
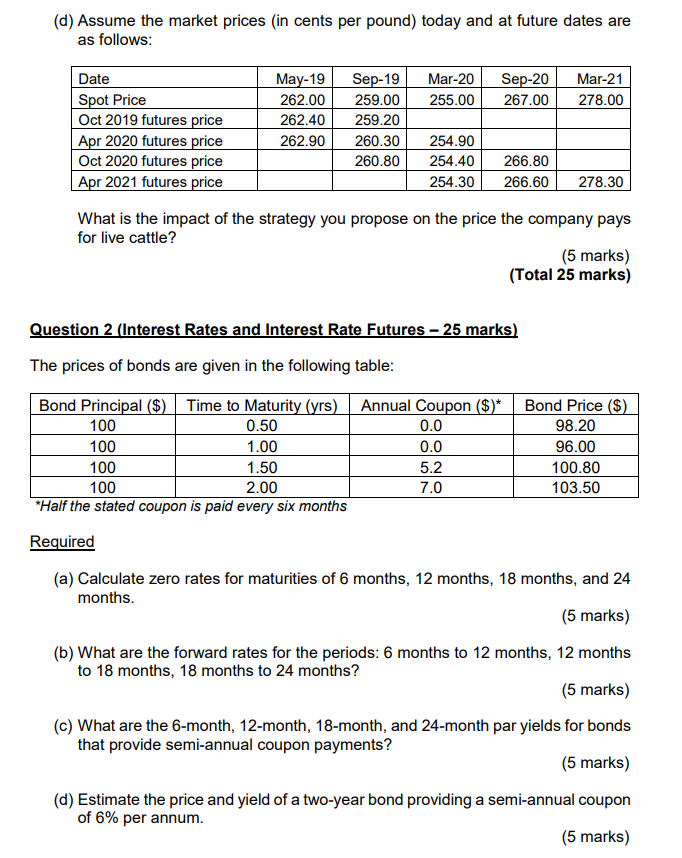



Required Question 1 (Futures/Forward Markets and Hedging 25 marks) Required (a) A company based in United Kingdom expects that it has to pay 1 million dollars in nine months for imports from United States. How can the treasury manager hedge the exchange rate risk using (i) a forward contract and (ii) an option? What is the difference between the two strategies? (5 marks) (b) You recently got a job as a treasury manager at Helium One Plc, a young oil producing company. You are proposing to the executive management of the company the use of futures contracts to hedge oil price risk. The response of the chief executive is that using futures is similar to betting in a casino as you can never predict whether oil prices at maturity are going to be greater or lower than futures price. I don't see the need therefore for using futures contracts". Discuss the executive's viewpoint. (10 marks) Assume that in May 2019, a company anticipates that it will purchase 2 million pounds of live cattle in each of September 2019, March 2020, September 2020, and March 2021. The company has decided to use the futures contracts traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange to hedge its risk. One contract is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of live cattle. The company's policy is to hedge 70% of its exposure. Contracts with maturities up to 15 months into the future are considered to have sufficient liquidity to meet the company's needs. Required (c) Propose a hedging strategy for the company. (5 marks) (d) Assume the market prices (in cents per pound) today and at future dates are as follows: Mar-20 Mar-21 May-19 262.00 Sep-19 259.00 259.20 Sep-20 267.00 255.00 278.00 262.40 Date Spot Price Oct 2019 futures price Apr 2020 futures price Oct 2020 futures price Apr 2021 futures price 262.90 260.30 254.90 260.80 254.40 266.80 254.30 266.60 278.30 What is the impact of the strategy you propose on the price the company pays for live cattle? (5 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 2 (Interest Rates and Interest Rate Futures - 25 marks) The prices of bonds are given in the following table: Bond Principal ($) Time to Maturity (yrs) Annual Coupon ($)* Bond Price ($) 98.20 100 0.0 0.0 96.00 0.50 100 1.00 100 1.50 100 2.00 *Half the stated coupon is paid every six months 5.2 7.0 100.80 103.50 Required (a) Calculate zero rates for maturities of 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months. (5 marks) (b) What are the forward rates for the periods: 6 months to 12 months, 12 months to 18 months, 18 months to 24 months? (5 marks) (c) What are the 6-month, 12-month, 18-month, and 24-month par yields for bonds that provide semi-annual coupon payments? (5 marks) (d) Estimate the price and yield of a two-year bond providing a semi-annual coupon of 6% per annum. (5 marks) A five-year bond with a yield of 10% (continuously compounded) pays a 7% coupon at the end of each year. 3 Page Required (e) Estimate the bond's duration and use the duration to calculate the effect on the bond's price of a 0.2% decrease in its yield. Calculate the bond's price on the basis of a 9.8% per annum yield and verify that the result is in agreement with your answer. (5 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 3 (Futures and Forward Prices - 25 marks) An investor has just taken a short position in a six-month forward contract on a dividend-paying stock. The stock price is 132.00, and the risk-free rate of interest is 6% per annum with continuous compounding for all maturities. The stock is expected to pay a dividend of 2 per share in two months and in five months. Required (a) What are the forward price and the initial value of the forward contract? (4 marks) (b) Three months later, the price of the stock is 48 and the risk-free rate of interest is still 6% per annum. What are the forward price and the value of the short position in the forward contract? (4 marks) The risk-free rate of interest is 6% per annum with continuous compounding, and the dividend yield on a stock index is 3.0% per annum. The current value of the index is 500. Required (c) What is the