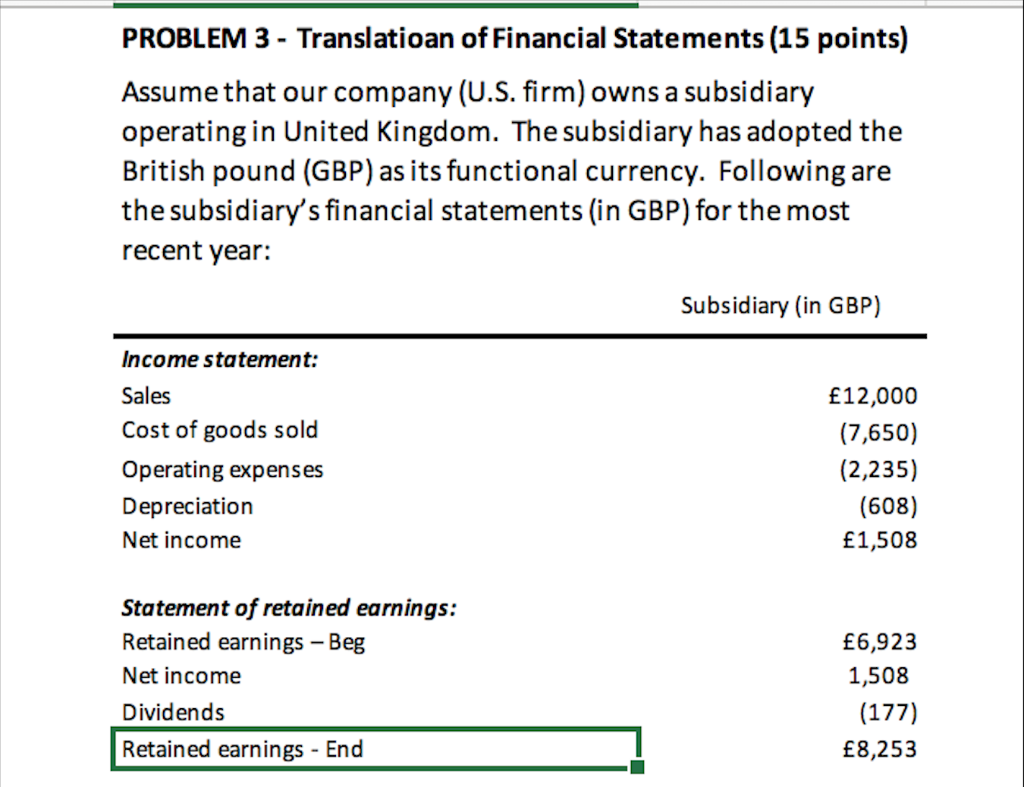
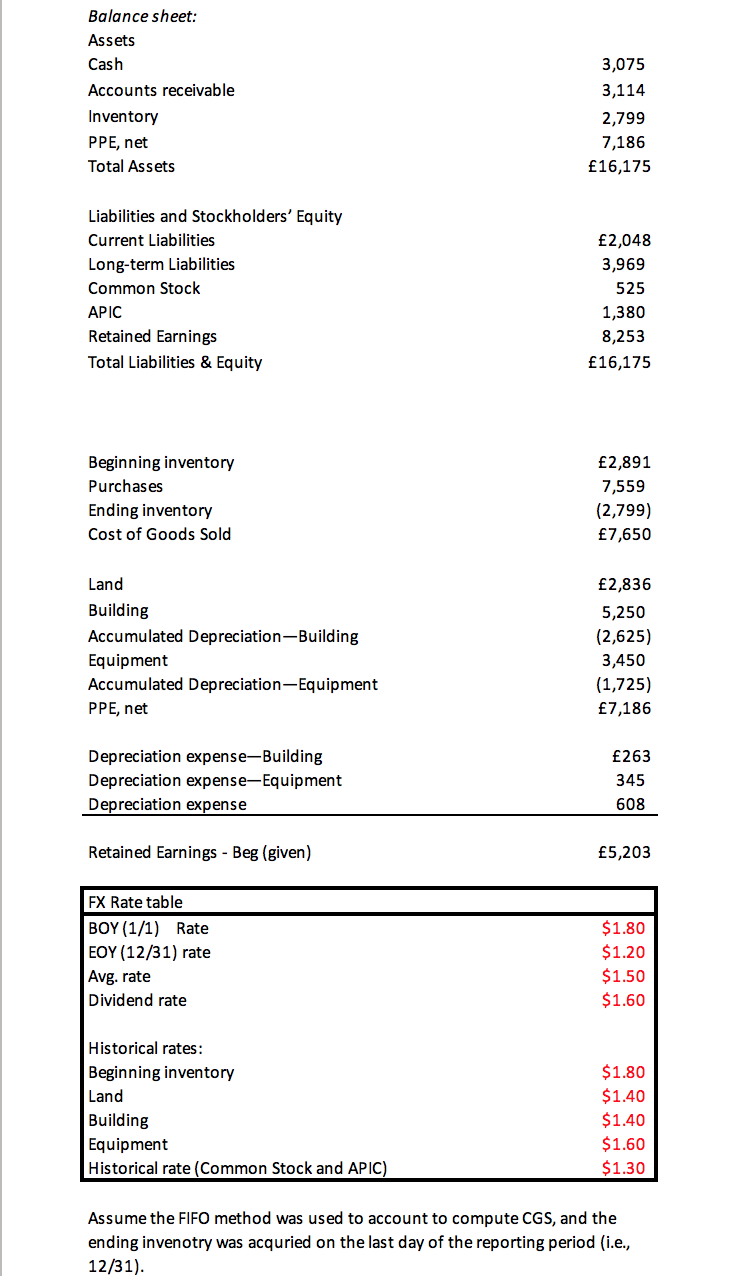
Required: 1. When the subsidiary's local currency is the functional currency, which method of translation is used? Please circle one, (Current Rate Method or Temporal Method) 2. Convert the subsidiary's income statement, statement of retained earnings, and balance sheet into US dollars for the current year. Use the template provided below. If needed, you can insert new rows or delete rows 3. USE the Current Rate Method regardless of your answer to question #1 Translation Rate Subsidiary (in GBP) Subsidiary (in $) Income statement: Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Depreciation Translation gain or loss Net income 12,000 (7,650) (2,235) (608) 1,508 = Statement of retained earnings: Retained earnings - Beg Net income Dividends Retained earnings - End 6,923 1,508 (177) 8,253 Subsidiary (in GBP) Translation Rate Subsidiary (in $) Balance sheet: Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory PPE, net Total Assets 3,075 3,114 2,799 7,186 16,175 - Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current Liabilities Long-term Liabilities Common Stock Additional Paid in Capital Retained Earnings 2,048 3,969 525 1,380 8,253 Total Liabilities & Equity 16,175 = PROBLEM 3 - Translatioan of Financial Statements (15 points) Assume that our company (U.S. firm) owns a subsidiary operating in United Kingdom. The subsidiary has adopted the British pound (GBP) as its functional currency. Following are the subsidiary's financial statements (in GBP) for the most recent year: Subsidiary (in GBP) Income statement: Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Depreciation Net income 12,000 (7,650) (2,235) (608) 1,508 Statement of retained earnings: Retained earnings - Beg Net income Dividends Retained earnings - End 6,923 1,508 (177) 8,253 Balance sheet: Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory PPE, net Total Assets 3,075 3,114 2,799 7,186 16,175 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current Liabilities Long-term Liabilities Common Stock APIC Retained Earnings Total Liabilities & Equity 2,048 3,969 525 1,380 8,253 16,175 Beginning inventory Purchases Ending inventory Cost of Goods Sold 7,559 (2,799) 7,650 Land Building Accumulated Depreciation-Building Equipment Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment PPE, net 2,836 5,250 (2,625) 3,450 (1,725) 7,186 Depreciation expense-Building Depreciation expense-Equipment Depreciation expense 263 345 608 Retained Earnings - Beg (given) 5,203 FX Rate table BOY (1/1) Rate EOY (12/31) rate Avg. rate Dividend rate $1.80 $1.20 $1.50 $1.60 Historical rates: Beginning inventory Land Building Equipment Historical rate (Common Stock and APIC) $1.80 $1.40 $1.40 $1.60 $1.30 Assume the FIFO method was used to account to compute CGS, and the ending invenotry was acquried on the last day of