Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Requirement 1. Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the FIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory,
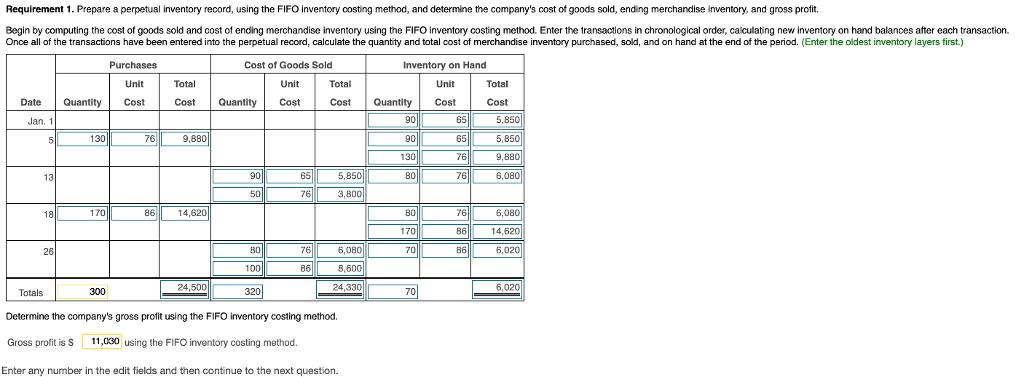
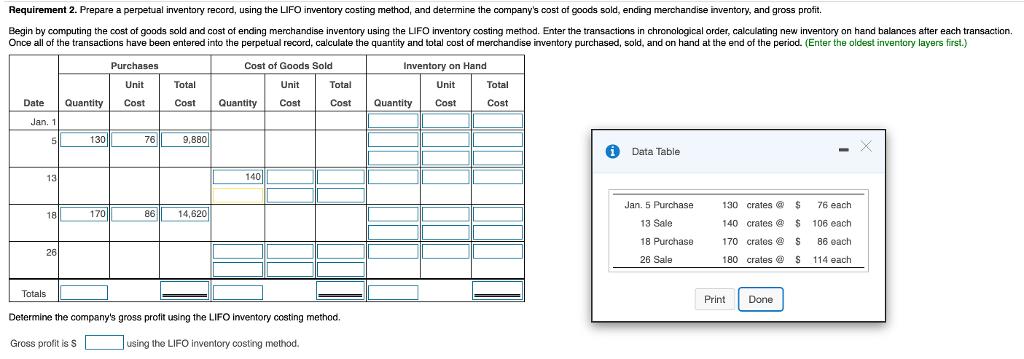
Requirement 1. Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the FIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Cost of Goods Sold Inventory on Hand Unit Cost Date Jan. 11 5 13 18 26 Quantity 130 170 300 Purchases Unit Cost 76 Total Cost 9,880 861 14,620 24,500 Unit Quantity Cost 90 50 80 100 320 65 76 76 86 Total Cost 5,850 3,800 Totals Determine the company's gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. Gross profit is S 11,030 using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter any number in the edit fields and then continue to the next question. 6,080 8,600 24,330 Quantity 90 90 130 80 80 170 70 70 65 65 76 76 76 86 86 Total Cost 5.850 5,850 9,880 6,080 6.080 14,620 6,020 6,020 Requirement 2. Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the LIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the LIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Cost of Goods Sold Inventory on Hand Unit Cost Unit Cost Date Jan. 1 Totals 5 13 18 26 Quantity 130 170 Purchases Unit Cost 76 86 Total Cost 9.880 14,620 Quantity 140 Total Cost Determine the company's gross profit using the LIFO inventory costing method. Gross profit is S using the LIFO inventory costing method. Quantity Total Cost Data Table Jan. 5 Purchase 13 Sale 18 Purchase 26 Sale 130 crates @ $ 140 crates @ $ 170 crates @ S 180 crates S Print Done 76 each 106 each 86 each 114 each
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.34 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Requirement 1 Jan01 Jan05 Jan13 Jan18 Jan26 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