six-month futures price? (3 marks) (d) Assume that the futures price for a contract deliverable in six months is 510. What arbitrage opportunities does this create? (4 marks) (e) The futures price of gold can be calculated from its spot price and other observable variables whereas the futures price of copper cannot. Discuss why this is the case. (10 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 4 (SWAPS - 25 marks) Suppose that the term structure of interest rates is flat in the United States and Switzerland. The dollar interest rate is 5.8% per annum, and the market interest rate is 4.2% per annum. The current exchange rate is 2.71 Swiss francs per dollar. Under the terms of a swap agreement, a financial institution pays 5% per annum in Swiss francs and receives 7.0% per annum in dollars. The principals in the two currencies are 10 million dollars and 30 million Swiss francs. Payments are exchanged every year, with one exchange having just taken place. The swap will last for two more years. Required a) What is the value of the swap to the financial institution? Assume all interest rates are continuously compounded. (5 marks) b) How you would value a swap that is the exchange of a floating rate in one currency for a fixed rate in another currency? Explain in detail. (5 marks) Companies Alpha Plc and Bravo Plc face the following interest rates (adjusted for the differential impact of taxes): Alpha plc Bravo Pic US Dollars (floating rate) LIBOR+0.4% LIBOR+1.4% Swiss Francs (fixed rate) 4.9% 5.9% Assume that Alpha Plc wants to borrow U.S. dollars at a floating rate of interest and Bravo Plc wants to borrow Swiss Francs at a fixed rate of interest. A financial institution is planning to arrange a swap and requires a 50-basis-point spread. Required c) If the swap is equally attractive to Alpha and Bravo, what rates of interest will Alpha and Bravo end up paying? (5 marks) d) Are there any kinds of risk the bank is exposed to when it enters into two offsetting swap contracts? (5 marks) e) Critically discuss the comparative advantage argument in relation to swaps. (5 marks) (Total 25 marks) Required Question 1 (Futures/Forward Markets and Hedging 25 marks) Required (a) A company based in United Kingdom expects that it has to pay 1 million dollars in nine months for imports from United States. How can the treasury manager hedge the exchange rate risk using (i) a forward contract and (ii) an option? What is the difference between the two strategies? (5 marks) (b) You recently got a job as a treasury manager at Helium One Plc, a young oil producing company. You are proposing to the executive management of the company the use of futures contracts to hedge oil price risk. The response of the chief executive is that using futures is similar to betting in a casino as you can never predict whether oil prices at maturity are going to be greater or lower than futures price. I don't see the need therefore for using futures contracts". Discuss the executive's viewpoint. (10 marks) Assume that in May 2019, a company anticipates that it will purchase 2 million pounds of live cattle in each of September 2019, March 2020, September 2020, and March 2021. The company has decided to use the futures contracts traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange to hedge its risk. One contract is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of live cattle. The company's policy is to hedge 70% of its exposure. Contracts with maturities up to 15 months into the future are considered to have sufficient liquidity to meet the company's needs. Required (c) Propose a hedging strategy for the company. (5 marks) (d) Assume the market prices (in cents per pound) today and at future dates are as follows: Mar-20 Mar-21 May-19 262.00 Sep-19 259.00 259.20 Sep-20 267.00 255.00 278.00 262.40 Date Spot Price Oct 2019 futures price Apr 2020 futures price Oct 2020 futures price Apr 2021 futures price 262.90 260.30 254.90 260.80 254.40 266.80 254.30 266.60 278.30 What is the impact of the strategy you propose on the price the company pays for live cattle? (5 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 2 (Interest Rates and Interest Rate