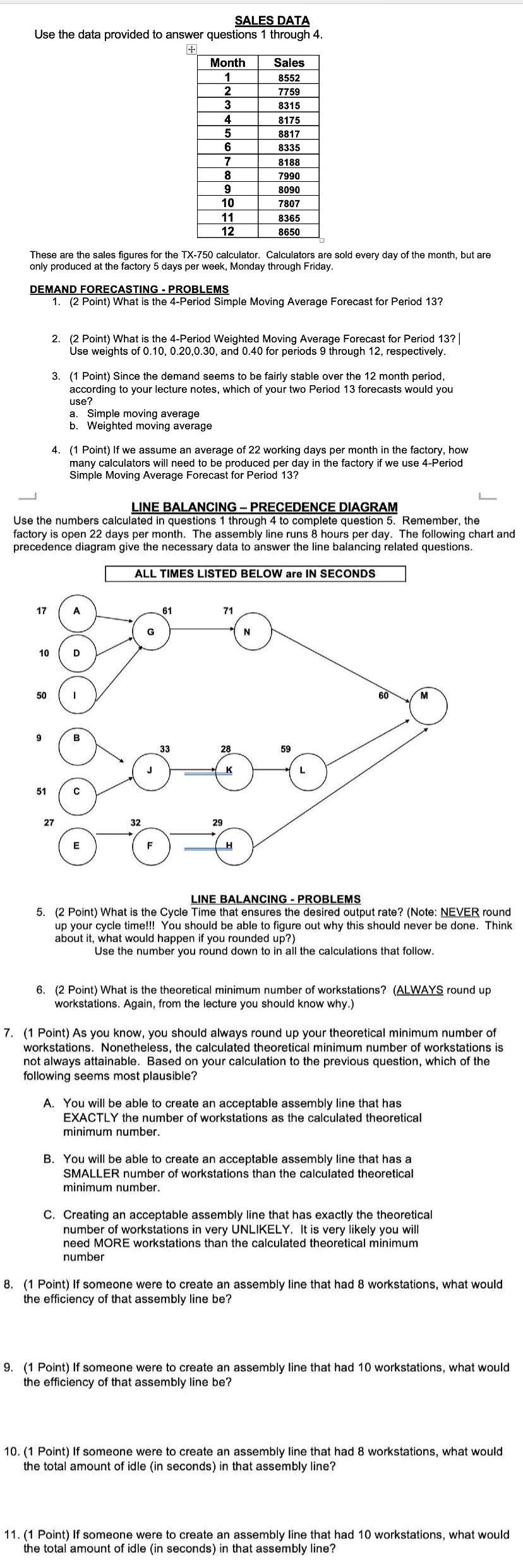
SALES DATA Use the data provided to answer questions 1 through 4. Month Sales 8552 7759 8315 8175 8817 8335 8188 7990 8090 7807 8365 8650 10 11 12 These are the sales figures for the TX-750 calculator. Calculators are sold every day of the month, but are only produced at the factory 5 days per week, Monday through Friday. DEMAND FORECASTING - PROBLEMS 1. (2 Point) What is the 4-Period Simple Moving Average Forecast for Period 13? 2. (2 Point) What is the 4-Period Weighted Moving Average Forecast for Period 13? | Use weights of 0.10, 0.20,0.30, and 0.40 for periods 9 through 12, respectively. 3. (1 Point) Since the demand seems to be fairly stable over the 12 month period, according to your lecture notes, which of your two Period 13 forecasts would you use? a. Simple moving average b. Weighted moving average 4. (1 Point) If we assume an average of 22 working days per month in the factory, how many calculators will need to be produced per day in the factory if we use 4-Period Simple Moving Average Forecast for Period 13? LINE BALANCING - PRECEDENCE DIAGRAM Use the numbers calculated in questions 1 through 4 to complete question 5. Remember, the factory is open 22 days per month. The assembly line runs 8 hours per day. The following chart and precedence diagram give the necessary data to answer the line balancing related questions. ALL TIMES LISTED BELOW are IN SECONDS :900 "Oo LINE BALANCING - PROBLEMS 5. (2 Point) What is the Cycle Time that ensures the desired output rate? (Note: NEVER round up your cycle time!!! You should be able to figure out why this should never be done. Think about it, what would happen if you rounded up?) Use the number you round down to in all the calculations that follow. 6. (2 Point) What is the theoretical minimum number of workstations? (ALWAYS round up workstations. Again, from the lecture you should know why.) 7. (1 Point) As you know, you should always round up your theoretical minimum number of workstations. Nonetheless, the calculated theoretical minimum number of workstations is not always attainable. Based on your calculation to the previous question, which of the following seems most plausible? A. You will be able to create an acceptable assembly line that has EXACTLY the number of workstations as the calculated theoretical minimum number. B. You will be able to create an acceptable assembly line that has a SMALLER number of workstations than the calculated theoretical minimum number. C. Creating an acceptable assembly line that has exactly the theoretical number of workstations in very UNLIKELY. It is very likely you will need MORE workstations than the calculated theoretical minimum number 8. (1 Point) If someone were to create an assembly line that had 8 workstations, what would the efficiency of that assembly line be? 9. (1 Point) If someone were to create an assembly line that had 10 workstations, what would the efficiency of that assembly line be? 10. (1 Point) If someone were to create an assembly line that had 8 workstations, what would the total amount of idle (in seconds) in that assembly line? 11. (1 Point) If someone were to create an assembly line that had 10 workstations, what would the total amount of idle (in seconds) in that assembly line







