Question: Roadrunner Bookstore uses the perpetual inventory system. Roadrunner Bookstore is owned by Tina Smith. The company had the following transactions for the month of


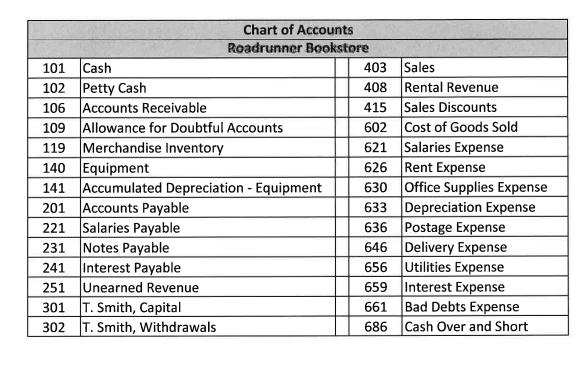
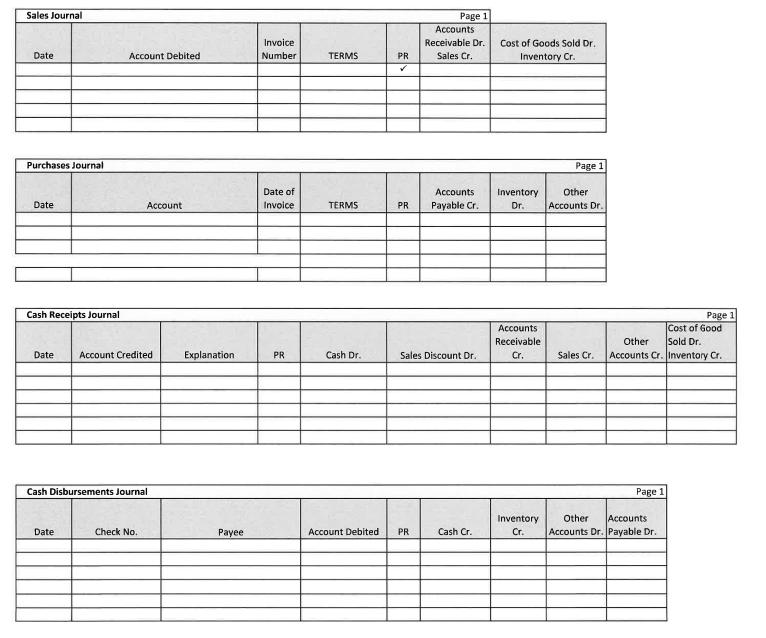
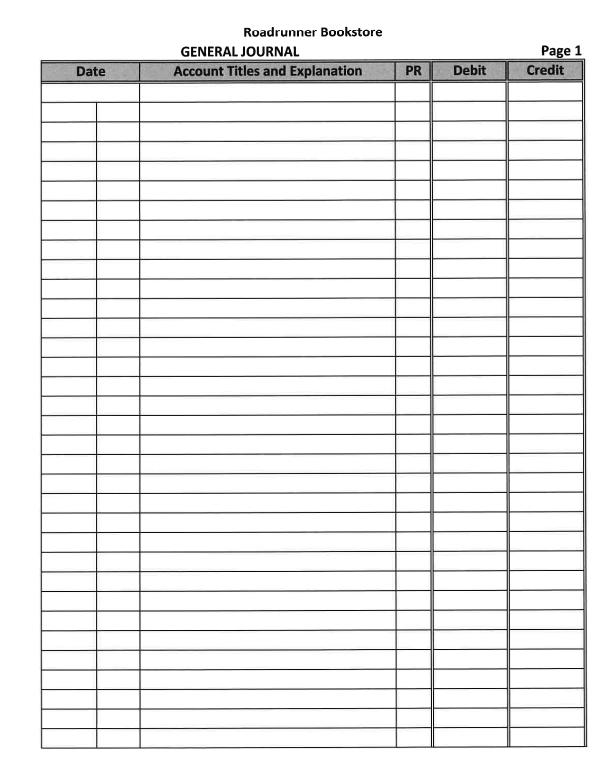
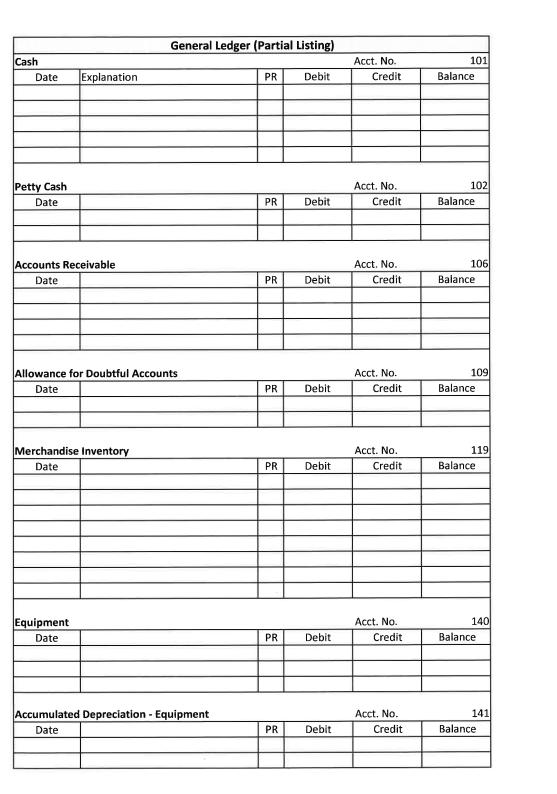

Roadrunner Bookstore uses the perpetual inventory system. Roadrunner Bookstore is owned by Tina Smith. The company had the following transactions for the month of November. Nov 1 Nov 2 Nov 3 Nov 5 Nov 7 Nov 9 Nov 11 Nov 13 Nov 15 Nov 17 Nov 18 Nov 21 Nov 23 Nov 24 Nov 25 Nov 27 Nov 29 Tina Smith invested $80,000 cash and Equipment worth $15,000 in Roadrunner Bookstore. Roadrunner Bookstore rented a portion of their warehouse to Davis Consulting for $4,000 per month. Davis paid Roadrunner Bookstore three months of rent in advance. Purchased $60,000 of merchandise inventory on credit, Invoice # 123 dated Nov 2 from Cengage, terms 2/20, n/30. Sold merchandise to Rowan University for $20,000 on credit, terms 2/10, n/45. Invoice no. 345. Cost of the merchandise sold is $10,000. Issued check #210 payable to Cash to establish a petty cash fund in the amount of $500. Purchased additional equipment totaling $8,000 on credit from Great Buy, terms 2/10, n/30, Invoice # 467 dated Nov 9. Sold merchandise to Rutgers University for $10,000 with terms 2/10, n/45. Invoice no. 346. Cost of the merchandise sold is $5,000. The cash register's record shows $7,000 at the end of the shift, but the count of cash in the register is $7,010. Cost of the merchandise sold is $3,000. Prepare the journal entry to record the day's cash sales. Rowan University paid the balance due from the sale on Nov 5. Sold merchandise to Rowan University for $15,000, terms 2/10, n/45. Invoice No. 347. Cost of the merchandise sold is $10,000. Roadrunner Bookstore signed a short-term note payable in the amount of $20,000 with an interest rate of 6% due in 90 days. Issued check #211 to Cengage for the purchase recorded on Nov 3rd. Issued check # 212 made payable to you, the company accountant, for your salary totaling $5,000. The cash balance in the petty cash drawer is $25. Receipts in the drawer show $150 for Postage Expense, $100 for Transportation In, $200 for delivery expenses, and $30 for office supplies expenses. Replenish petty cash using check # 213 made payable to Cash. Received $6,000 payment from Rutgers University towards the Nov 11 sale. Issued check # 214 made payable to Tina Smith for $6,000 for personal use. Issued check # 215 for $5,000 payable to Hartford Property Management for November Rent. Roadrunner Bookstore uses the following Special Journals: Sales, Purchases, Cash Receipts, and Cash Disbursements. 