Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
RITY (Percent of terrorists caught) The blue curve on the following graph shows the tradeoff between security and tourism; that is, combinations of security
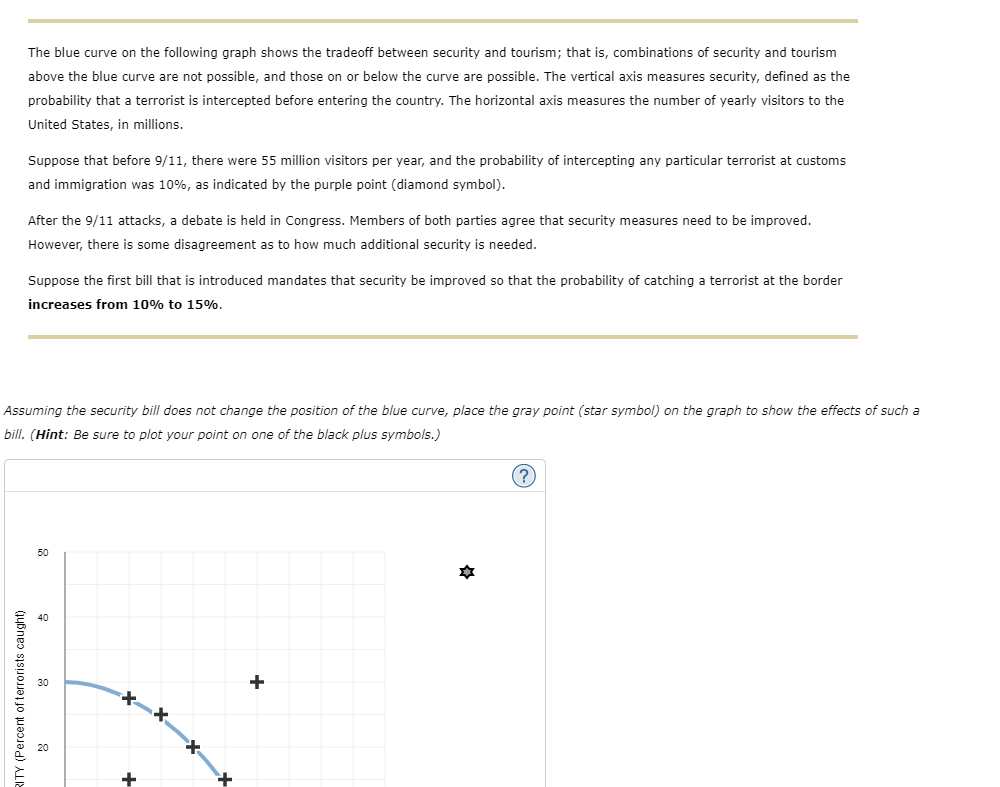
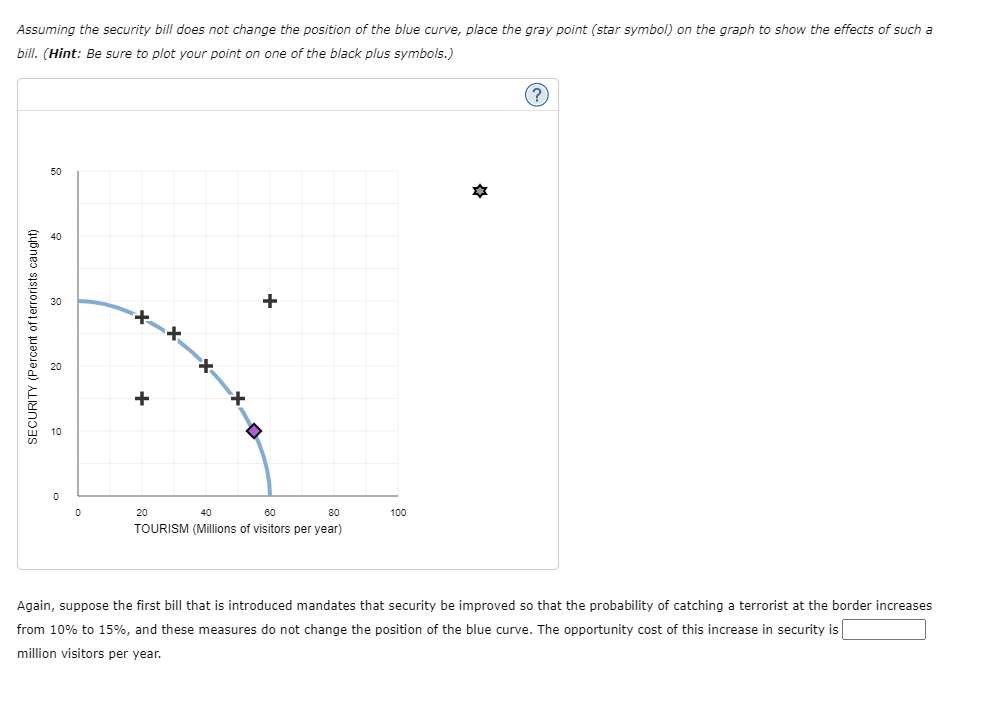
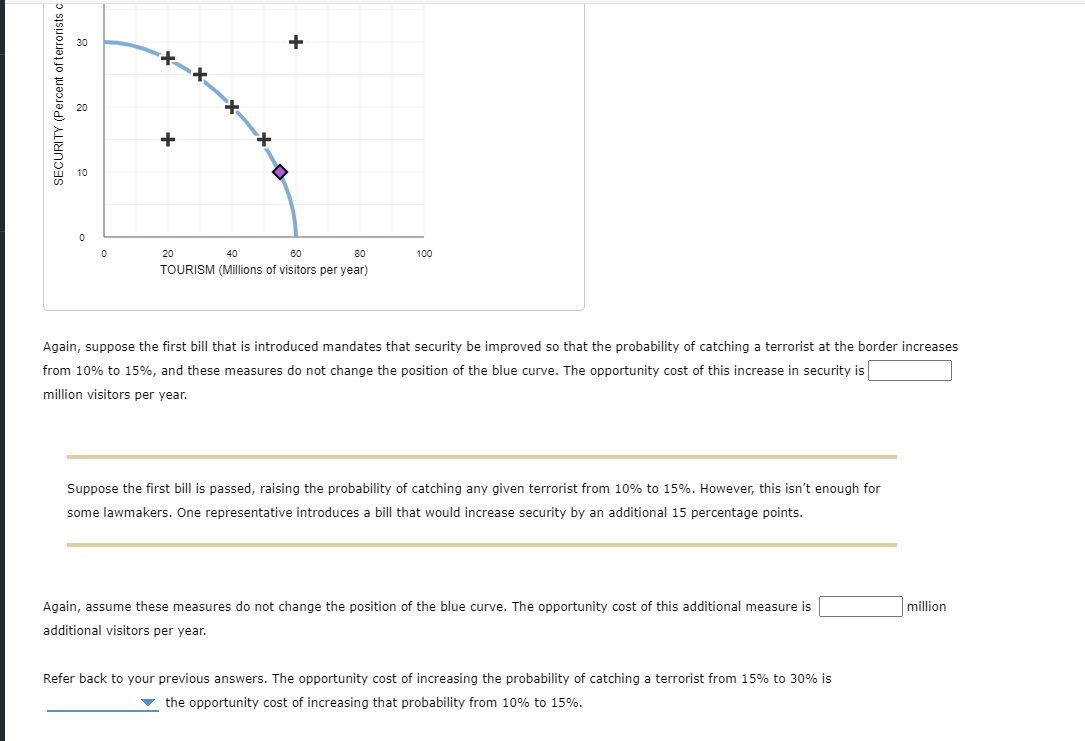
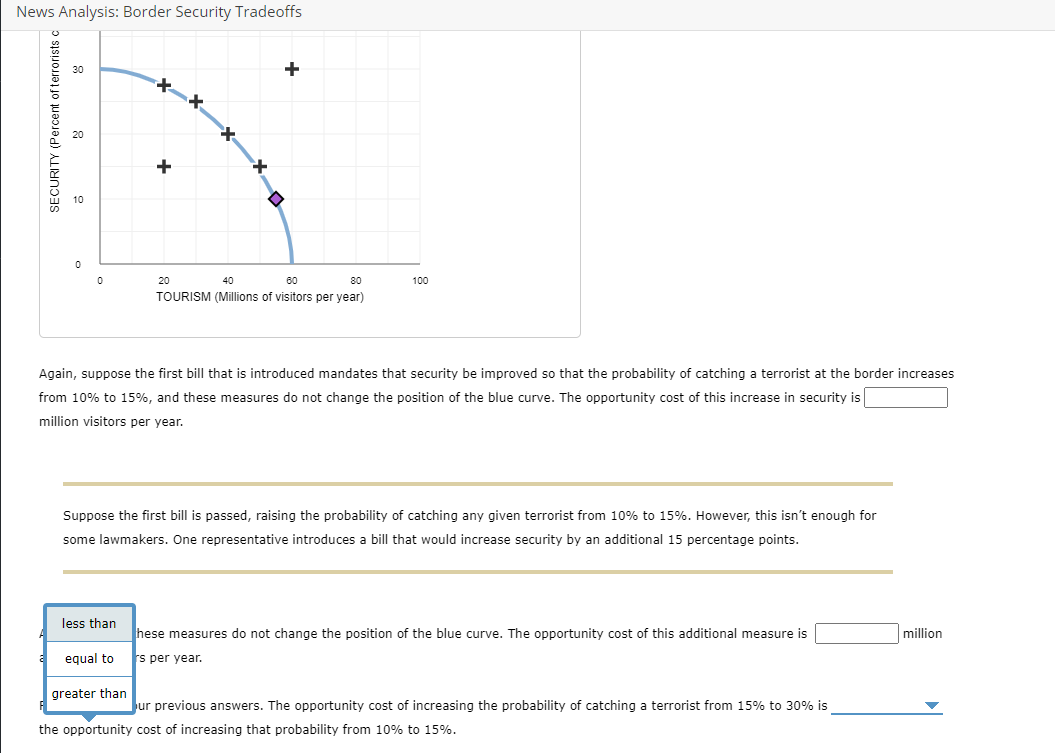
RITY (Percent of terrorists caught) The blue curve on the following graph shows the tradeoff between security and tourism; that is, combinations of security and tourism above the blue curve are not possible, and those on or below the curve are possible. The vertical axis measures security, defined as the probability that a terrorist is intercepted before entering the country. The horizontal axis measures the number of yearly visitors to the United States, in millions. Suppose that before 9/11, there were 55 million visitors per year, and the probability of intercepting any particular terrorist at customs and immigration was 10%, as indicated by the purple point (diamond symbol). After the 9/11 attacks, a debate is held in Congress. Members of both parties agree that security measures need to be improved. However, there is some disagreement as to how much additional security is needed. Suppose the first bill that is introduced mandates that security be improved so that the probability of catching a terrorist at the border increases from 10% to 15%. Assuming the security bill does not change the position of the blue curve, place the gray point (star symbol) on the graph to show the effects of such a bill. (Hint: Be sure to plot your point on one of the black plus symbols.) 