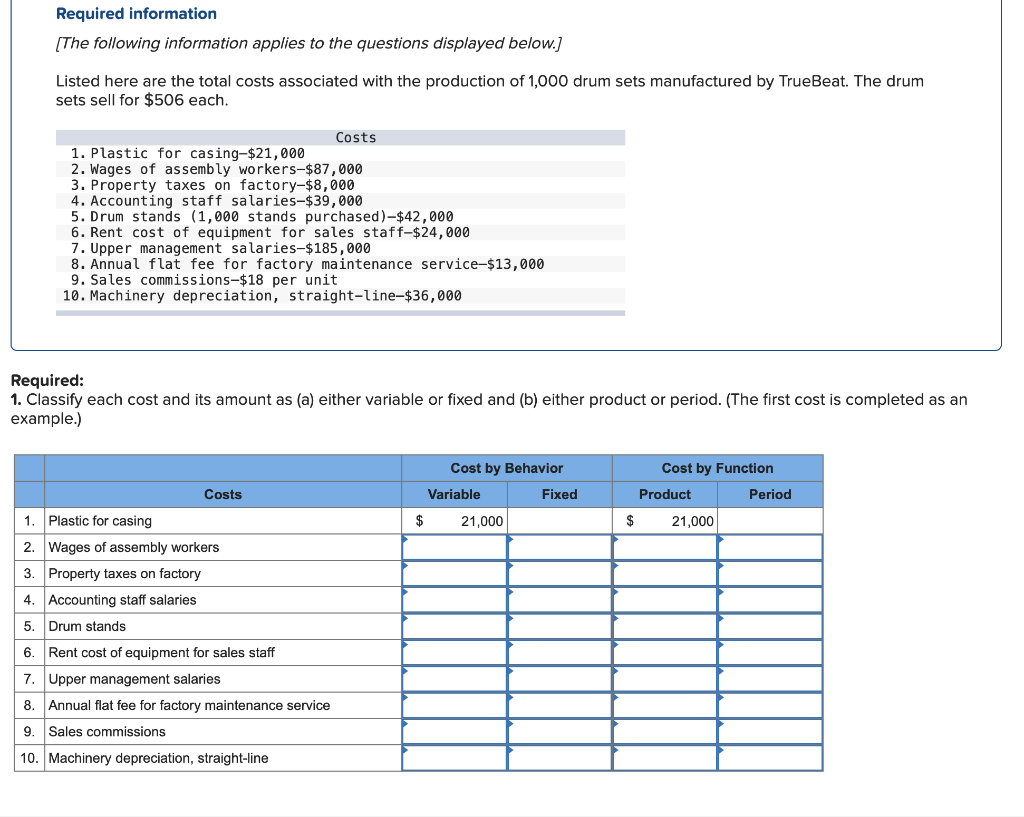
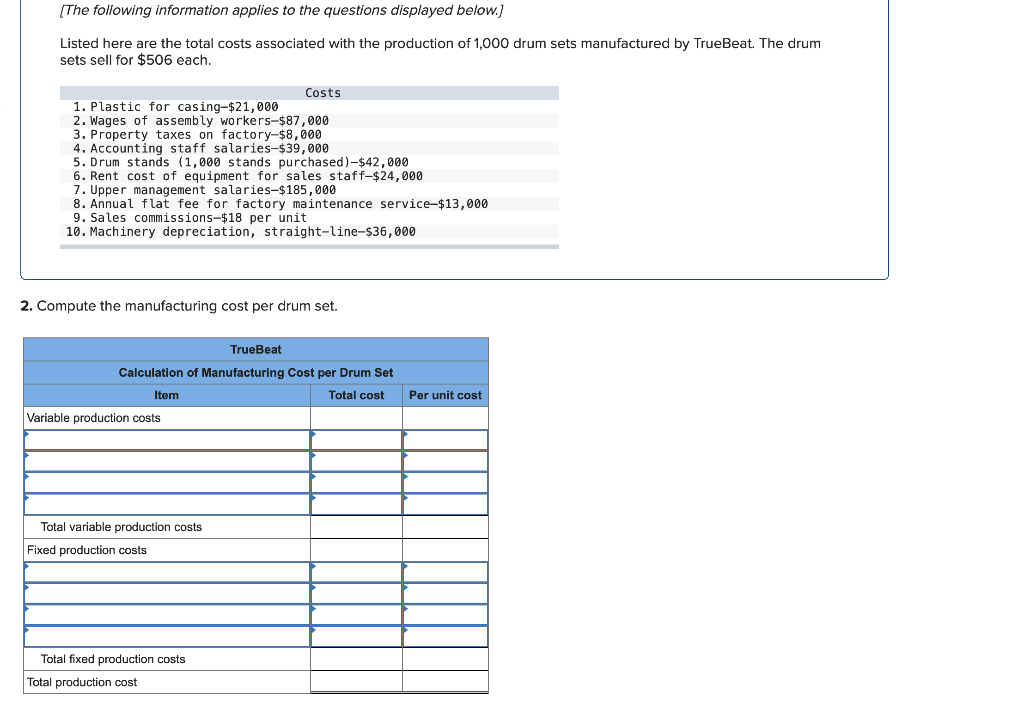
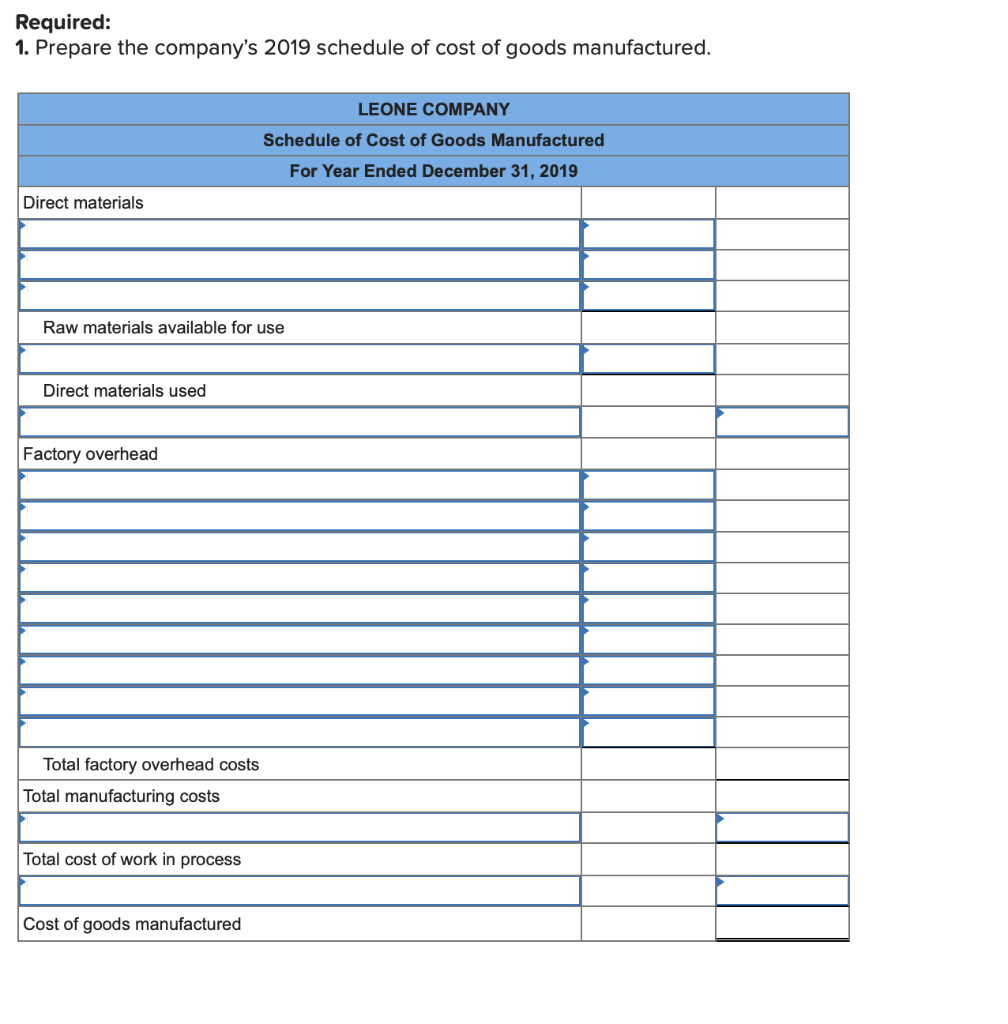
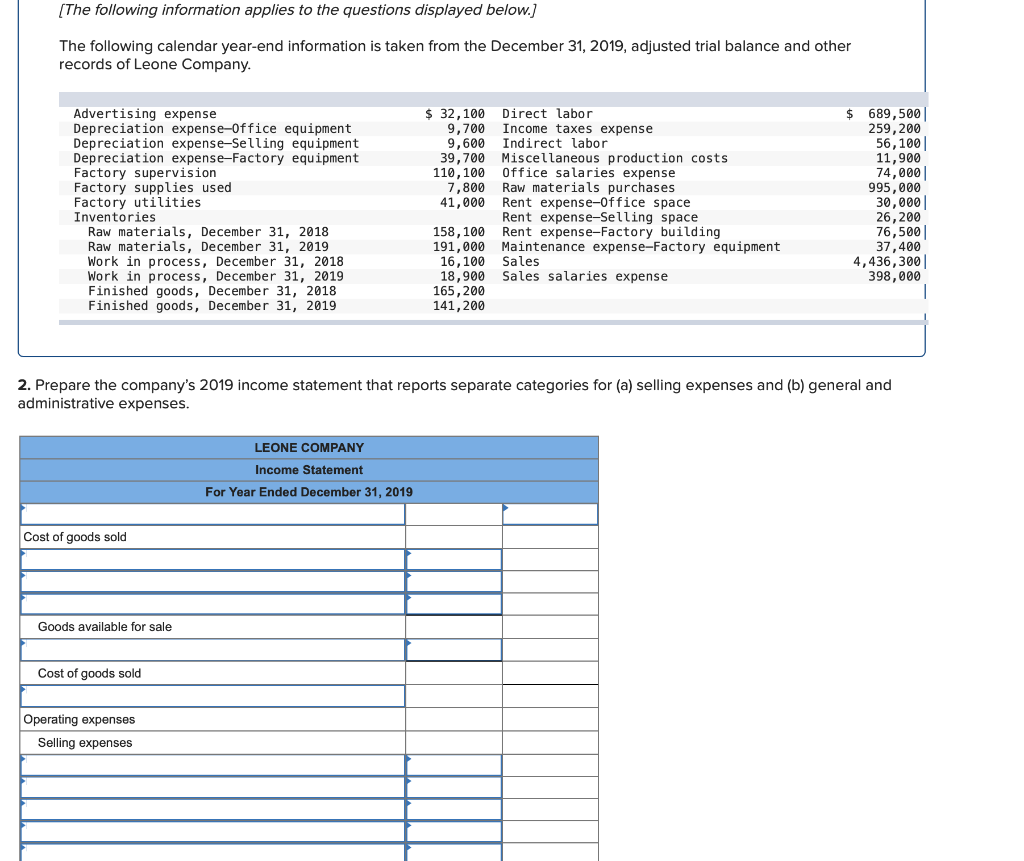
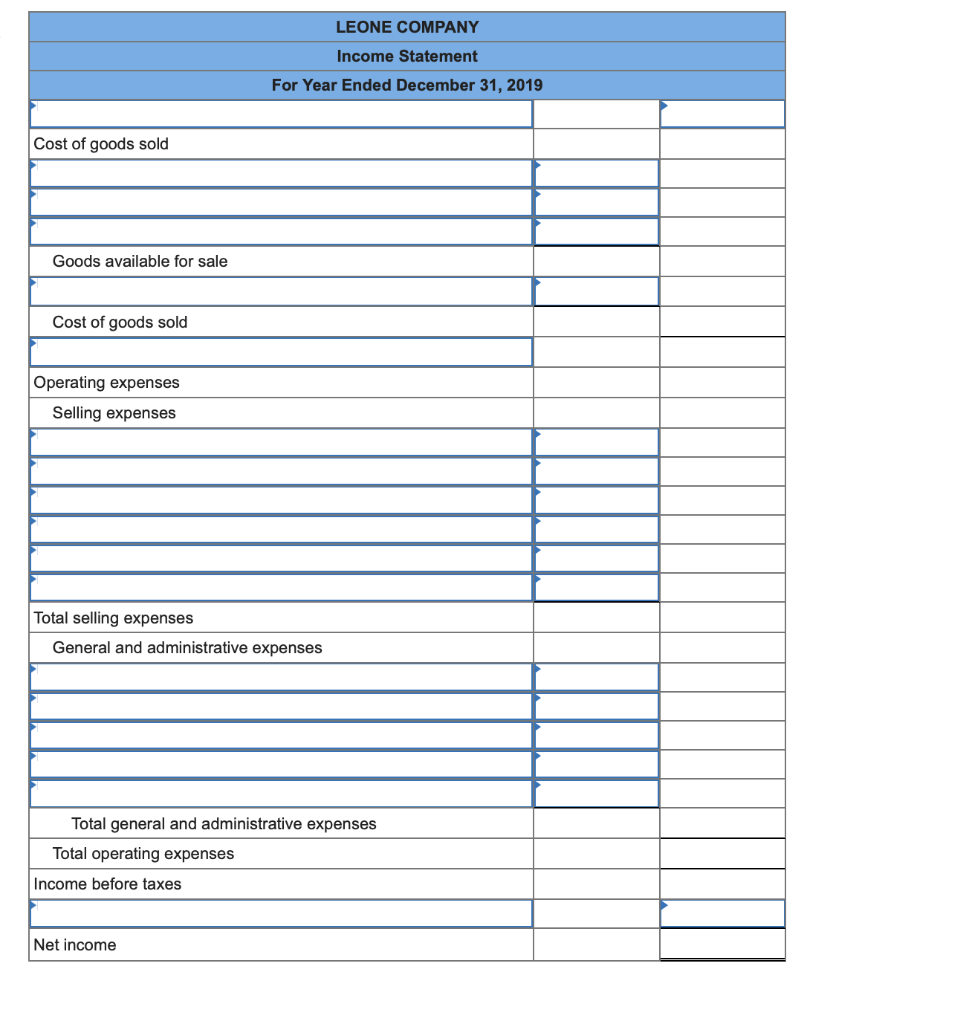
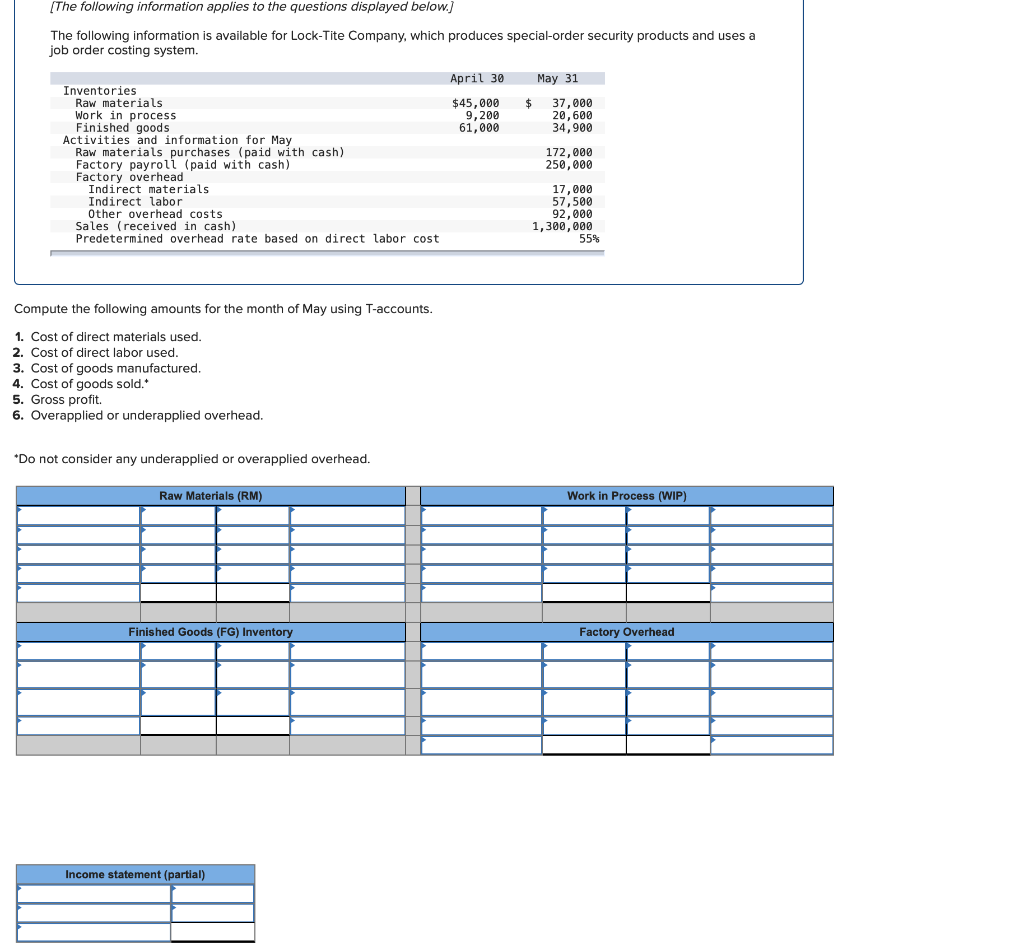
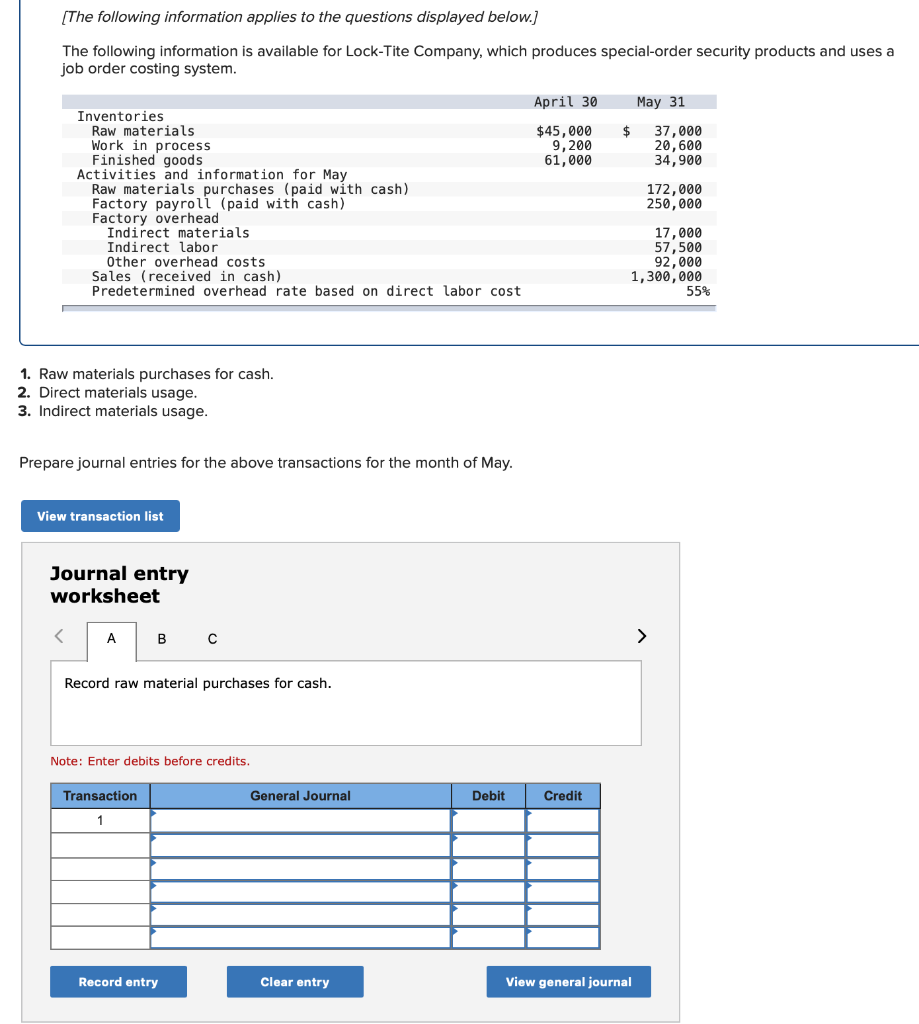
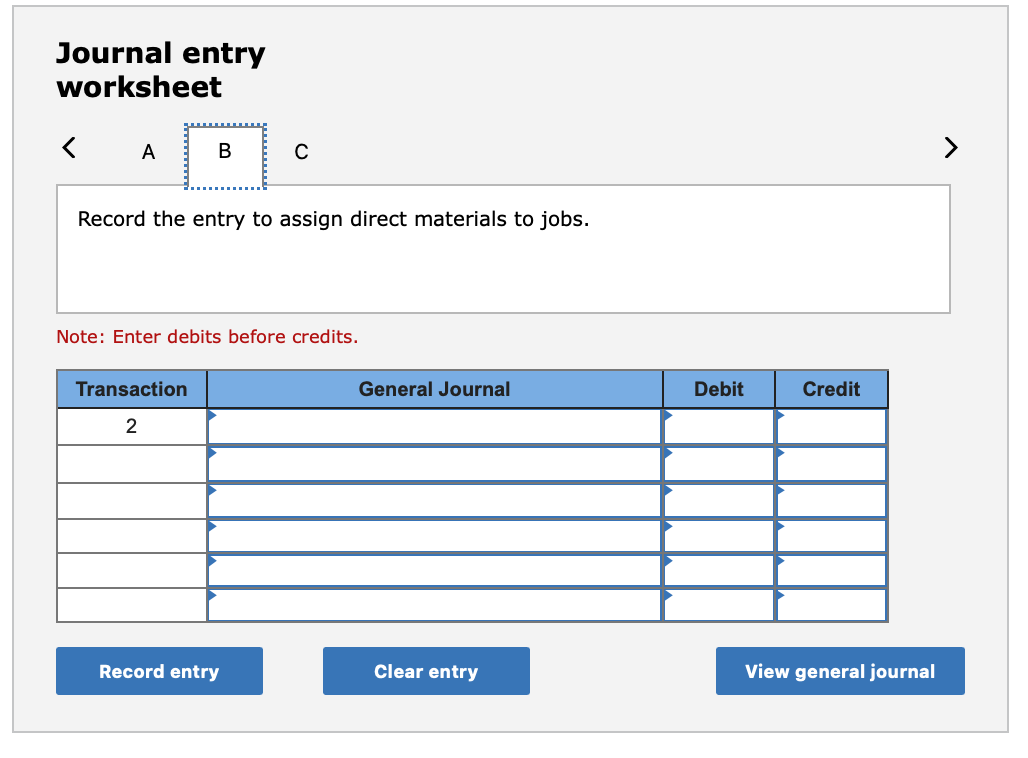
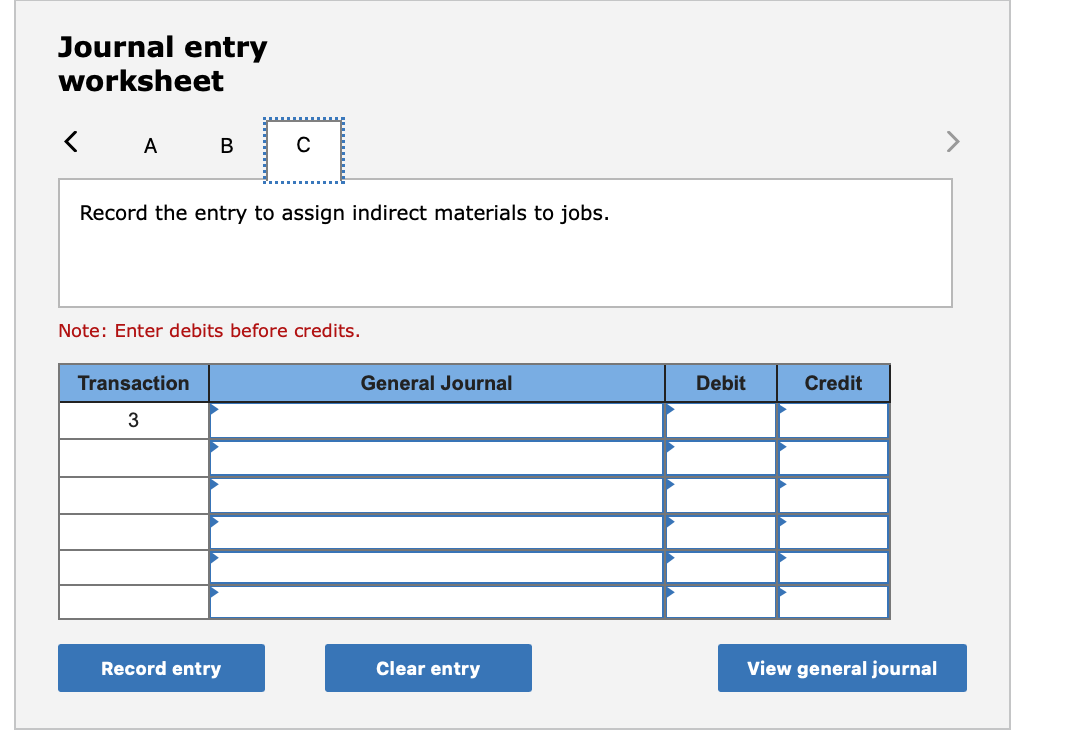
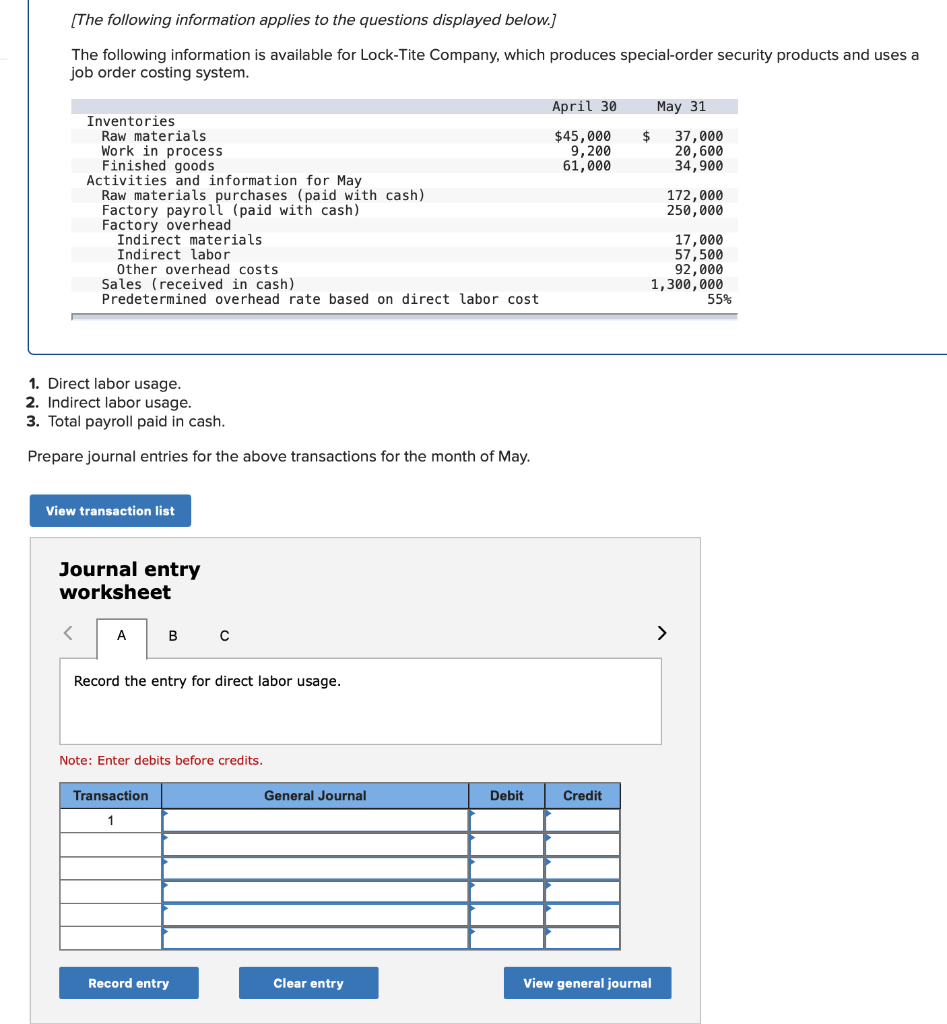
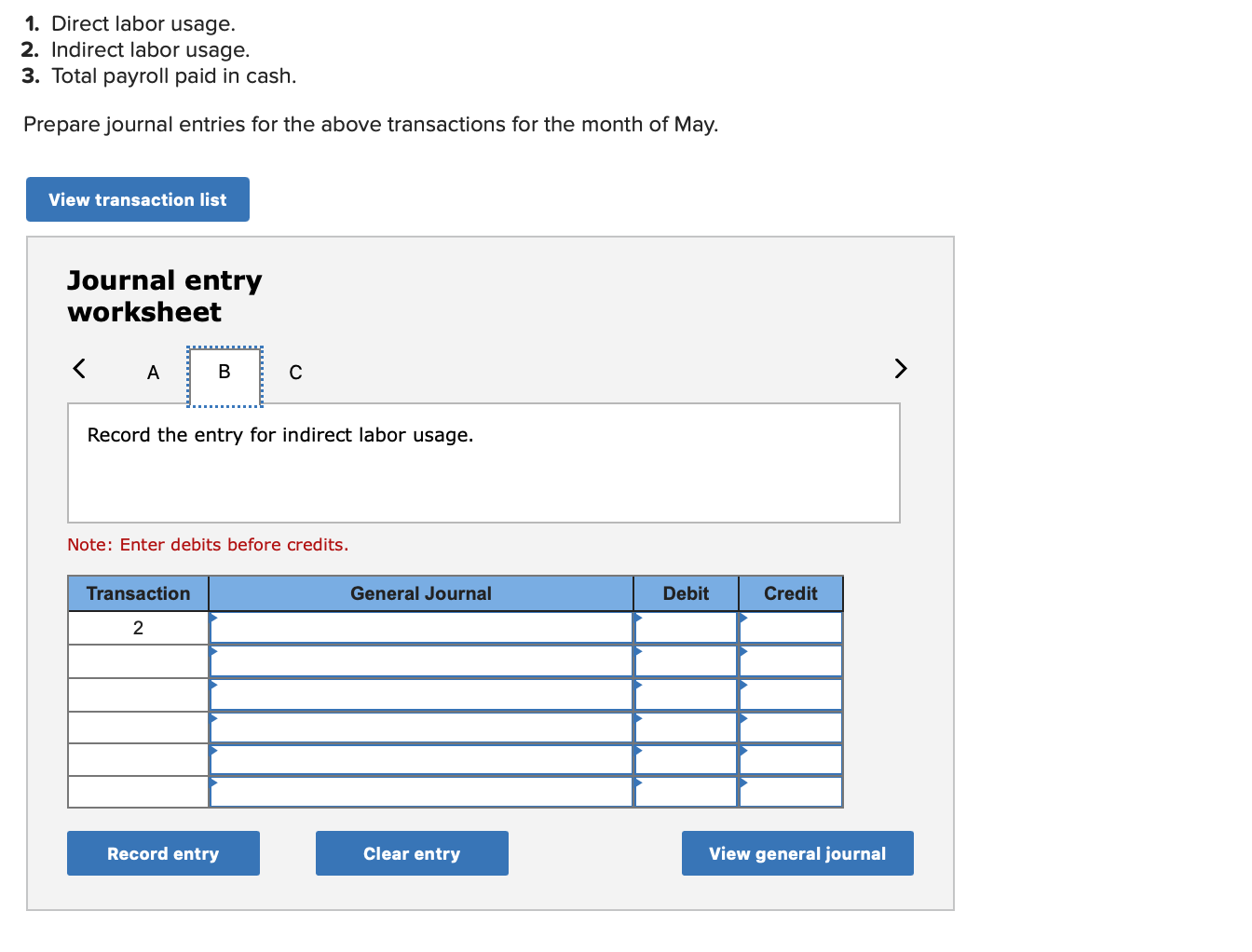
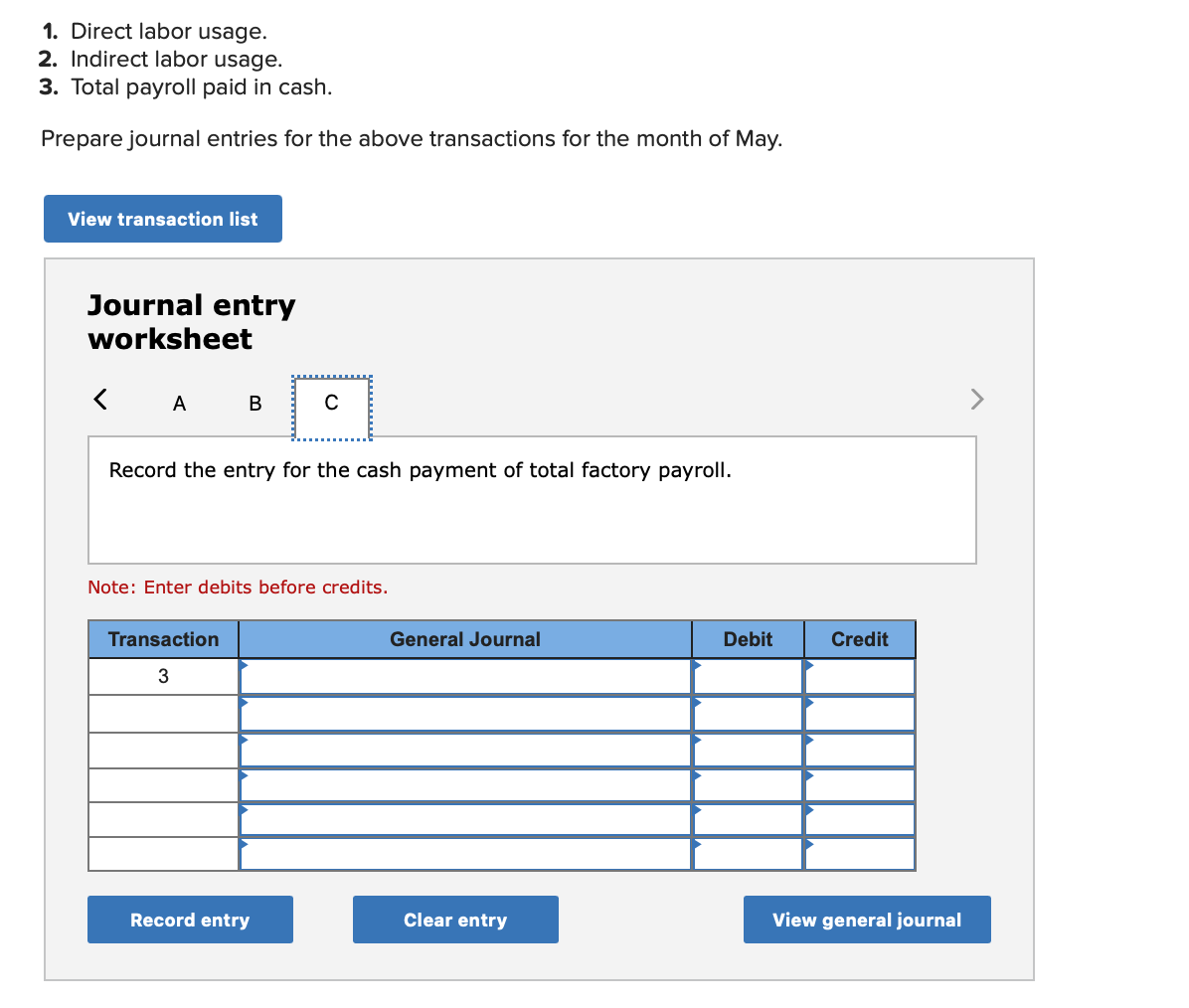
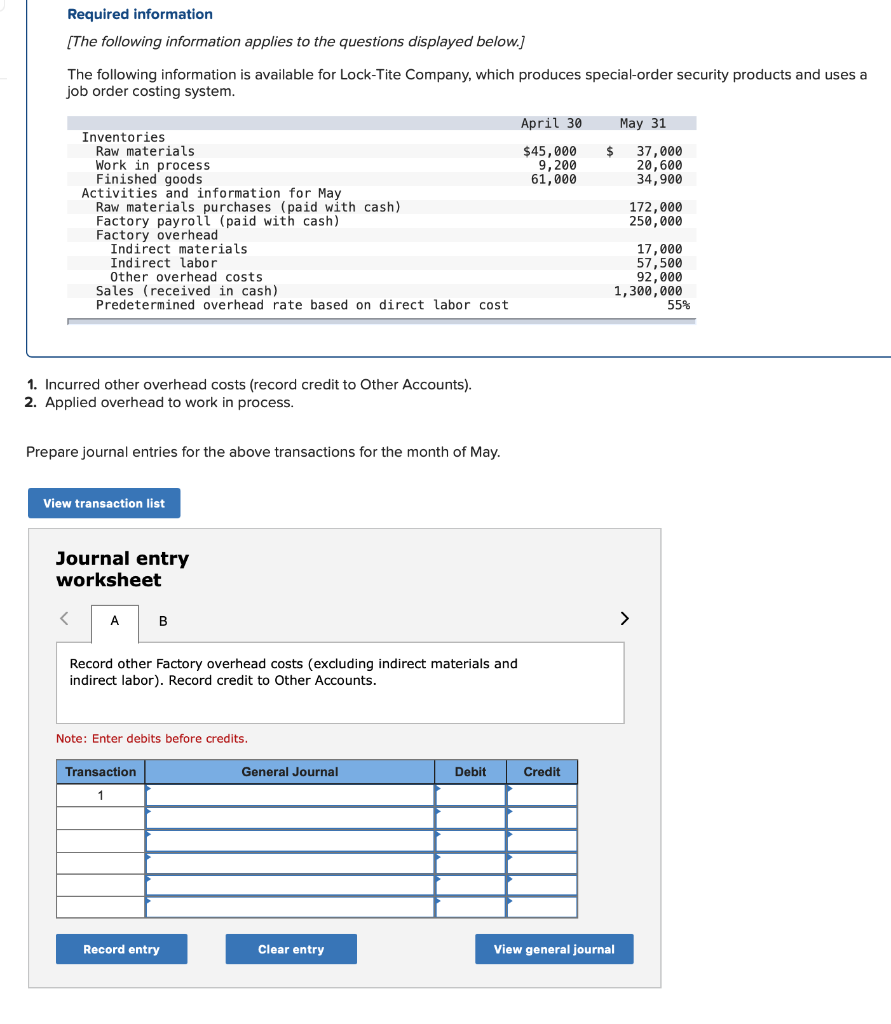
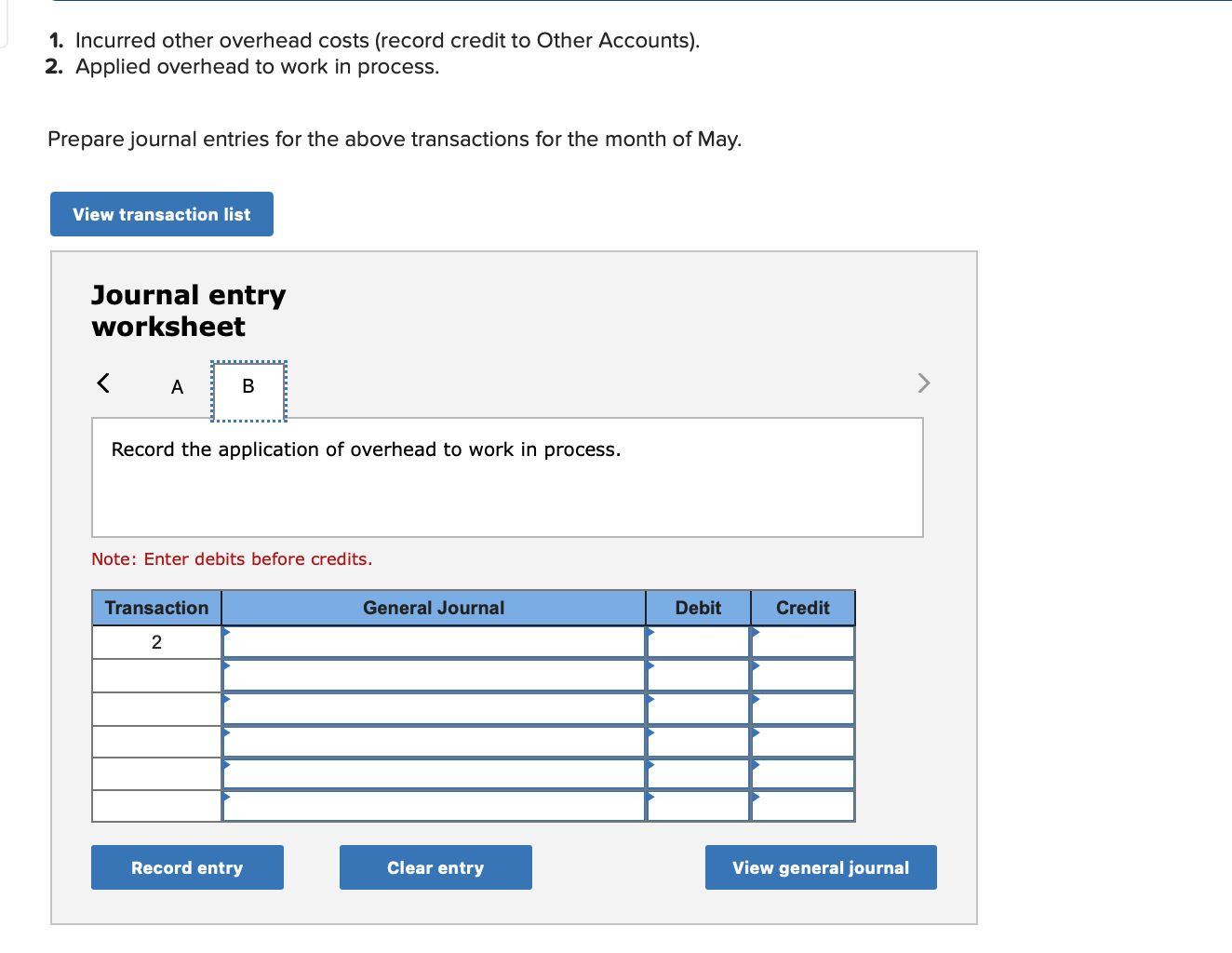
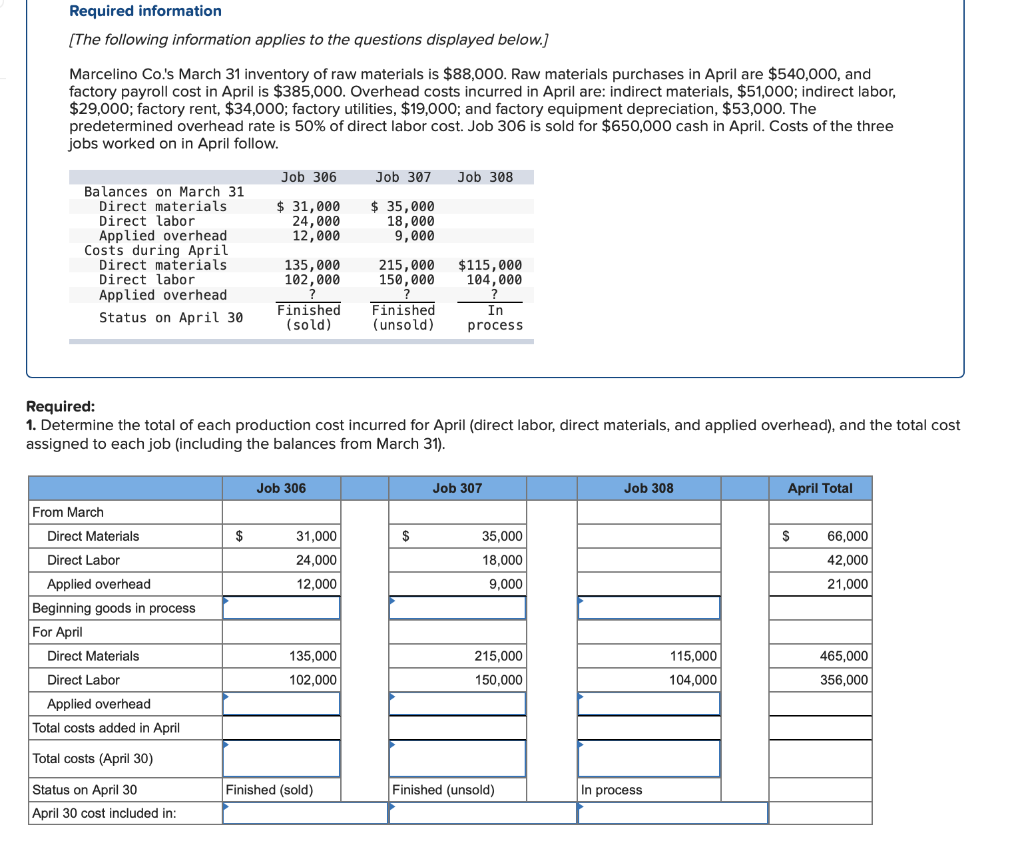
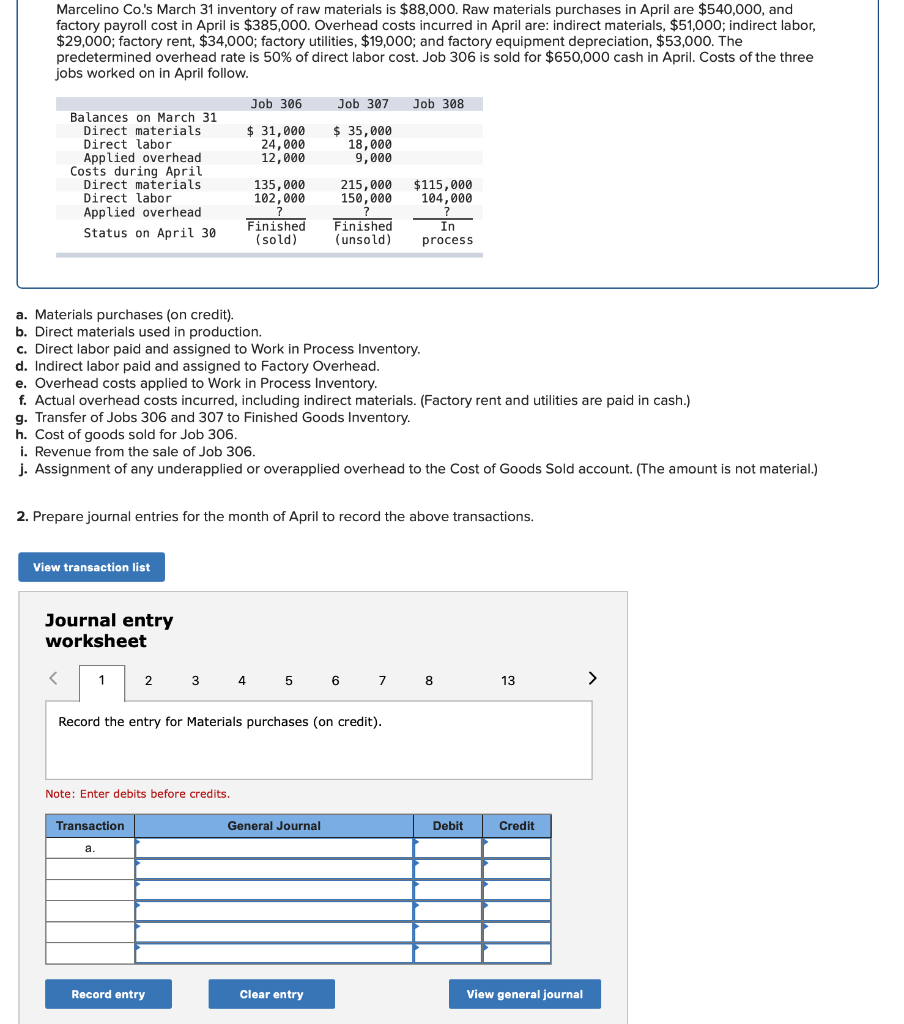
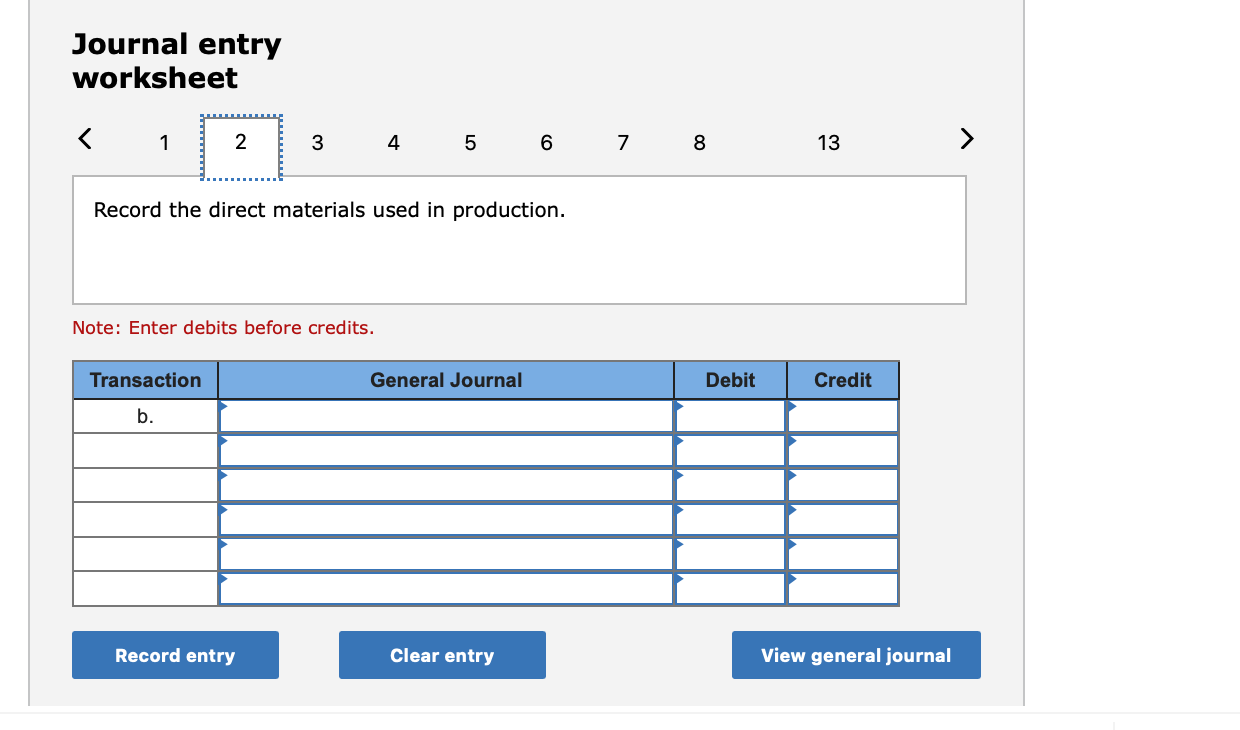
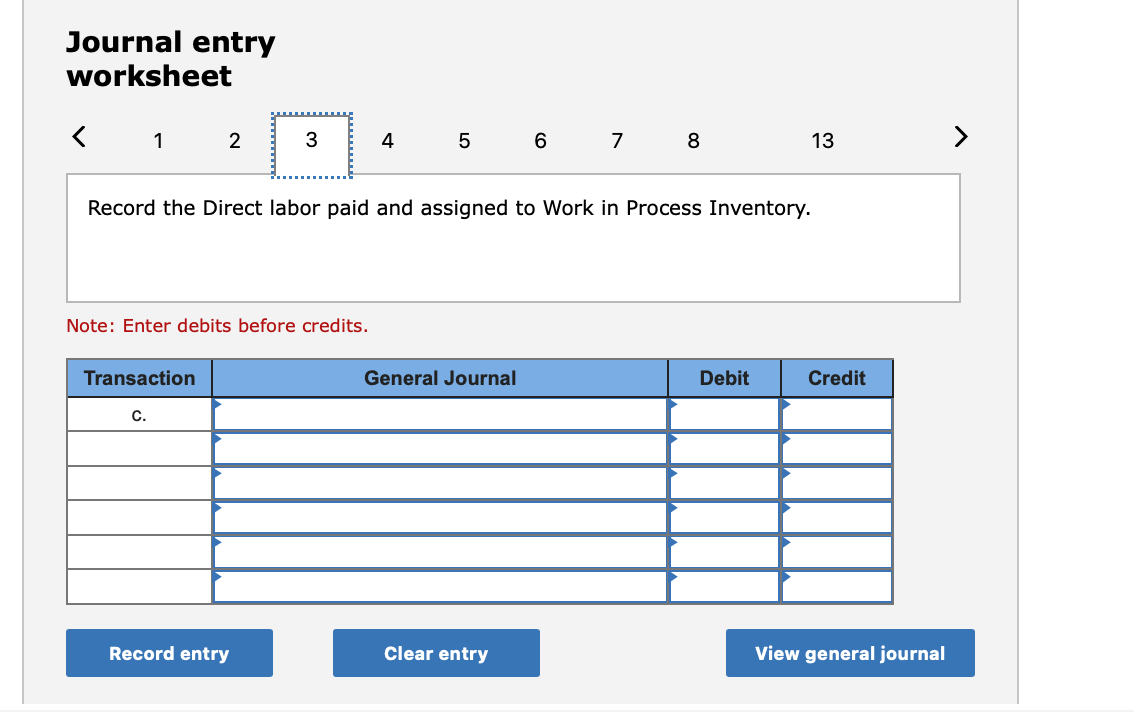
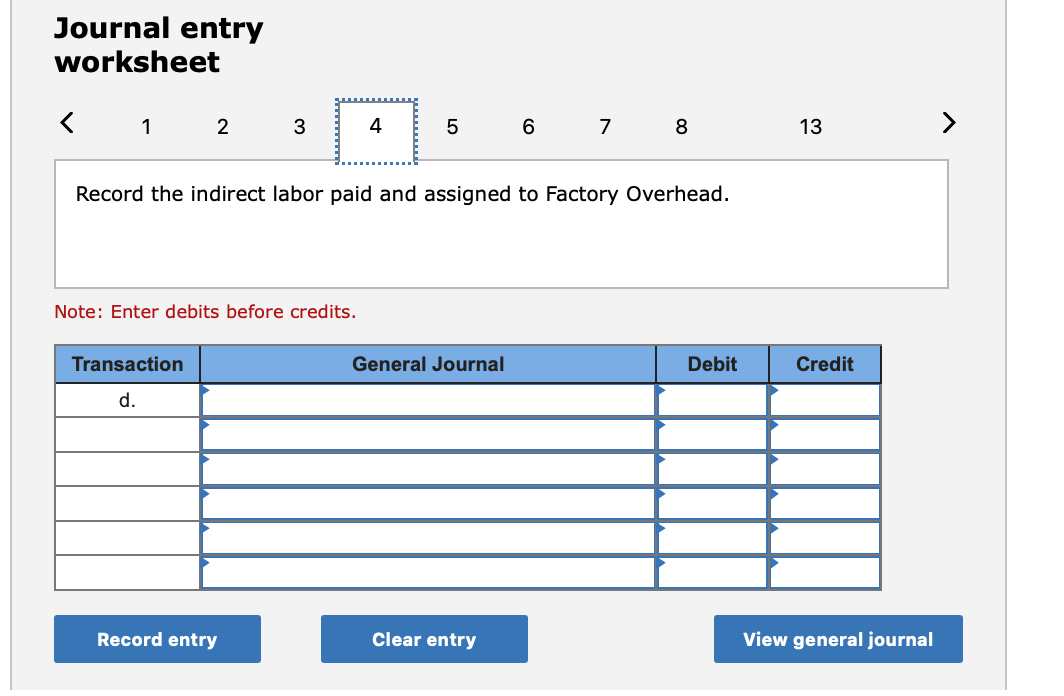
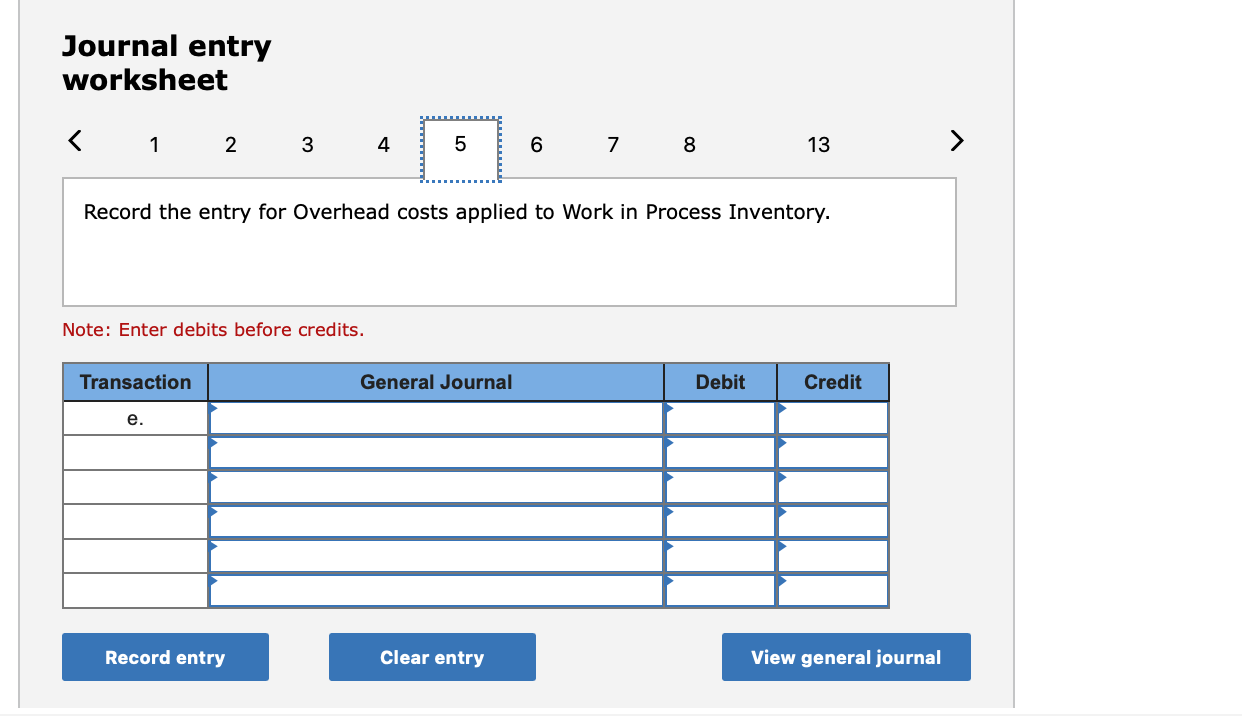
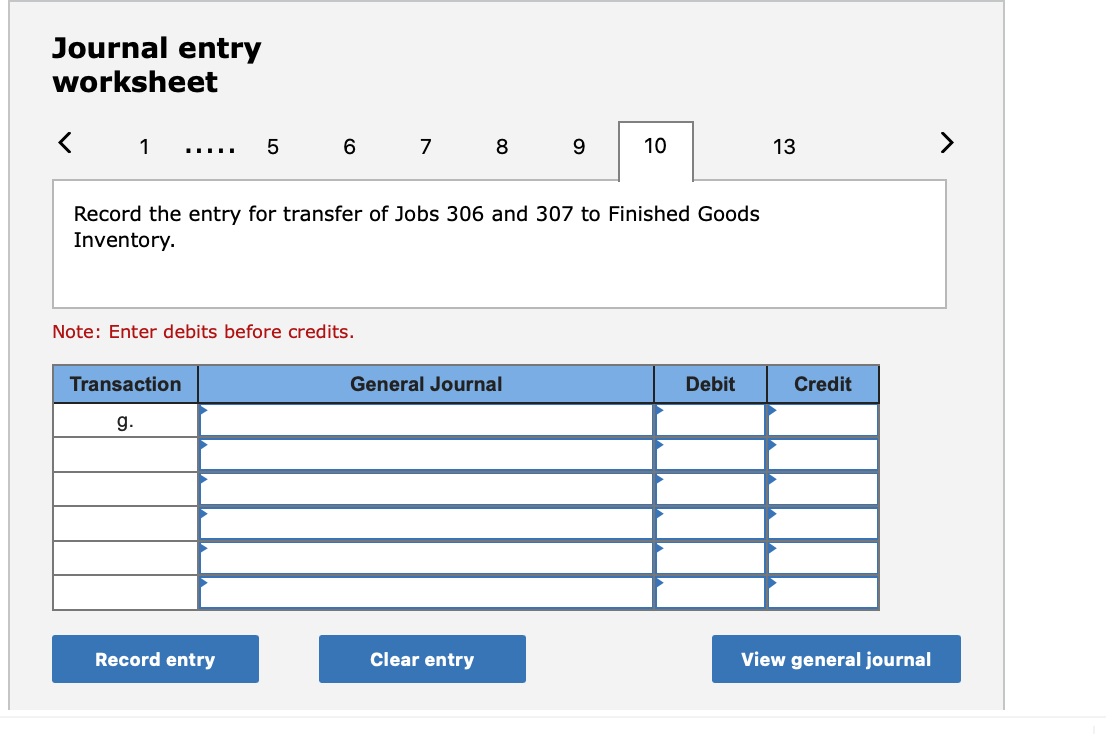
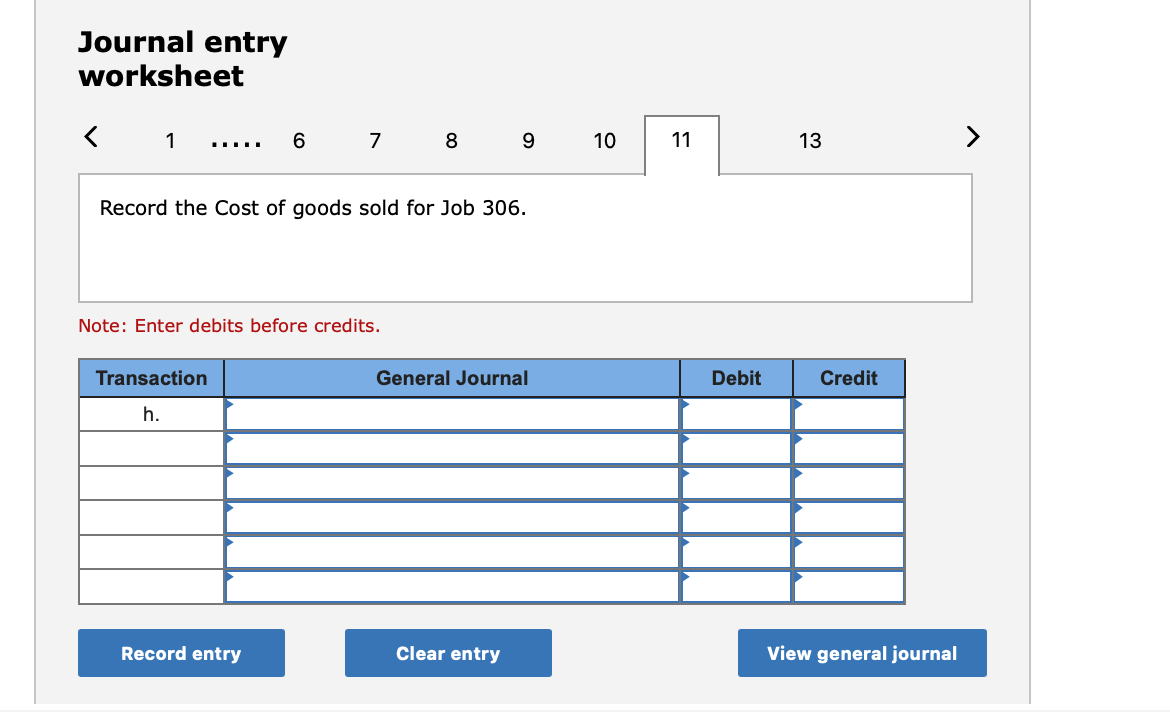
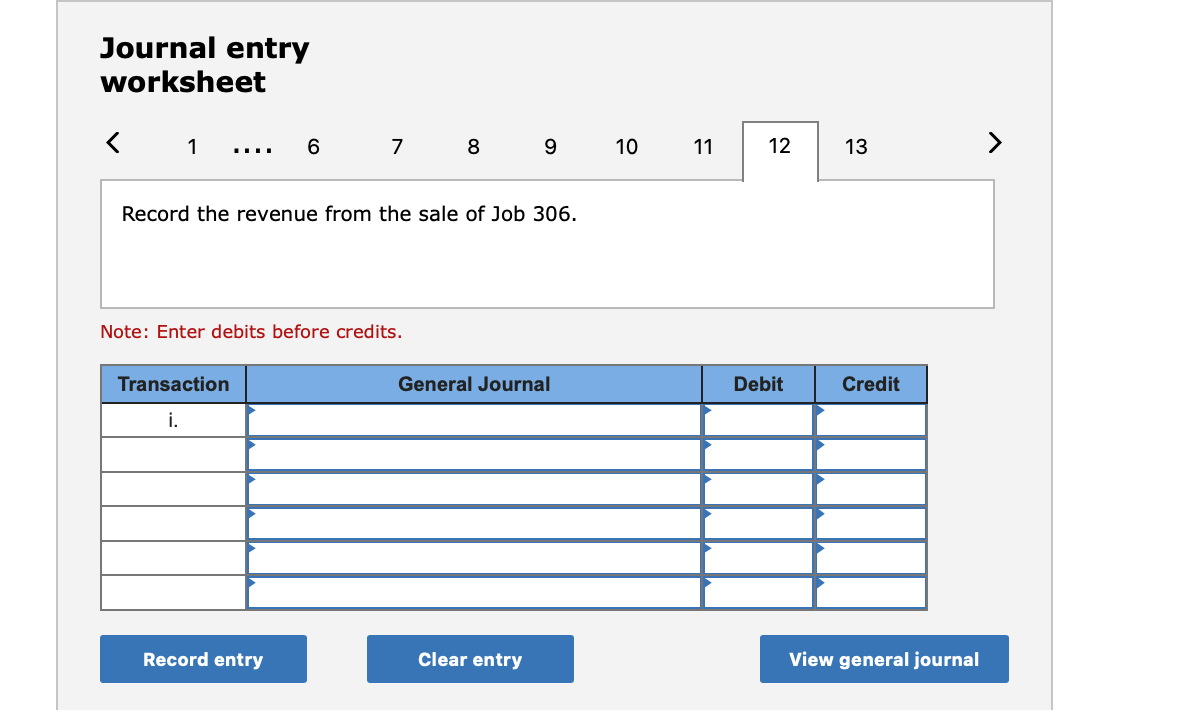
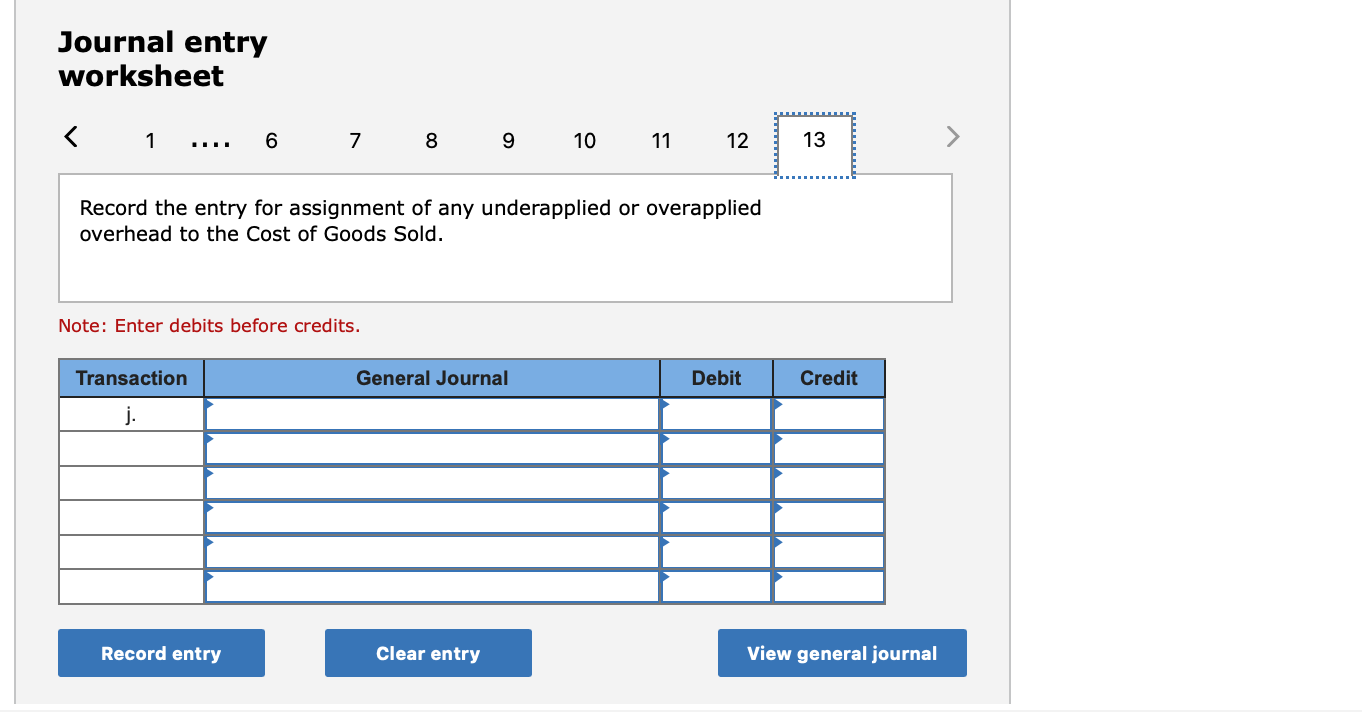
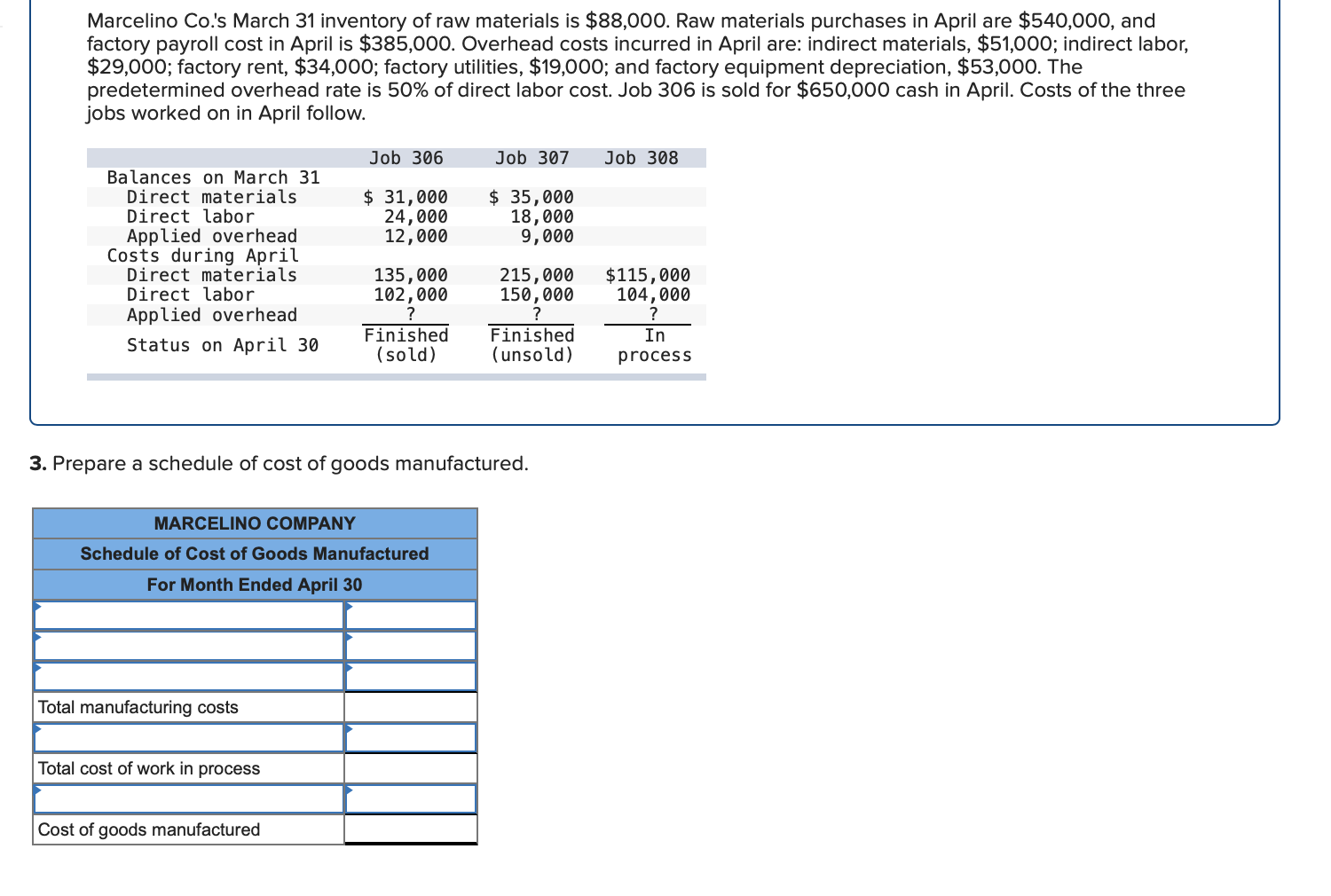
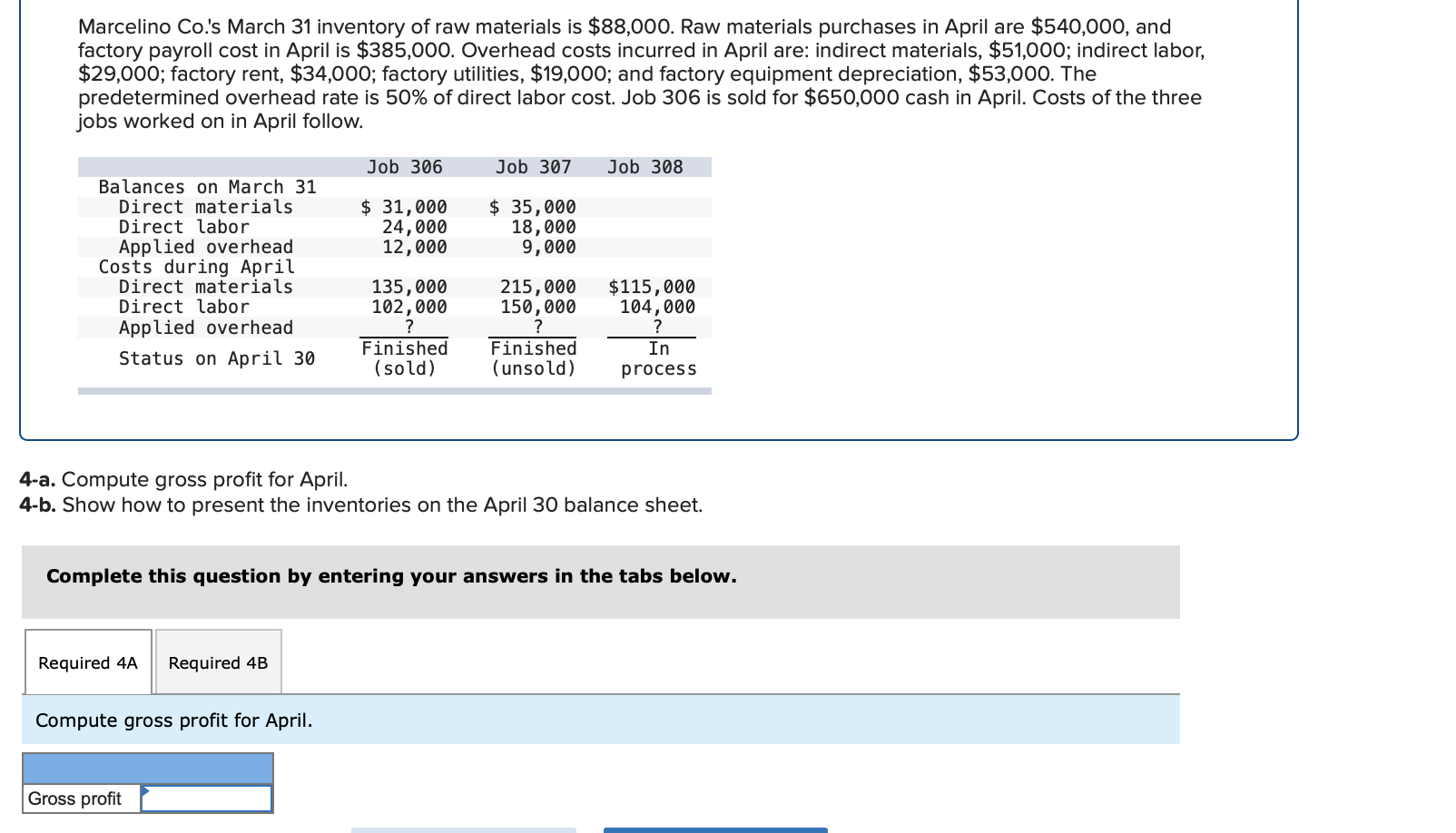
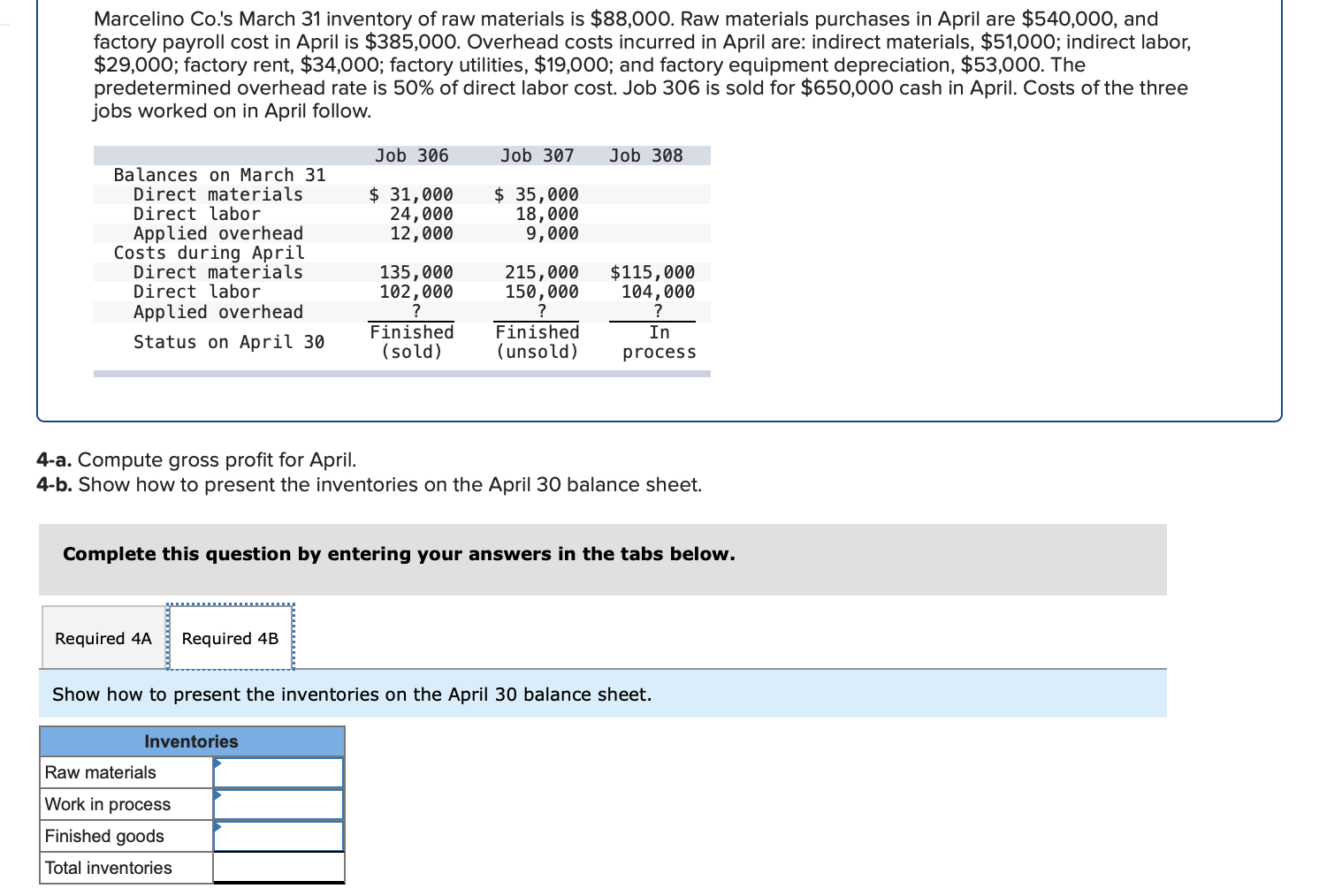
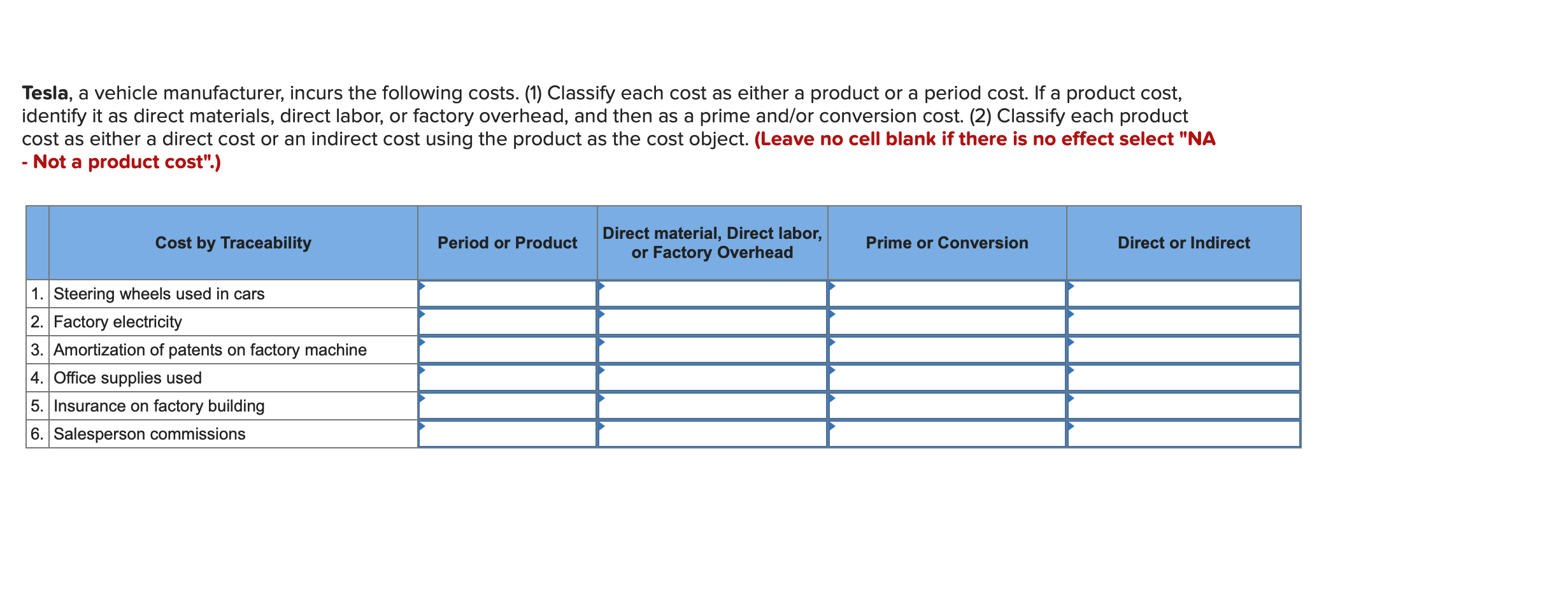
Required information (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Listed here are the total costs associated with the production of 1,000 drum sets manufactured by TrueBeat. The drum sets sell for $506 each. Costs 1. Plastic for casing-$21,000 2. Wages of assembly workers $87,000 3. Property taxes on factory-$8,000 4. Accounting staff salaries-$39,000 5. Drum stands (1,000 stands purchased) $42,000 6. Rent cost of