Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
researchers typically specify the alternative hypothesis to align with the expected outcome from the test, so rejection of the null hypothesis provides support for this
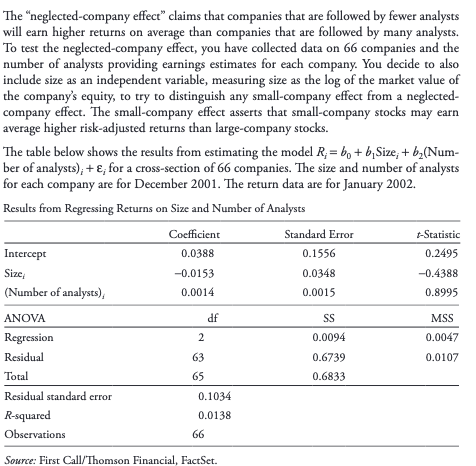
researchers typically specify the alternative hypothesis to align with the expected outcome from the test, so rejection of the null hypothesis provides support for this outcome. Accordingly, would you specify the alternative hypothesis for the "neglected company effect" as positive or negative? Would you specify the alternative hypothesis for the "small company effect" as positive or negative? Based on the individual t-statistics for these coefficients, does it appear that either effect is supported by the evidence in these fitted models?
The "neglected company effect" claims that companies that are followed by fewer analysts will earn higher returns on average than companies that are followed by many analysts. To test the neglected company effect, you have collected data on 66 companies and the number of analysts providing earnings estimates for each company. You decide to also include size as an independent variable, measuring size as the log of the market value of the company's equity, to try to distinguish any small-company effect from a neglected- company effect. The small-company effect asserts that small-company stocks may earn average higher risk-adjusted returns than large-company stocks. The table below shows the results from estimating the model R;= b + b Size: + b(Num- ber of analysts); + E; for a cross-section of 66 companies. The size and number of analysts for each company are for December 2001. The return data are for January 2002. Results from Regressing Returns on Size and Number of Analysts Coefficient Standard Error -Statistic Intercept 0.0388 0.1556 0.2495 Size -0.0153 0.0348 -0.4388 (Number of analysts), 0.0014 0.0015 0.8995 ANOVA df SS MSS Regression 2 0.0094 0.0047 Residual 63 0.6739 0.0107 Total 65 0.6833 Residual standard error 0.1034 R-squared 0.0138 Observations 66 2 Source: First Call/Thomson Financial, FactSet. The "neglected company effect" claims that companies that are followed by fewer analysts will earn higher returns on average than companies that are followed by many analysts. To test the neglected company effect, you have collected data on 66 companies and the number of analysts providing earnings estimates for each company. You decide to also include size as an independent variable, measuring size as the log of the market value of the company's equity, to try to distinguish any small-company effect from a neglected- company effect. The small-company effect asserts that small-company stocks may earn average higher risk-adjusted returns than large-company stocks. The table below shows the results from estimating the model R;= b + b Size: + b(Num- ber of analysts); + E; for a cross-section of 66 companies. The size and number of analysts for each company are for December 2001. The return data are for January 2002. Results from Regressing Returns on Size and Number of Analysts Coefficient Standard Error -Statistic Intercept 0.0388 0.1556 0.2495 Size -0.0153 0.0348 -0.4388 (Number of analysts), 0.0014 0.0015 0.8995 ANOVA df SS MSS Regression 2 0.0094 0.0047 Residual 63 0.6739 0.0107 Total 65 0.6833 Residual standard error 0.1034 R-squared 0.0138 Observations 66 2 Source: First Call/Thomson Financial, FactSetStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