the reporting period (i.e., 12/31). Required: 1. When the subsidiary's local currency is the functional currency, which method of translation is used? Please circle one, (Current Rate Method or Temporal Method) 2. Convert the subsidiary's income statement, statement of retained earnings, and balance sheet into US dollars for the current year. Use the template provided below. If needed, you can insert new rows or delete rows 3. USE the Current Rate Method regardless of your answer to question #1 Translation Rate Subsidiary (in GBP) Subsidiary (in $) Income statement: Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Depreciation Translation gain or loss Net income 12,000 (7,650) (2,235) (608) 1,508 = Statement of retained earnings: Retained earnings - Beg Net income Dividends Retained earnings - End 6,923 1,508 (177) 8,253 Subsidiary (in GBP) Translation Rate Subsidiary (in $) Balance sheet: Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory PPE, net Total Assets 3,075 3,114 2,799 7,186 16,175 - Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current Liabilities Long-term Liabilities Common Stock Additional Paid in Capital Retained Earnings 2,048 3,969 525 1,380 8,253 Total Liabilities & Equity 16,175 = PROBLEM 3 - Translatioan of Financial Statements (15 points) Assume that our company (U.S. firm) owns a subsidiary operating in United Kingdom. The subsidiary has adopted the British pound (GBP) as its functional currency. Following are the subsidiary's financial statements (in GBP) for the most recent year: Subsidiary (in GBP) Income statement: Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Depreciation Net income 12,000 (7,650) (2,235) (608) 1,508 Statement of retained earnings: Retained earnings - Beg Net income Dividends Retained earnings - End 6,923 1,508 (177) 8,253 Balance sheet: Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory PPE, net Total Assets 3,075 3,114 2,799 7,186 16,175 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current Liabilities Long-term Liabilities Common Stock APIC Retained Earnings Total Liabilities & Equity 2,048 3,969 525 1,380 8,253 16,175 Beginning inventory Purchases Ending inventory Cost of Goods Sold 7,559 (2,799) 7,650 Land Building Accumulated Depreciation-Building Equipment Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment PPE, net 2,836 5,250 (2,625) 3,450 (1,725) 7,186 Depreciation expense-Building Depreciation expense-Equipment Depreciation expense 263 345 608 Retained Earnings - Beg (given) 5,203 FX Rate table BOY (1/1) Rate EOY (12/31) rate Avg. rate Dividend rate $1.80 $1.20 $1.50 $1.60 Historical rates: Beginning inventory Land Building Equipment Historical rate (Common Stock and APIC) $1.80 $1.40 $1.40 $1.60 $1.30 Assume the FIFO method was used to account to compute CGS, and the ending invenotry was acquried on the last day of the reporting period (i.e., 12/31)