equipment for sales staff-$24,000 7. Upper management salaries-$185,000 8. Annual flat fee for factory maintenance service-$13,000 9. Sales commissions $18 per unit 10. Machinery depreciation, straight-line-$36,000 Required: 1. Classify each cost and its amount as (a) either variable or fixed and (b) either product or period. (The first cost is completed as an example.) Cost by Behavior Cost by Function Costs Variable Fixed Product Period $ 21,000 $ 21,000 1 Plastic for casing 2. Wages of assembly workers 3. Property taxes on factory 4. Accounting staff salaries 5. Drum stands 6. Rent cost of equipment for sales staff 7. Upper management salaries 8. Annual flat fee for factory maintenance service 9. Sales commissions 10. Machinery depreciation, straight-line (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Listed here are the total costs associated with the production of 1,000 drum sets manufactured by TrueBeat. The drum sets sell for $506 each. Costs 1. Plastic for casing-$21,000 2. Wages of assembly workers-$87,000 3. Property taxes on factory-$8,000 4. Accounting staff salaries-$39,000 5. Drum stands (1,000 stands purchased)-$42,000 6. Rent cost of equipment for sales staff-$24,000 7. Upper management salaries-$185,000 8. Annual flat fee for factory maintenance service-$13,000 9. Sales commissions $18 per unit 10. Machinery depreciation, straight-line-$36,000 2. Compute the manufacturing cost per drum set. TrueBeat Calculation of Manufacturing Cost per Drum Set Item Total cost Per unit cost Variable production costs Total variable production costs