Futures - 25 marks) The prices of bonds are given in the following table: Bond Principal ($) Time to Maturity (yrs) Annual Coupon ($)* Bond Price ($) 98.20 100 0.0 0.0 96.00 0.50 100 1.00 100 1.50 100 2.00 *Half the stated coupon is paid every six months 5.2 7.0 100.80 103.50 Required (a) Calculate zero rates for maturities of 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months. (5 marks) (b) What are the forward rates for the periods: 6 months to 12 months, 12 months to 18 months, 18 months to 24 months? (5 marks) (c) What are the 6-month, 12-month, 18-month, and 24-month par yields for bonds that provide semi-annual coupon payments? (5 marks) (d) Estimate the price and yield of a two-year bond providing a semi-annual coupon of 6% per annum. (5 marks) A five-year bond with a yield of 10% (continuously compounded) pays a 7% coupon at the end of each year. 3 Page Required (e) Estimate the bond's duration and use the duration to calculate the effect on the bond's price of a 0.2% decrease in its yield. Calculate the bond's price on the basis of a 9.8% per annum yield and verify that the result is in agreement with your answer. (5 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 3 (Futures and Forward Prices - 25 marks) An investor has just taken a short position in a six-month forward contract on a dividend-paying stock. The stock price is 132.00, and the risk-free rate of interest is 6% per annum with continuous compounding for all maturities. The stock is expected to pay a dividend of 2 per share in two months and in five months. Required (a) What are the forward price and the initial value of the forward contract? (4 marks) (b) Three months later, the price of the stock is 48 and the risk-free rate of interest is still 6% per annum. What are the forward price and the value of the short position in the forward contract? (4 marks) The risk-free rate of interest is 6% per annum with continuous compounding, and the dividend yield on a stock index is 3.0% per annum. The current value of the index is 500. Required (c) What is the six-month futures price? (3 marks) (d) Assume that the futures price for a contract deliverable in six months is 510. What arbitrage opportunities does this create? (4 marks) (e) The futures price of gold can be calculated from its spot price and other observable variables whereas the futures price of copper cannot. Discuss why this is the case. (10 marks) (Total 25 marks) Question 4 (SWAPS - 25 marks) Suppose that the term structure of interest rates is flat in the United States and Switzerland. The dollar interest rate is 5.8% per annum, and the market interest rate is 4.2% per annum. The current exchange rate is 2.71 Swiss francs per dollar. Under the terms of a swap agreement, a financial institution pays 5% per annum in Swiss francs and receives 7.0% per annum in dollars. The principals in the two currencies are 10 million dollars and 30 million Swiss francs. Payments are exchanged every year, with one exchange having just taken place. The swap will last for two more years. Required a) What is the value of the swap to the financial institution? Assume all interest rates are continuously compounded. (5 marks) b) How you would value a swap that is the exchange of a floating rate in one currency for a fixed rate in another currency? Explain in detail. (5 marks) Companies Alpha Plc and Bravo Plc face the following interest rates (adjusted for the differential impact of taxes): Alpha plc Bravo Pic US Dollars (floating rate) LIBOR+0.4% LIBOR+1.4% Swiss Francs (fixed rate) 4.9% 5.9% Assume that Alpha Plc wants to borrow U.S. dollars at a floating rate of interest and Bravo Plc wants to borrow Swiss Francs at a fixed rate of interest. A financial institution is planning to arrange a swap and requires a 50-basis-point spread. Required c) If the swap is equally attractive to Alpha and Bravo, what rates of interest will Alpha and Bravo end up paying? (5 marks) d) Are there any kinds of risk the bank is exposed to when it enters into two offsetting swap contracts? (5 marks) e) Critically discuss the comparative advantage argument in relation to swaps. (5 marks) (Total 25 marks)











