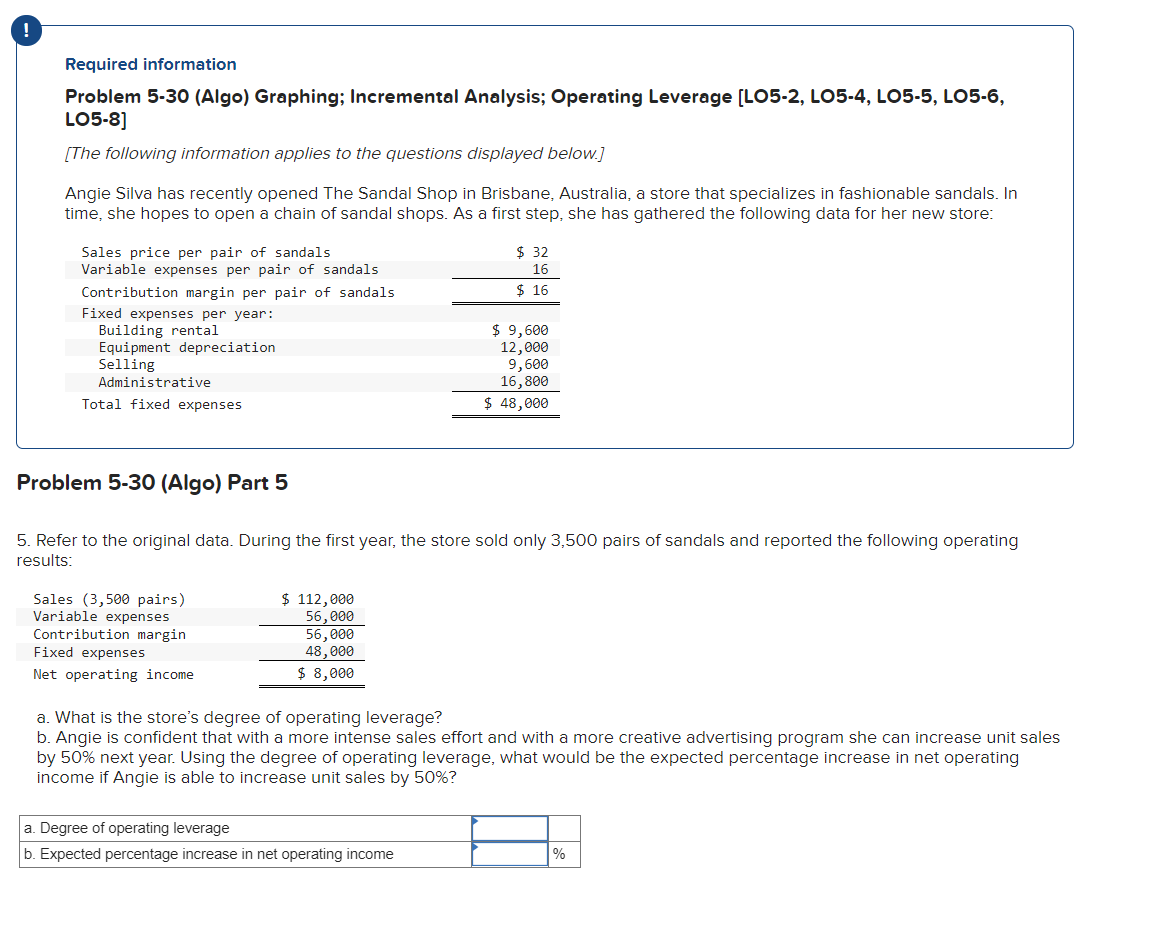
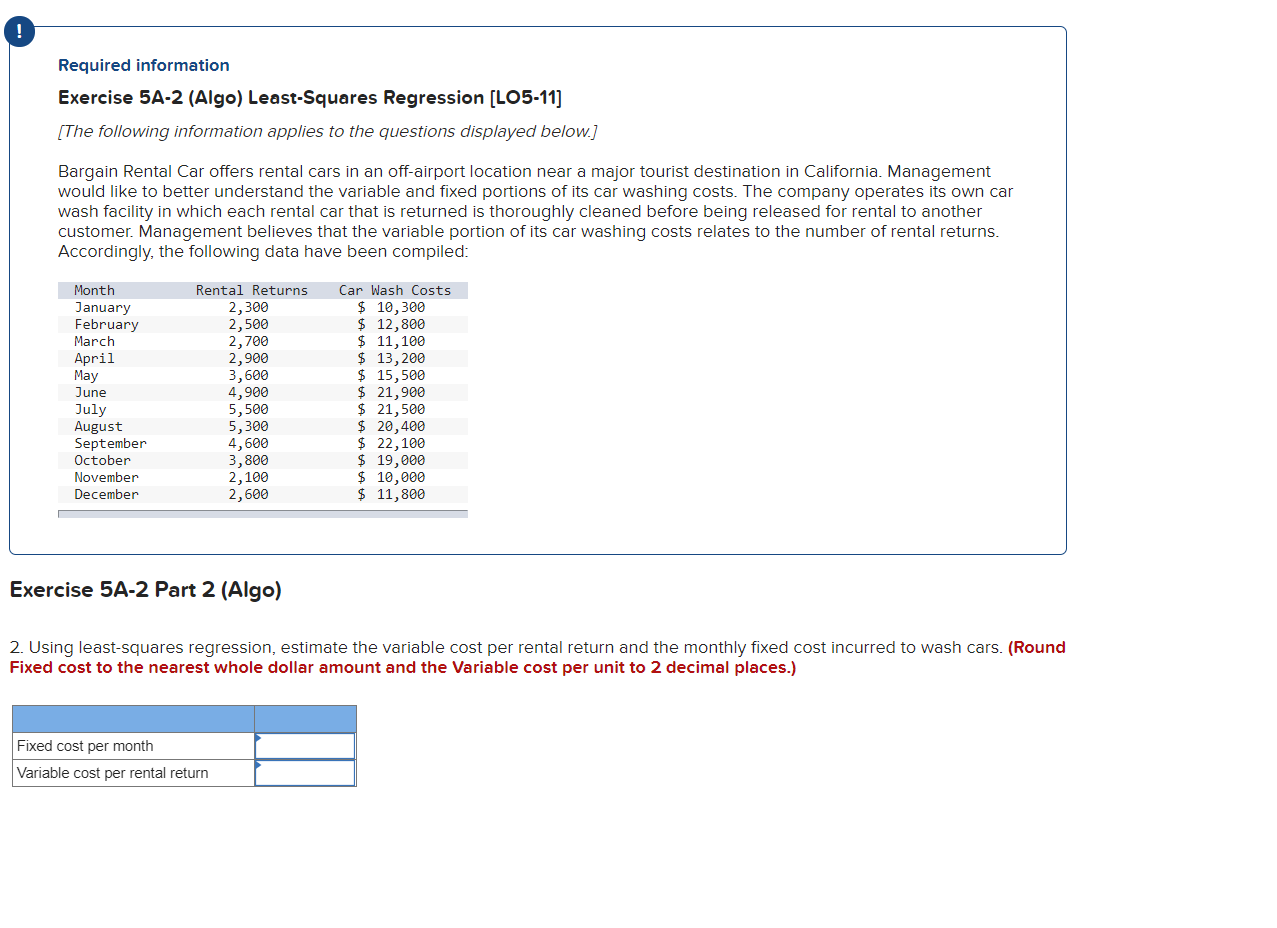
! Required information Problem 5-30 (Algo) Graphing; Incremental Analysis; Operating Leverage (L05-2, LO5-4, LO5-5, LO5-6, LO5-8] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Angie Silva has recently opened The Sandal Shop in Brisbane, Australia, a store that specializes in fashionable sandals. In time, she hopes to open a chain of sandal shops. As a first step, she has gathered the following data for her new store: $ 32 16 $ 16 Sales price per pair of sandals Variable expenses per pair of sandals Contribution margin per pair of sandals Fixed expenses per year: Building rental Equipment depreciation Selling Administrative Total fixed expenses $ 9,600 12,000 9,600 16,800 $ 48,000 Problem 5-30 (Algo) Part 5 5. Refer to the original data. During the first year, the store sold only 3,500 pairs of sandals and reported the following operating results: Sales (3,500 pairs) Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating income $ 112,000 56,000 56,000 48,000 $ 8,000 a. What is the store's degree of operating leverage? b. Angie is confident that with a more intense sales effort and with a more creative advertising program she can increase unit sales by 50% next year. Using the degree of operating leverage, what would be the expected percentage increase in net operating income if Angie is able to increase unit sales by 50%? a. Degree of operating leverage b. Expected percentage increase in net operating income % ! Required information Exercise 5A-2 (Algo) Least-Squares Regression (LO5-11] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Bargain Rental Car offers rental cars in an off-airport location near a major tourist destination in California. Management would like to better understand the variable and fixed portions of its car washing costs. The company operates its own car wash facility in which each rental car that is returned is thoroughly cleaned before being released for rental to another customer. Management believes that the variable portion of its car washing costs relates to the number of rental returns. Accordingly, the following data have been compiled: Month January February March April May June July August September October November December Rental Returns 2,300 2,500 2,700 2,900 3,600 4,900 5,500 5,300 4,600 3,800 2,100 2,600 Car Wash Costs $ 10,300 $ 12,800 $ 11,100 $ 13,200 $ 15,500 $ 21,900 $ 21,500 $ 20,400 $ 22,100 $ 19,000 $ 10,000 $ 11,800 Exercise 5A-2 Part 2 (Algo) 2. Using least-squares regression, estimate the variable cost per rental return and the monthly fixed cost incurred to wash cars. (Round Fixed cost to the nearest whole dollar amount and the Variable cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Fixed cost per month Variable cost per rental return