Fixed production costs Total fixed production costs Total production cost Required: 1. Prepare the company's 2019 schedule of cost of goods manufactured. LEONE COMPANY Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Direct materials Raw materials available for use Direct materials used Factory overhead Total factory overhead costs Total manufacturing costs Total cost of work in process Cost of goods manufactured [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) The following calendar year-end information is taken from the December 31, 2019, adjusted trial balance and other records of Leone Company. $ 9,600 Advertising expense Depreciation expense-Office equipment Depreciation expense-Selling equipment Depreciation expense-Factory equipment Factory supervision Factory supplies used Factory utilities Inventories Raw materials, December 31, 2018 Raw materials, December 31, 2019 Work in process, December 31, 2018 Work in process, December 31, 2019 Finished goods, December 31, 2018 Finished goods, December 31, 2019 $ 32, 100 Direct labor 9,700 Income taxes expense Indirect labor 39,700 Miscellaneous production costs 110,100 Office salaries expense 7,800 Raw materials purchases 41,000 Rent expense-office space Rent expense-Selling space 158, 100 Rent expense-Factory building 191,000 Maintenance expense-Factory equipment 16,100 Sales 18,900 Sales salaries expense 165,200 141,200 689,500 259, 200 56,100 11,900 74,000 995,000 30,000 26,200 76,500 37,400 4,436,300 398,000 2. Prepare the company's 2019 income statement that reports separate categories for (a) selling expenses and (b) general and administrative expenses. LEONE COMPANY Income Statement For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Cost of goods sold Goods available for sale Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Selling expenses LEONE COMPANY Income Statement For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Cost of goods sold Goods available for sale Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Selling expenses Total selling expenses General and administrative expenses Total general and administrative expenses Total operating expenses Income before taxes Net income (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system. May 31 April 30 $45,000 9,200 61,000 $ 37,000 20,600 34,900 Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Activities and information for May Raw materials purchases (paid with cash) Factory payroll (paid with cash) Factory overhead Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead costs Sales (received in cash) Predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost 172,000 250,000 17,000 57,500 92,000 1,300,000 55% Compute the following amounts for the month of May using T-accounts. 1. Cost of direct materials used. 2. Cost of direct labor used. 3. Cost of goods manufactured. 4. Cost of goods sold. 5. Gross profit 6. Overapplied or underapplied overhead. *Do not consider any underapplied or overapplied overhead. Raw Materials (RM) Work in Process (WIP) Finished Goods (FG) Inventory Factory Overhead Income statement (partial) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below. The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system. April 30 May 31 $ $45,000 9,200 61,000 37,000 20,600 34,900 Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Activities and information for May Raw materials purchases (paid with cash) Factory payroll (paid with cash) Factory overhead Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead costs Sales (received in cash) Predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost 172,000 250,000 17,000 57,500 92,000 1,300,000 55% 1. Raw materials purchases for cash. 2. Direct materials usage. 3. Indirect materials usage. Prepare journal entrie for transactions for mc of May. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record raw material purchases for cash. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 1 Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the entry to assign direct materials to jobs. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 2 Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the entry for direct labor usage. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 1 Record entry clear entry View general journal 1. Direct labor usage. 2. Indirect labor usage. 3. Total payroll paid in cash. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record other factory overhead costs (excluding indirect materials and indirect labor). Record credit to Other Accounts. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 1 Record entry Clear entry View general journal 1. Incurred other overhead costs (record credit to Other Accounts). 