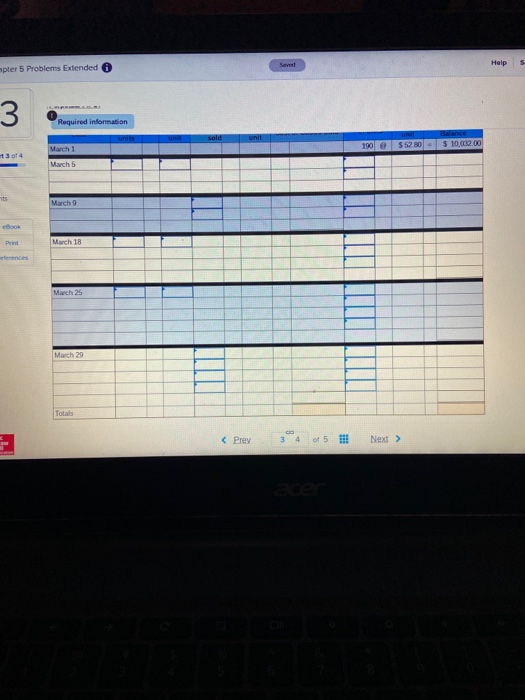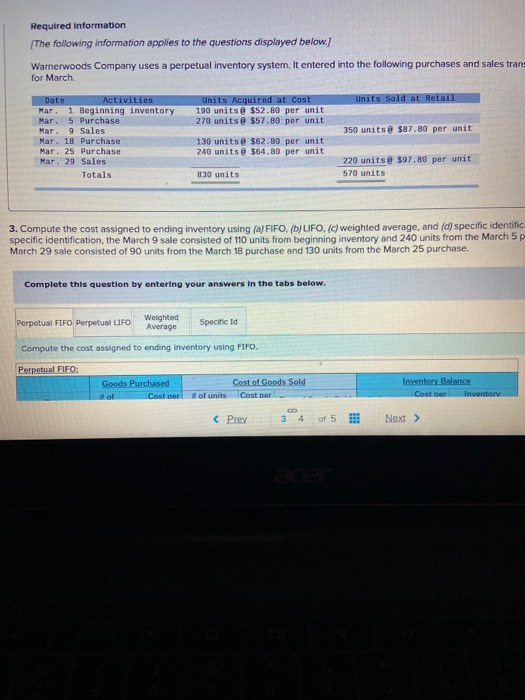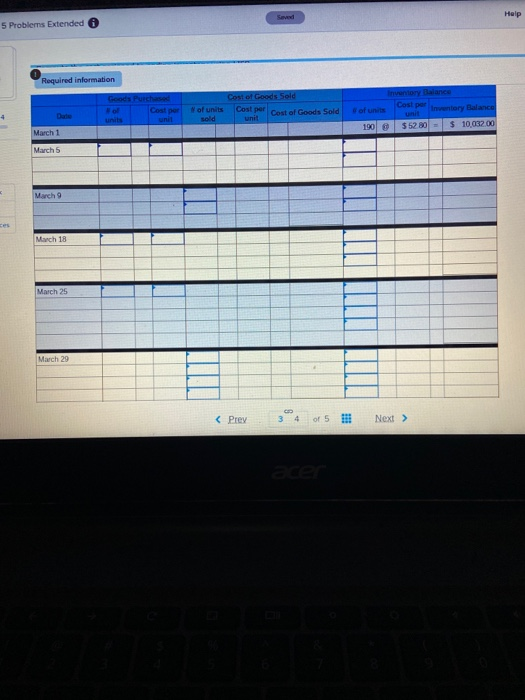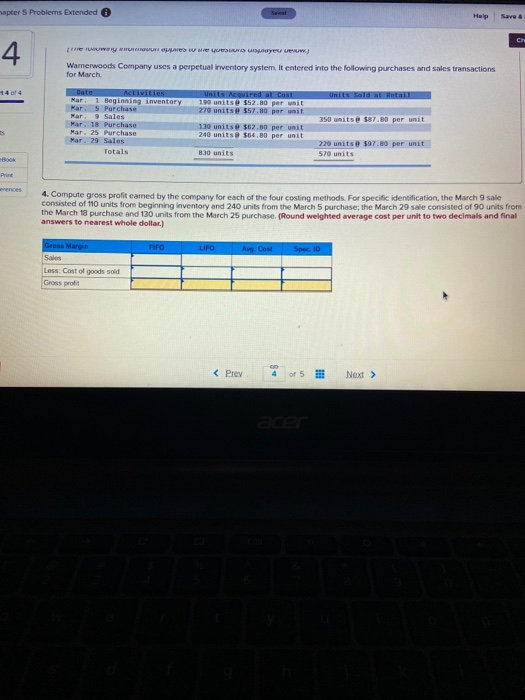
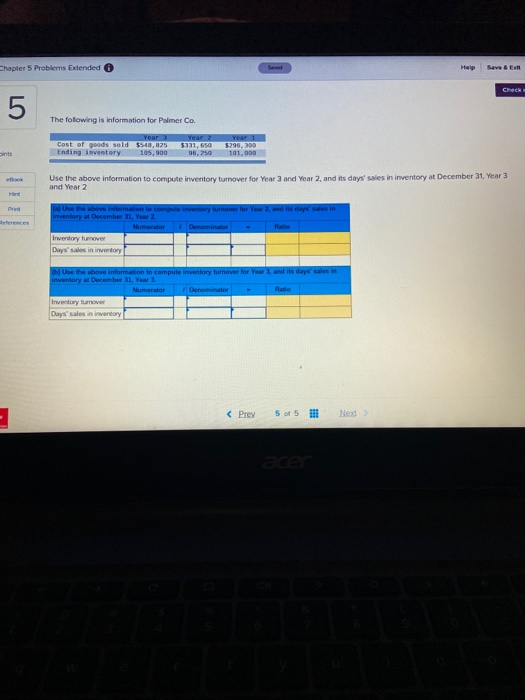
Sa Help 5 apter 5 Problems Extended 3 Required information sold 190 $12.80 $ 10,000.00 March 1 March 5 March 9 Book Print March 18 eferences March 25 March 20 Totals 17 Required information {The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales trans for March Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 196 units@ $52.89 per unit 270 units@ $57.89 per unit 350 units@ $87.80 per unit Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 1B Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 130 units@ $62.00 per unit 240 units@ $64.80 per unit 220 units @ $97.80 per unit 570 units 830 units 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b)LIFO. (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identific specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 110 units from beginning inventory and 240 units from the March 5 p March 29 sale consisted of 90 units from the March 18 purchase and 130 units from the March 25 purchase. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Weighted Average Specific id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using FIFO. Perpetual FIFO Goods Purchased W of Coster Cost of Goods Sold Coster Inventory Balance Coster Inventor #of units (Prey 3 4 of 5 !! Next > Help 5 Problems Extended Required information Goods Purchased Cost por of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit of units Inventory Balance Cost per inwentary Balance 552 80 = $ 10,032.00 unit 190 March 1 March 5 March 9 ces March 18 March 25 March 29 wapter 5 Problems Extended Help Save Hea uue eu veuw 4 Wamerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March +4 of 4 Units Sold at Retail Date MCLIVIEN 1 Beginning inventory Mar Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals units equired at cost 190 units $52.00 per wit 270 units 357.80 per unit 130 units @ $62.00 per unit 240 units $64.80 per unit 350 units@ 87.80 per unit 830 units 220 units 597.80 per unit 570 units Print ences 4. Compute gross profit camed by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 110 units from beginning inventory and 240 units from the March 5 purchase, the March 29 sale consisted of 90 units from the March 18 purchase and 130 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) FIFD LIFO Aug. Cost Spec ID Gross Margin Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit Chapter 5 Problems Extended Help Save BE Check 5 The following is information for Palmer Co. Year 2 Year 3 Cost of goods sold 3440,125 Ending inventory 105,900 Year 1 $296,300 101,000 ins 96,250 Use the above information to compute inventory turnover for Year 2 nd Year 2, and its days' sales in inventory at December 31, Year 3 and Year 2 Print tumover for Year and its Use the above Wormation to Inventory at December 1 Year 2 Numerator Inventory tumover Durys sales in inventory Domina Rasio Use