Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Retained earnings versus new common stock Using the data for each firm shown in the following table. calculate the cost of retained earnings and
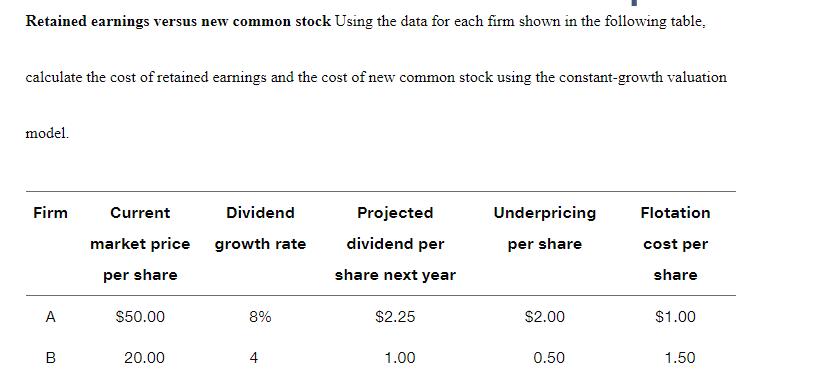

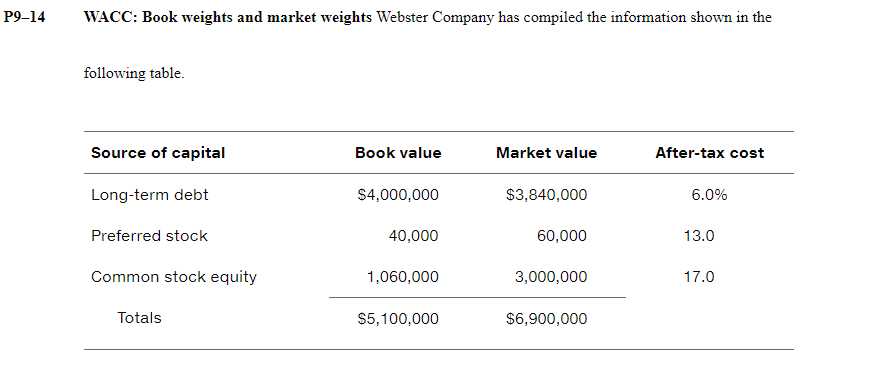

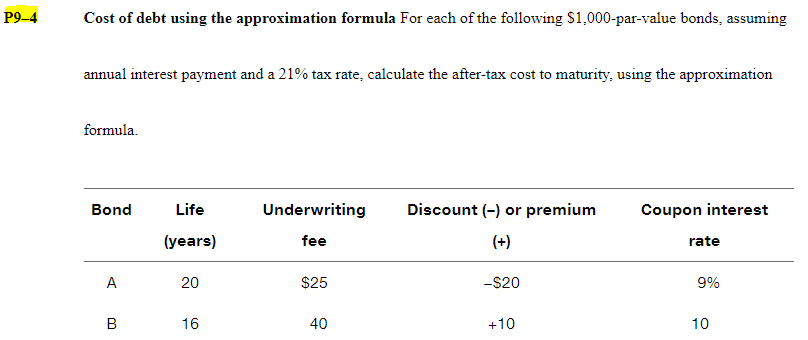
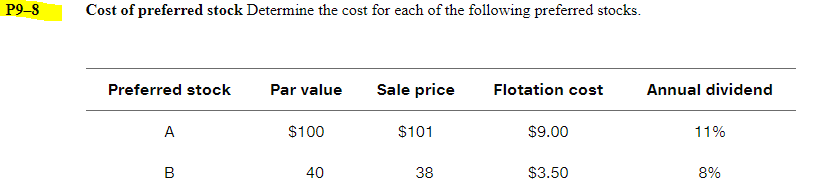
Retained earnings versus new common stock Using the data for each firm shown in the following table. calculate the cost of retained earnings and the cost of new common stock using the constant-growth valuation model. Firm Current Dividend Projected Underpricing Flotation market price growth rate dividend per per share cost per per share share next year share A $50.00 8% $2.25 $2.00 $1.00 B 20.00 4 1.00 0.50 1.50 WACC= (rd At) (wd) + (rp)(wp) + (rror'n)(ws) rda-t- after tax cost of debt wd=weight of debt over total capital structure rp=cost of preferred dividends wp-weight of preferred stock over total capital structure rs=cost of equity, could be rr or rn ws-weight of equity over total capital structure = Dp/(Pp - F) = Dp/(NP) Dp the annual dividend payment in dollars Np= the net proceeds from the sale of the preferred stock "F" represents flotation costs (in $) Before-tax cost of the debt. rd= I + [($1,000- Na)] n (Na+ $1,000) 2 I the annual interest payment in dollars Nd = the net proceeds from the sale of a bond n = the term of the bond in years Cost of Common Stock Equity (rs) rs = rn or rr 3 Ways to determine rs: Using DDM (Dividend Discount Models) rs = (D/P) + g Using CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Models) s = + b(k - ) Own-Bond-Yield-Plus-Risk Premium rs rd + Bond RP After-tax debt cost (ri) rd (at) = rdx (1-T) Where T is the firm's tax rate. And rd = YTM P9-14 WACC: Book weights and market weights Webster Company has compiled the information shown in the following table. Source of capital Book value Market value After-tax cost Long-term debt $4,000,000 $3,840,000 6.0% Preferred stock 40,000 60,000 13.0 Common stock equity 1,060,000 3,000,000 17.0 Totals $5,100,000 $6,900,000 P9-21 Ethics Problem During the 1990s, General Electric put together a long string of consecutive quarters in which the firm managed to meet or beat the earnings forecasts of Wall Street stock analysts. Some skeptics wondered if GE "managed" earnings to meet Wall Street's expectations, meaning that GE used accounting gimmicks to conceal the true volatility in its business. How do you think GE's long-run track record of meeting or beating earnings forecasts affected its cost of capital? If investors learn that GE's performance was achieved largely through accounting gimmicks, how do you think they would respond? P9-4 Cost of debt using the approximation formula For each of the following $1,000-par-value bonds, assuming annual interest payment and a 21% tax rate, calculate the after-tax cost to maturity, using the approximation formula. Bond Life (years) Underwriting fee Discount (-) or premium Coupon interest (+) rate A 20 $25 -$20 9% B 16 40 +10 10 P9-8 Cost of preferred stock Determine the cost for each of the following preferred stocks. Preferred stock Par value Sale price Flotation cost Annual dividend A $100 $101 $9.00 11% B 40 38 $3.50 8%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