2. Applied overhead to work in process. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet A B Record the application of overhead to work in process. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit 2 Record entry Clear entry View general journal Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Marcelino Co.'s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $88,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $540,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $385,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $51,000; indirect labor, $29,000; factory rent, $34,000; factory utilities, $19,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $53,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $650,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow. Job 306 Job 307 Job 308 $ 31,000 24,000 $ 35,000 18,000 9,000 12,000 Balances on March 31 Direct materials Direct labor Applied overhead Costs during April Direct materials Direct labor Applied overhead Status on April 30 135,000 102,000 $115,000 104,000 215,000 150,000 ? Finished (unsold) Finished (sold) In process Required: 1. Determine the total of each production cost incurred for April (direct labor, direct materials, and applied overhead), and the total cost assigned to each job (including the balances from March 31). Job 306 Job 307 Job 308 April Total From March Direct Materials $ $ $ 66,000 31,000 24,000 12,000 35,000 18,000 42,000 9,000 21,000 Direct Labor Applied overhead Beginning goods in process For April Direct Materials Direct Labor Applied overhead Total costs added in April 135,000 215,000 150,000 115,000 104,000 465,000 356,000 102,000 Total costs (April 30) Finished (sold) Finished (unsold) In process Status on April 30 April 30 cost included in: Marcelino Co.'s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $88,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $540,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $385,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $51,000; indirect labor, $29,000; factory rent, $34,000; factory utilities, $19,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $53,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $650,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow. Job 306 Job 307 Job 308 Balances on March 31 Direct materials Direct labor Applied overhead Costs during April Direct materials Direct labor Applied overhead Status on April 30 $ 31,000 24,000 12,000 135,000 102,000 ? Finished (sold) $ 35,000 18,000 9,000 215,000 150,000 $115,000 104,000 Finished (unsold) In process a. Materials purchases (on credit). b. Direct materials used in production. c. Direct labor paid and assigned to Work in Process Inventory. d. Indirect labor paid and assigned to Factory Overhead. e. Overhead costs applied to Work in Process Inventory. f. Actual overhead costs incurred, including indirect materials. (Factory rent and utilities are paid in cash.) g. Transfer of Jobs 306 and 307 to Finished Goods Inventory. h. Cost of goods sold for Job 306. i. Revenue from the sale of Job 306. j. Assignment of any underapplied or overapplied overhead to the Cost of Goods Sold account. (The amount is not material.) 2. Prepare journal entries for the month of April to record the above transactions. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record the entry for Materials purchases (on credit). Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit a. Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the entry for Overhead costs applied to Work in Process Inventory. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit e. Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the cost of indirect materials used. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit f(1). Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the cost of factory utilities, paid in cash. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit f(2). Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record depreciation on factory equipment. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit f(3). Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 13 > Record the cost of factory rent, paid in cash. Note: Enter debits before credits. General Journal Debit Credit Transaction f(4). Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the entry for transfer of Jobs 306 and 307 to Finished Goods Inventory. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit g. Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet Record the revenue from the sale of Job 306. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit i. Record entry Clear entry View general journal Journal entry worksheet






