1.) Record the above transactions to the appropriate Journal and post as necessary to the Subsidiary Ledgers and General Ledger Accounts. Make sure to foot and cross foot totals at month-end. 2.) Complete the unadjusted trial balance columns on the worksheet for Roadrunner Bookstore as of November 30, 2021, and the Schedules of Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable. Roadrunner Bookstore must consider the following for adjusting entry purposes: a) A utility bill was received totaling $500 that will be paid in December. b) Depreciation on the Equipment for the month totaled $250. c) November rent from Davis Consulting has been earned. d) Interest on the short-term note through Nov 30th has accrued but has not been paid. (Round to a whole number) e) Salaries have accrued in the amount of $300 per day for six days. f) A count of inventory showed remaining inventory had a cost of $30,000. g) Bad debt is estimated to be .5% of total net credit sales. Prepare adjusting entries and post to the General Ledger Accounts. Post adjusting entries to the adjustments column on the worksheet and prepare the adjusted trial balance columns. Complete the remaining columns on the worksheet. Prepare Financial Statements, including a Classified Balance Sheet, for Roadrunner Bookstore considering the following: Depreciation Expense, Delivery Expense, Bad Debts Expenses, and Cash Overages are selling expenses Postage and Utilities Expenses are general and administrative expenses Salaries Expense and Rent Expense are split between selling and general and administrative expenses. Prepare Closing Entries for Roadrunner Bookstore. Prepare Post Closing Trial Balance for Roadrunner Bookstore. 101 Cash 102 Petty Cash 106 Accounts Receivable 109 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 119 Merchandise Inventory 140 Equipment 141 Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment 201 Accounts Payable 221 Salaries Payable 231 Notes Payable 241 251 301 T. Smith, Capital 302 Interest Payable Unearned Revenue Chart of Accounts Roadrunner Bookstore T. Smith, Withdrawals 403 Sales 408 Rental Revenue 415 Sales Discounts 602 Cost of Goods Sold 621 Salaries Expense 626 630 633 Depreciation Expense 636 Postage Expense 646 Delivery Expense 656 Utilities Expense 659 Interest Expense 661 Bad Debts Expense 686 Cash Over and Short Rent Expense Office Supplies Expense Sales Journal Date Purchases