the above information to compute inventory turnover for years, and its days' sales in inventary December 31 Year Numerator Denominator Ratio Inventory turnover Days'sales in inventory 17 Required information {The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales trans for March Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 196 units@ $52.89 per unit 270 units@ $57.89 per unit 350 units@ $87.80 per unit Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 1B Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 130 units@ $62.00 per unit 240 units@ $64.80 per unit 220 units @ $97.80 per unit 570 units 830 units 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b)LIFO. (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identific specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 110 units from beginning inventory and 240 units from the March 5 p March 29 sale consisted of 90 units from the March 18 purchase and 130 units from the March 25 purchase. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Weighted Average Specific id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using FIFO. Perpetual FIFO Goods Purchased W of Coster Cost of Goods Sold Coster Inventory Balance Coster Inventor #of units (Prey 3 4 of 5 !! Next > Help 5 Problems Extended Required information Goods Purchased Cost por of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit of units Inventory Balance Cost per inwentary Balance 552 80 = $ 10,032.00 unit 190 March 1 March 5 March 9 ces March 18 March 25 March 29 wapter 5 Problems Extended Help Save Hea uue eu veuw 4 Wamerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March +4 of 4 Units Sold at Retail Date MCLIVIEN 1 Beginning inventory Mar Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals units equired at cost 190 units $52.00 per wit 270 units 357.80 per unit 130 units @ $62.00 per unit 240 units $64.80 per unit 350 units@ 87.80 per unit 830 units 220 units 597.80 per unit 570 units Print ences 4. Compute gross profit camed by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 110 units from beginning inventory and 240 units from the March 5 purchase, the March 29 sale consisted of 90 units from the March 18 purchase and 130 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) FIFD LIFO Aug. Cost Spec ID Gross Margin Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit Chapter 5 Problems Extended Help Save BE Check 5 The following is information for Palmer Co. Year 2 Year 3 Cost of goods sold 3440,125 Ending inventory 105,900 Year 1 $296,300 101,000 ins 96,250 Use the above information to compute inventory turnover for Year 2 nd Year 2, and its days' sales in inventory at December 31, Year 3 and Year 2 Print tumover for Year and its Use the above Wormation to Inventory at December 1 Year 2 Numerator Inventory tumover Durys sales in inventory Domina Rasio Use the above information to compute inventory turnover for years, and its days' sales in inventary December 31 Year Numerator Denominator Ratio Inventory turnover Days'sales in inventory