30 40 50 (?) Assuming the security bill does not change the position of the blue curve, place the gray point (star symbol) on the graph to show the effects of such a bill. (Hint: Be sure to plot your point on one of the black plus symbols.) SECURITY (Percent of terrorists caught) 50 30 8 10 + 20 40 + 60 80 100 TOURISM (Millions of visitors per year) Again, suppose the first bill that is introduced mandates that security be improved so that the probability of catching a terrorist at the border increases from 10% to 15%, and these measures do not change the position of the blue curve. The opportunity cost of this increase in security is million visitors per year. SECURITY (Percent of terrorists c 30 8 + 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 TOURISM (Millions of visitors per year) Again, suppose the first bill that is introduced mandates that security be improved so that the probability of catching a terrorist at the border increases from 10% to 15%, and these measures do not change the position of the blue curve. The opportunity cost of this increase in security is million visitors per year. Suppose the first bill is passed, raising the probability of catching any given terrorist from 10% to 15%. However, this isn't enough for some lawmakers. One representative introduces a bill that would increase security by an additional 15 percentage points. Again, assume these measures do not change the position of the blue curve. The opportunity cost of this additional measure is additional visitors per year. million Refer back to your previous answers. The opportunity cost of increasing the probability of catching a terrorist from 15% to 30% is the opportunity cost of increasing that probability from 10% to 15%. News Analysis: Border Security Tradeoffs SECURITY (Percent of terrorists c 30 10 + 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 TOURISM (Millions of visitors per year) Again, suppose the first bill that is introduced mandates that security be improved so that the probability of catching a terrorist at the border increases from 10% to 15%, and these measures do not change the position of the blue curve. The opportunity cost of this increase in security is million visitors per year. Suppose the first bill is passed, raising the probability of catching any given terrorist from 10% to 15%. However, this isn't enough for some lawmakers. One representative introduces a bill that would increase security by an additional 15 percentage points. less than hese measures do not change the position of the blue curve. The opportunity cost of this additional measure is equal to s per year. greater than Jur previous answers. The opportunity cost of increasing the probability of catching a terrorist from 15% to 30% is the opportunity cost of increasing that probability from 10% to 15%. million
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the stepbystep workings Before 911 there were 55 million yearly visitors given in the quest...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