Journal Date Cash Receipts Journal Account Debited Date Account Credited Date Account Cash Disbursements Journal Check No. Explanation Payee Invoice Number Date of Invoice PR TERMS TERMS Cash Dr. PR PR Page 1 Account Debited. PR Accounts Receivable Dr. Sales Cr. Accounts Payable Cr. Sales Discount Dr. Cash Cr. Cost of Goods Sold Dr. Inventory Cr. Inventory Dr. Accounts Receivable Cr. Inventory Cr. Page 1 Other Accounts Dr. Sales Cr. Cost of Good Other Sold Dr. Accounts Cr. Inventory Cr. Page 1 Page 1 Other Accounts Accounts Dr. Payable Dr. Date Roadrunner Bookstore GENERAL JOURNAL Account Titles and Explanation PR Debit Page 1 Credit Cash Date Explanation Petty Cash Date Accounts Receivable Date Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Date Merchandise Inventory Date General Ledger (Partial Listing) Equipment Date Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment Date PR PR PR PR Debit PR PR Debit PR Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit 101 Balance 102 Balance 106 Balance 109 Balance 119 Balance 140 Balance 141 Balance Accounts Payable Date Salaries Payable Date Notes Payable Date Interest Payable Date Unearned Revenue Date T. Smith, Capital Date Explanation T. Smith, Withdrawals Date Explanation PR Debit PR PR Debit PR Debit PR Debit PR PR Debit Debit Debit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit 201 Balance 221 Balance 231 Balance 241 Balance 251 Balance 301 Balance 302 Balance Sales Date Rental Revenue Date Sales Discounts Date Cost of Goods Sold Date Salaries Expense Date Rent Expense Date Office Supplies Expense Date PR Debit PR PR PR Debit PR Debit Debit PR Debit Debit PR Debit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No.. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit 403 Balance 408 Balance 415 Balance 602 Balance 621 Balance 626 Balance 630 Balance Depreciation Expense Date Postage Expense Date Delivery Expense Date Utilities Expense Date Interest Expense Date Bad Debts Expense Date Cash Over and Short Date Income Summary Date PR PR PR PR Debit PR PR PR Debit PR Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit Acct. No. Credit 633 Balance 636 Balance 646 Balance 656 Balance 659 Balance 661 Balance 686 Balance 901 Balance Date Date Date Accounts Receivable Ledger Credit PR PR PR Debit Debit Debit Credit Credit Balance Balance Balance Date Date PR PR Accounts Payable Ledger Debit Debit Credit Credit Balance Balance Schedule of Accounts Receivable Schedule of Accounts Payable Post-Closing Trial Balance Debit Credit
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


